Q: 1 The time required for fetching and execution of one simple machine instruction is known as?
Delay Time
CPU Cycle
Real Time
Seek Time
[ Option B ]
The CPU executes instructions in a fixed sequence, fetching the instruction from memory, decoding it, and then executing it. The total time taken to complete one full instruction, including both fetching and execution, is called a CPU cycle or instruction cycle.
Q: 2 Why is the width of a data bus so important to the processing speed of a computer?
The narrower it is, the greater the computer’s processing speed
The wider it is, the more data can fit into the main memory
The wider it is, the greater the computer’s processing speed
The wider it is, the slower the computer’s processing speed
[ Option C ]
The Data Bus is a set of parallel lines used to transfer data between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices.
The width of the data bus determines how many bits of data can be transferred simultaneously in a single clock cycle. A wider data bus allows more bits to be moved at the same time, which reduces the number of transfers required to move large amounts of data.
As a result, the CPU can fetch instructions and data faster, leading to an improvement in the overall processing speed of the computer.
| BUS TYPE | DESCRIPTION | DIRECTION |
|---|---|---|
| Data Bus | Transfers actual data (information or instructions) between CPU, memory, and I/O devices. | Bi-directional |
| Control Bus | Carries control signals (like Read, Write, Clock, Interrupt) to manage operations. | Bi-directional |
| Address Bus | Carries the address/location of memory or I/O device where data is to be read or written. | Uni-directional |
Q: 3 What is the name of the storage device that compensates the difference in rates of flow of data from one device to another?
Cache
Buffer
Concentrator
RAM
[ Option B ]
A Buffer is a temporary storage area used to adjust the difference in data transfer speeds between two devices. When one device sends data faster than the other can receive it, the buffer temporarily holds the data and releases it at a suitable rate. This prevents data loss and ensures smooth data flow.
Q: 4 Which of the following units is used to supervise each instruction in the CPU?
Control Unit
Accumulator
ALU
Control Register
[ Option A ]
The Control Unit (CU) is the part of the CPU that controls and supervises the execution of every instruction. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and then generates the necessary control signals to ensure that each step of the instruction is performed in the correct sequence.
The control unit directs other components such as the ALU, Registers, and Memory on what operations to perform and when to perform them.
Q: 5 Which of the following is true about Von Neuman architecture?
It has separate storage for input/output operations
It has a separate processing unit for data and instructions
It has separate memory for data and instructions
It has a single memory unit for both data and instructions
[ Option D ]
In Von Neumann architecture, a computer uses one single memory to store both data and program instructions. The CPU fetches instructions and data from the same memory using the same buses.
This design makes the system simple, but it can cause a performance limitation known as the Von Neumann bottleneck, because data and instructions cannot be accessed at the same time.
Q: 6 Microprogrammed control unit is?
Faster than hard wired unit
Slower than hard wired unit
To facilitate easy implementation of new instruction
Both (B) and (C)
[ Option C ]
Microprogrammed control units store a sequence of microinstructions in control memory, which makes it easier to implement and modify instructions. This is because changes can be made by updating microcode rather than redesigning hardware logic.
Q: 7 Which one of the following is a stored program machine?
Micro-computer
Calculator
Analog-computer
Micro-processor
[ Option A ]
A Stored Program machine is a computer system in which both the program instructions and the data are stored in the same memory. This concept is based on the von Neumann architecture, where instructions can be stored, modified, and executed from memory.
A micro-computer such as a desktop or personal computer follows the stored program concept. It stores programs and data in its main memory and executes instructions sequentially as required.
Q: 8 Which of the following is the fastest means of memory access of CPU?
Register
Cache
Main Memory
Stack
[ Option A ]
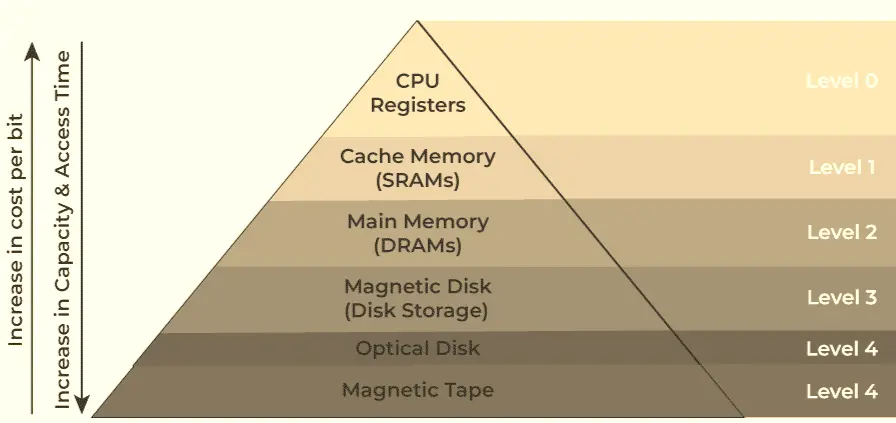
The CPU needs very fast access to data while executing instructions. Among all memory types, registers are located inside the CPU itself, so they can be accessed almost instantly. This makes registers the fastest means of memory access.
Cache memory is also very fast, but it is still slower than registers because it is located outside the CPU core.
Q: 9 Which of the following is NOT one of the four major data processing function of a computer?
Gathering Data
Processing data into information
Analyzing the data or information
Storing the data or information
[ Option C ]
The four major data processing functions of a computer are Input, Processing, Output, and Storage (IPOS).
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Input | Collecting or entering raw data into the computer using input devices. |
| Processing | Converting raw data into meaningful information using CPU operations. |
| Output | Presenting processed information to the user. |
| Storage | Saving data or information for future use. |
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.