The Senior Computer Instructor (SCI) Paper Solution 2022 by Suraku Academy offers complete, reliable, and well-explained answers to every question of the Senior Computer Instructor (SCI) exam 2022 held on 19 June 2022. Our team has carefully prepared this solution to provide clear explanations that make concepts easier to understand and help students build a strong foundation. With this resource, candidates can prepare with confidence and improve their chances of success in the exam.
In addition, this solution guide is not just about answers, it is designed as a learning companion. By studying these explanations, students can strengthen their problem-solving skills and approach future exams with greater clarity and confidence.
| S.N. | Name of Subjects | No. of Questions Asked |
|---|---|---|
| 01. | Pedagogy | 04 |
| 02. | Mental Ability | 08 |
| 03. | Computer Fundamentals | 08 |
| 04. | Operating System (OS), Computer Organization & Architecture (COA) | 14 |
| 05. | Data & Computer Networks (DCN) | 08 |
| 06. | Basics of Communication (Channel Capacity, Attenuation, PCM, WDM, GSM, CDMA) | 10 |
| 07. | Network Security (Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption, Viruses, Firewalls, Backup & Restoring, Ethical Hacking) | 10 |
| 08. | Programming Languages &OOPS Concepts (C, C++, Java, Python, .NET, AI & ML) | 11 |
| 09. | Data Structure and Algorithms (DSA) | 11 |
| 10. | Database Management System (DBMS) | 02 |
| 11. | Web Development (HTML, DOM, DHTML, CSS, XML, PHP, JavaScript) | 05 |
| 12. | Software Engineering (SE) | 07 |
| 13. | Digital Logic System (Boolean Algebra, TTL and CMOS Logic Families, Combinational & Sequential Circuit) | 02 |
Q: Which of the following is a type of computer architecture and its subcategories?
Von Neumann and micro architecture
Instruction set architecture
System design
All of the mentioned
[ Option A ]
Von Neumann architecture is one of the primary foundational computer architectures that describes the basic structure of computer systems with a shared memory for instructions and data.
The Microarchitecture refers to how the architectural instructions are implemented in hardware, detailing the processor’s internal structure.
Q: The minimum positive integers p such that 3p modulo 17 = 1 is –
5
8
12
16
[ Option D ]
Q: What will be the path loss in dB for an open-air site?
-8.27 dB
-80.27 dB
80.27 dB
8.27 dB
[ Option C ]
Q: What does OS X has?
Monolithic kernel with modules
Microkernel
Monolithic kernel
Hybrid kernel
[ Option D ]
The MacOS (formerly OS X) uses the XNU kernel, which is a hybrid kernel. This kernel architecture combines features from both the microkernel and monolithic kernel designs.
| Kernel Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Monolithic Kernel | A monolithic kernel is an operating system architecture where the entire OS, including device drivers, file system, and memory management, runs in kernel space. It is very fast but less modular, and a single fault can crash the whole system. An example is Linux. |
| Microkernel | A microkernel keeps only essential services such as CPU scheduling, memory management, and interprocess communication in kernel space. Other services run in user space. This makes the system more modular and stable, but it is slower due to message passing. An example is Minix. |
| Hybrid Kernel | A hybrid kernel combines features of monolithic and microkernel architectures. Critical services run in kernel space while others are modularized in user space. It balances performance and stability but is more complex in design. Examples include MacOS (XNU) and Windows NT. |
Q: Which of the following highly uses the concept of an array?
Binary search tree
Caching
Spatial locality
Scheduling of processes
[ Option C ]
Spatial Locality is a principle of memory access that states if a memory location is accessed, nearby memory locations are likely to be accessed soon. Since arrays store data in contiguous memory locations, accessing elements sequentially benefits heavily from spatial locality. Thus, arrays highly utilize this concept.
Q: Which CSS property can provide to add an effect when changing from one style to another, without using flash animations or JavaScript?
Associations
Transitions
Transistor
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The CSS transition property allows you to add smooth effects when changing from one style to another without using flash animations or JavaScript. Transitions enhance user experience by providing visually appealing animations with minimal effort and without complex scripting.
It provides control over the duration, timing function, and delay of the change, enabling smooth gradual changes, such as fading colors, resizing elements, or moving components when a user interacts with a page.
button {
background-color: yellow;
transition: background-color 1s ease;
}
button:hover {
background-color: green;
}In this example, when the user hovers over the button, the background color smoothly changes from yellow to green in 1 seconds.
Q:
Match the following—
| List – I | List – II |
|---|---|
| A. Disk Scheduling | 1. Round Robin |
| B. Batch Processing | 2. Scan |
| C. Time Sharing | 3. LIFO |
| D. Interrupt Processing | 4. FIFO |
A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
[ Option C ]
Disk scheduling algorithms manage the order in which disk I/O requests are processed. Common methods are FCFS (FIFO), SSTF, SCAN, LOOK, etc. The SCAN (also called Elevator algorithm) which moves the disk arm across the disk servicing requests in one direction.
In Batch Processing, jobs are processed in the order they arrive or according to some simple sequence. A common scheduling method is FIFO (First In First Out), where the first job to arrive is the first to be processed.
Time-sharing systems use Round Robin Scheduling to give each process a fair share of CPU.
Interrupts are handled in the reverse order of occurrence, often following a LIFO (Last In First Out) scheme where the most recent interrupt is serviced first.
Q: Which of the following architecture is suitable for a wide range of data types?
IA-32
ARM
ASUS firebird
68000
[ Option A ]
IA-32 (Intel Architecture, 32-bit) is a widely used computer architecture known for its support of a wide range of data types such as bytes (8 bits), words (16 bits), double words (32 bits), and quad words (64 bits).
It defines various data sizes and supports complex instruction sets for handling these different types efficiently, making it versatile across many computing applications.
Q: In Wi-Fi security, which of the following protocol is more used?
WPA
WPA2
WPS
Both (a) and (c)
[ Option B ]
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) is the most widely used Wi-Fi security protocol. It was introduced in 2004 and uses AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for strong encryption and security.
Q: What does CSA stand for?
Computer Service Architecture
Computer Speed Addition
Carry Save Addition
None of the mentioned
[ Option B ]
CSA stands for Computer Speed Addition. It refers to techniques used in computer arithmetic to perform addition faster, often by reducing the time required to handle carries during binary addition.
By designing circuits that can process sums and carries efficiently, computers can speed up arithmetic operations, which is critical in processors and digital systems.
Q: Match TCP/IP layers and protocol –
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| (P) Transport Layer | 1. ICMP |
| (Q) Network (Internet) Layer | 2. FTP |
| (R) Application Layer | 3. UDP |
Match Column — I and Column — II.
P-2, Q-1, R-3
P-1, Q-2, R-3
P-3, Q-1, R-2
P-3, Q-2, R-1
[ Option C ]
In the TCP/IP model, the Transport Layer uses protocols like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), where UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is connectionless and lightweight. The Network (Internet) Layer is responsible for routing and error reporting, and uses protocols like ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol).
Finally, the Application layer supports end-user services such as FTP for file transfer, HTTP for web access, and SMTP for email.
Q: If we implement heap as maximum heap, adding a new node of value 15 to the left most node of right subtree, what value will be at leaf nodes of the right subtree of the heap?
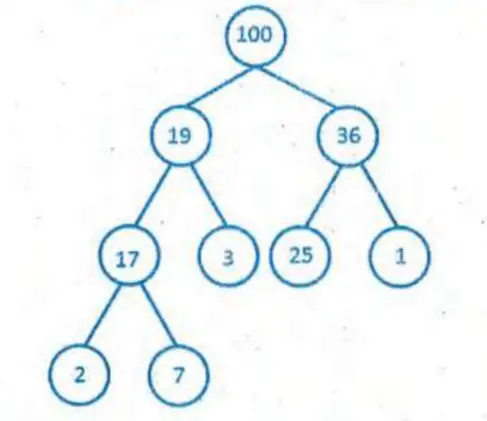
15 and 1
25 and 1
3 and 1
2 and 3
[ Option A ]
Q: CPU scheduling is the basis of –
Multiprogramming Operating System
Large Memory Sized Systems
Multiprocessor Systems
None of the mentioned
[ Option A ]
CPU Scheduling is the foundation of a Multiprogramming Operating System. In multiprogramming, several processes are kept in memory at the same time, and CPU scheduling decides which process will be given the CPU when it becomes available. This ensures efficient CPU utilization by keeping the processor busy as much as possible. CPU scheduling ensures that the CPU is never idle when there are processes ready to execute, improving throughput.
Q: Software Quality Assurance (SQA) encompasses –
Verification
Validation
Both (a) and (b)
None of the above
[ Option C ]
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is a broad activity that ensures the software meets the required quality standards. It is not limited to just testing but covers the entire software development process.
Verification ensures that the software is being built correctly according to specifications and design documents ("Are we building the product right?"). It focuses on the process of development.
Validation ensures that the final product meets the user's needs and requirements ("Are we building the right product?"). It focuses on the product itself.
| Verification | Validation |
|---|---|
| Checks whether the product is built correctly according to specifications. | Checks whether the right product is built that meets user needs. |
| “Are we building the product right?” | “Are we building the right product?” |
| Focuses on design, standards, and requirements. | Focuses on customer expectations and real-world use. |
| Done during development (reviews, inspections, walkthroughs). | Done after development (testing, acceptance). |
| Uses reviews, inspections, static analysis. | Uses functional testing, system testing, acceptance testing. |
| Preventive : finds errors early. | Detective : finds errors after implementation. |
Q: In K-Map, those groups which cover at least one minterm that can't be covered by any other prime implicant is called –
Prime Implicit
Essential Prime Implicit
Redundant Prime Implicit
Selective Prime Implicit
[ Option B ]
Q: Binary 101110.11 is equal to -
(56.6)8 only
(46.75)10 only
(2E.C)16 only
All options are correct
[ Option D ]
| Number System | Value | Conversion Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Binary | 101110.11 | Given, original number. |
| Decimal | 46.75 | Integer: 101110 : 46 Fraction: .11 : 0.75 |
| Octal | 56.6 | Integer: 101110 : 101 110 : 56 Fraction: .11 : .110 : 6 |
| Hexadecimal | 2E.C | Integer: 101110 : 0010 1110 : 2E Fraction: .11 : .1100 : C |
Q:
Match the following:
| List – I | List – II |
|---|---|
| (i) A method used to create an instantiation of a class. | (a) Bitmap |
| (ii) A signal that something has happened to stop normal execution of a program. | (b) Type Casting |
| (iii) A graphical image that is usually stored in a file. | (c) Exception |
| (iv) Converting one type of value to another type is called. | (d) Constructor |
(i)-b, (ii)-c, (iii)-d, (iv)-a
(i)-c, (ii)-d, (iii)-b, (iv)-a
(i)-a, (ii)-b, (iii)-c, (iv)-d
(i)-d, (ii)-c, (iii)-a, (iv)-b
[ Option D ]
A constructor is a special member method in a class that automatically called when an object of that class is created. Its main purpose is to initialize the newly created object, such as setting initial values for its attributes. The name of constructor method is same as name the class and no return type (not even void).
public class Bike {
String modelName;
public Bike(String model) {
modelName = model;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Bike Model Name : " + modelName);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Bike obj = new Bike("Rampayari");
obj.display();
}
}
OUTPUT
Bike Model Name : RampayariAn exception is an unwanted or unexpected event that occurs during the execution of a program and disrupts the normal flow. It indicates that an error or unexpected condition has occurred.
public class ExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
int result = 10/0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred.");
System.out.println("Error: Cannot divide by zero");
}
}
}A bitmap is a type of digital image made of pixels arranged in a grid. Bitmaps are commonly stored in files with extensions like .bmp.
Type casting refers to converting a value from one data type to another. In Java, type casting can be implicit (Widening) or explicit (Narrowing).
Q: ___________ is an indirect measure of software development process.
Cost
Effort Applied
Efficiency
All of the mentioned
[ Option C ]
Direct Measure are the values we can observe or record directly. For example, how many people worked on a project (effort), how much money was spent (cost), or the number of lines of code written. They do not need extra calculation.
Indirect Measure are values we derive or calculate from direct measures. For example, productivity (lines of code per person-month), efficiency (output vs. input), or defect density (defects per thousand lines of code). These cannot be measured directly but are obtained through formulas or analysis of direct measures.
Q: What is the port number of the HTTP?
80
25
20/21
23
[ Option A ]
The standard port number for HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is 80. Port 80 is the default port used for web servers serving unencrypted traffic over HTTP.
| Protocol | Port Number | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| FTP | 20 (Data) 21 (Command) | File Transfer Protocol. |
| SSH | 22 | Secure Shell for Encrypted Remote Login. |
| Telnet | 23 | Remote Login (Unencrypted). |
| SMTP | 25 | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (Email). |
| DNS | 53 | Domain Name System (Name Resolution). |
| HTTP | 80 | Hypertext Transfer Protocol (Web Browsing). |
| POP3 | 110 | Post Office Protocol Version 3 (Email Retrieval). |
| NTP | 123 | Network Time Protocol (Time Synchronization). |
| IMAP | 143 | Internet Message Access Protocol (Email Management). |
| HTTPS | 443 | Secure HTTP over TLS/SSL. |
| SMB | 445 | Server Message Block for File Sharing. |
| RDP | 3389 | Remote Desktop Protocol. |
| MySQL | 3306 | MySQL Database Service. |
| SIP | 5060/5061 | Session Initiation Protocol (VoIP Communication). |
| DHCP | 67 (Server) 68 (Client) | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. |
Q: Which of the following is the default authentication mode for IIS?
Anonymous
Windows
Basic authentication
None of these
[ Option A ]
By default, IIS (Internet Information Services) allows users to access web content without requiring credentials. This is called Anonymous Authentication, where the server uses a built-in account to handle requests from unauthenticated users.
Q: The use of technology to enhance learning process is called _________ in education.
IT
ICT
Information Technique
Communication Technology
[ Option B ]
In modern education, technology is integrated to support, enhance, and facilitate teaching and learning. The use of technology to enhance the learning process in education is called Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
The ICT focus on a broad range of digital tools and resources such as computers, the internet, multimedia software, educational apps, and communication technologies like email and video conferencing.
Q: Cascading termination refers to termination of all child processes, if the parent process terminates –
Normally or Abnormally
Abnormally
Normally
None of the mentioned
[ Option A ]
Cascading termination refers to the situation where the termination of a parent process leads to the automatic termination of all its child processes. This mechanism is implemented by the operating system to avoid the creation of orphan processes, which are child processes left without a parent to manage them.
Importantly, cascading termination occurs regardless of whether the parent process terminates normally after completing its execution or abnormally due to an error or external interruption. This policy helps maintain system stability by cleaning up all associated child processes when the parent ends.
Q: Which of the following format specifiers can be used to read floating type values in C programming?
%e
%f
%g
All options are correct
[ Option D ]
In C programming, when we deal with floating-point values (float or double), we use specific format specifiers inside printf() and scanf() function to write and read data respectively.
| Specifier | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| %f | Reads or writes floating-point numbers in decimal (fixed-point) notation. | 123.456000 |
| %e | Reads or writes floating-point numbers in scientific notation (exponential form). | 1.234560e+02 |
| %E | Same as %e, but uses uppercase E in scientific notation. | 1.234560E+02 |
| %g | Reads or writes floating-point numbers, automatically chooses between %f and %e, whichever is shorter. | 123.456 (for normal), 1.23e+06 (for large number) |
| %G | Same as %g, but uses uppercase E in scientific notation. | 123.456 or 1.23E+06 |
Q: Which of the following is an offline messaging app?
Vojer
Bing
Yandex
Lycos
[ Option A ]
Vojer is an offline messaging application that allows users to communicate without an active internet connection.
The Bing, Yandex, and Lycos are primarily web search engines or internet services and do not focus on offline messaging.
Q: Consider an undirected un-weighted graph G. Let a breadth first traversal of G be done starting from a node r. let d(r,u) and d(r,v) be the length of the shortest path from r to u and v respectively in G. if u is visited before v during the breadth first traversal, which of the following statement is correct?
D(r,u) < d(r,v)
D (r,u) > d(r,v)
D(r,u) <=d(r,v)
None of the above
[ Option C ]
Q: Which of these is fault base testing technique?
Stress Testing
Unit Testing
Beta Testing
Mutation Testing
[ Option D ]
Fault-Based Testing techniques are designed to evaluate how well a software system can handle errors or faults. The idea is to intentionally introduce faults and check whether the testing process can detect them.
Mutation Testing is a well-known fault-based testing technique. It involves making small modifications (called mutants) to the program’s source code intentionally, to check if the existing test cases can detect these faults.
Q: What will be the output of the program?
public class test2 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
StringBuffer S1 = new StringBuffer(“Complete”);
S1.setCharAt(1,’i’);
S1.setCharAt(7,’d’);
System.out.println(S1);
}
}
Complete
1omplede
Cimpletd
Coipletd
[ Option C ]
The given program demonstrates the use of the StringBuffer class in Java, which is mutable, meaning its content can be modified after creation. Initially, a StringBuffer object S1 is created with the value "Complete". The string has characters at the following indices:
Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Value: C o m p l e t e
The program then modifies the content using the setCharAt() method:
1. First modification: S1.setCharAt(1, 'i');
2. Second modification: S1.setCharAt(7, 'd');
Finally, System.out.println(S1); prints the modified string Cimpletd.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| append(String s) | Adds the given string at the end. |
| insert(int index, String s) | Inserts the given string at the specified index. |
| delete(int start, int end) | Removes characters from start index (inclusive) to end index (exclusive). |
| deleteCharAt(int index) | Removes the character at the given index. |
| setCharAt(int index, char c) | Replaces the character at the given index. |
| reverse() | Reverses the entire string. |
| capacity() | Returns the current capacity of the buffer. |
| length() | Returns the number of characters currently in the buffer. |
public class StringBufferExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Suraku");
System.out.println("Original String : " + sb);
sb.append(" Academy");
System.out.println("After Append : " + sb);
sb.insert(2, "YY");
System.out.println("After Insert : " + sb);
sb.delete(1, 3);
System.out.println("After Delete : " + sb);
sb.deleteCharAt(1);
System.out.println("After Delete Char At : " + sb);
sb.setCharAt(1, 'a');
System.out.println("After Set Char At : " + sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("After Reverse : " + sb);
System.out.println("Current Capacity : " + sb.capacity());
System.out.println("Current Length : " + sb.length());
}
}
OUTPUT
Original String : Suraku
After Append : Suraku Academy
After Insert : SuYYraku Academy
After Delete : SYraku Academy
After Delete Char At : Sraku Academy
After Set Char At : Saaku Academy
After Reverse : ymedacA ukaaS
Current Capacity : 22
Current Length : 13
Q: Global Positioning System uses –
CDMA
SDMA
FDMA
TDMA
[ Option A ]
The Global Positioning System (GPS) uses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) technology for signal transmission and access. GPS satellites transmit on the same frequency, but each satellite uses a unique code to allow receivers to distinguish signals. This is the principle of CDMA.
Q: The decimal equivalent of binary number 0.0111 is -
4.375
0.4375
0.5375
-0.4375
[ Option B ]
| Binary Digit | Position | Power of 2 | Decimal Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2-1 | 0 × 1/2 = 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 2-2 | 1 × 1/4 = 0.25 |
| 1 | 3 | 2-3 | 1 × 1/8 = 0.125 |
| 1 | 4 | 2-4 | 1 × 1/16 = 0.0625 |
Finally sum the number 0 + 0.25 + 0.125 + 0.0625 = 0.4375
Q: Which of the following values is the correct value of this hexadecimal code 1F.01B?
35.0065918
32.0065918
31.0065918
30.0065918
[ Option C ]
To convert the hexadecimal number (1F.01B)16 into its decimal equivalent, we first separate it into the integer part (1F) and the fractional part (.01B).
In integer part conversion, each digit is multiplied by 16 raised to the power of its position from right to left, starting with 0.
(1F)16 = 1⋅161+F⋅160 = 16+15 = 31
In fractional part conversion, each digit after the hexadecimal point is multiplied by 16 raised to a negative power corresponding to its position.
0⋅16−1+1⋅16−2+B⋅16−3 = 0 + 0.00390625 + 0.002685546875 = 006591796875 ≈ 0.0065918
After combining integer and fractional parts, 31 + 0.0065918 = 31.0065918
Q: Register renaming is done in pipelined processors -
As an alternative to register allocation at compile time
For efficient access to function parameters and local variables
To handle certain kinds of hazards
As part of address translation
[ Option C ]
Register renaming is a technique used in modern superscalar and pipelined processors to eliminate a specific type of data hazard called WAR (Write-After-Read) and WAW (Write-After-Write) hazards. These are also known as "Name Dependencies" because they arise not from a true data dependency, but from the reuse of a limited number of architectural registers.
Q: What efforts should be made by the teachers to explain technical terms or difficult concepts of a lesson?
Explaining with the help of examples.
Explaining with the help of TLM.
Explaining with the help of drawing a diagram on the blackboard.
All of the above.
[ Option D ]
Q: Choose the correct statement with respect to interfaces:
(i) Java does not support "multiple inheritance" however, it can be achieved by using interfaces.
(ii) Unless the class that implements the interface is abstract, all the methods of the interface need to be defined in the class.
(iii) To implement multiple interfaces, separate them with a comma (,).
Only (i)
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
[ Option D ]
Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes, i.e., a class cannot extend more than one class. However, Java allows a class to implement multiple interfaces. This provides a way to achieve multiple inheritance in Java.
When a class implements an interface, it must provide concrete definitions of all abstract methods defined in the interface. If the class does not implement all methods, it must be declared as abstract.
A class can implement multiple interfaces by separating them with a comma in the implements clause.
class Demo implements MyInterfaceP, MyInterfaceQ {
// Implementation of methods from both interfaces
}
interface MyInterfaceP {
void methodOne();
}
interface MyInterfaceQ {
void methodTwo();
}
class MyClass implements MyInterfaceP, MyInterfaceQ {
public void methodOne() {
System.out.println("Method One from MyInterfaceP implemented.");
}
public void methodTwo() {
System.out.println("Method Two from MyInterfaceQ implemented.");
}
}
public class Driver {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
obj.methodOne();
obj.methodTwo();
}
}
Q: ______ specification is also known as SRS document.
White box
Grey box
Black box
None of the above
[ Option C ]
The Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document is also known as the black box specification. It describes the what of the system, i.e., the functionality and requirements without detailing the internal workings or implementation (hence, "black box").
| Specification Type | Also Known As | Perspective | Focus | Used In |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Box | SRS Document | User View | What the system does. | Requirement Analysis |
| White Box | Structural Specification | Developer View | How the system works internally. | Design, Coding, Unit Testing |
| Grey Box | Hybrid Specification | Tester View | Combination of functional and some internal details. | Integration, System, Security Testing |
Q: Network devices _______ and _______ are used at physical layer.
Gateway, Bridge
Router, Repeater
Hub, Switch
Repeater, Hub
[ Option D ]
Physical Layer of the OSI model deals with the transmission of raw bitstreams over a physical medium. Network devices operating at the physical layer are responsible for transmitting and regenerating signals without interpreting the data.
Repeaters regenerate and amplify signals to extend the range of a network without any processing of the data.
Hubs serve as basic central connection points in Ethernet networks, forwarding signals to all ports and operating purely at the physical layer.
| Network Device | OSI Layer(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Repeater | Physical Layer | Regenerates and amplifies signals to extend network coverage. |
| Hub | Physical Layer | Multiport repeater that broadcasts incoming signals to all ports, no filtering or processing. |
| Network Interface Card (NIC) | Physical & Data Link Layer | Provides physical connection and MAC addressing. |
| Bridge | Data Link Layer | Connects two LAN segments and filters traffic based on MAC addresses. |
| Switch | Data Link Layer | Connects multiple devices on a LAN and selectively forwards data based on MAC addresses. |
| Router | Network Layer | Forwards packets based on IP addresses across different networks. |
| Gateway | All Layers | Connects different network architectures / protocols, can perform protocol translation. |
| Modem | Physical & Data Link Layer | Modulates and demodulates analog signals for digital data transmission. |
| Firewall | Network Layer & Higher Layers | Controls access, filters traffic based on rules, and protects networks from threats. |
| Access Point (AP) | Physical & Data Link Layer | Connects wireless devices to a wired LAN, bridges wireless and wired networks. |
Q: An advantage of chained hash table (external hashing) over the open addressing scheme is-
Worst case complexity of search operations is less
Space used is less
Deletion is easier
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In a chained hash table (external hashing), each slot in the hash table holds a linked list of all elements that hash to the same index. This makes deletion easier because elements can be removed from the linked list without affecting other entries in the main hash table array.
Unlike in open addressing, stores all elements directly in the array itself, which makes deletion more complex.
Another advantage of external hashing is it handles collisions efficiently, multiple elements can exist at the same slot without affecting other slots.
Q: The correct sequence of HTML tags for starting a webpage is –
Head, Title, HTML, Body
HTML, Body, Title, Head
Head, Title, HTML, Body
HTML, Head, Title, Body
[ Option D ]
The correct and standard sequence of HTML tags to start a web page is:
This sequence ensures proper structure and rendering of the web page in browsers.
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Displayable Content -->
</body>
</html>
Q: Reverse polish notation for infix expression
(A+B)*C-D/E will be –
-*+ABC/DE
AB+CD-*E/
AB+C*DE-/
AB+C*DE/-
[ Option D ]
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN), also known as Postfix Notation, is a way of writing arithmetic expressions where the operator placed after the operands. For example, the infix expression A+B is written as AB+in RPN.
Besides RPN, there are two other common notations, Infix Notation and Prefix (Polish) Notation. In infix notation, operators are placed between operands like A+B and prefix notation (Polish Notation), operators precede the operands like +AB. In Polish Notation and Reverse Polish Notation (RPN), there is no need of parentheses.
Q: Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) numbers express each digit in a –
Bit
Byte
Nibble
All of the above
[ Option C ]
Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) is a method of representing each decimal digit (0 to 9) using a fixed number of binary bits. Each decimal digit is encoded using 4 bits, which is exactly half a byte and commonly called a nibble.
| Decimal Digit | BCD Representation |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0000 |
| 1 | 0001 |
| 2 | 0010 |
| 3 | 0011 |
| 4 | 0100 |
| 5 | 0101 |
| 6 | 0110 |
| 7 | 0111 |
| 8 | 1000 |
| 9 | 1001 |
Q: Hexadecimal numbers are a mixture of -
Octal and decimal numbers
Binary and octal numbers
Letters and decimal digits
Binary and decimal numbers
[ Option C ]
The hexadecimal number system is a base-16 positional numeral system used widely in computing and digital electronics. It uses 16 distinct symbols to represent values from 0 to 15:
| Number System | Base | Symbols Used | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binary (Internally used by Computers) | 2 | 0 and 1 | 101001 |
| Octal (Rarely used Today) | 8 | 0 to 7 | 1702 |
| Decimal (Standard Number System used by Humans) | 10 | 0 to 9 | 47921 |
| Hexadecimal (Widely used in Computing for Memory Addresses and Color Codes) | 16 | 0 to 9, A to F Where A = 10 and F = 15 | 8F0AE |
Q: How many types of polymorphism are supported by C++?
1
2
3
4
[ Option B ]
Polymorphism in C++ means "one name, many forms", where the same function or operator can behave differently depending on the context (data types or implementations). C++ primarily supports two main types of polymorphism:
Compile-Time Polymorphism: Also called static or early binding, this is resolved during compilation and includes function overloading (same function name with different parameter lists) and operator overloading (redefining operators for user-defined data types).
class Demo
{
public:
void show(int a) { cout <<"Value: " << a; }
void show(double b) { cout <<"Value: " << b; }
};Run-Time Polymorphism: Also called dynamic or late binding, this is resolved during program execution and is achieved through inheritance and the use of virtual functions (function overriding).
class Base
{
public:
virtual void display() { cout <<"Base Class Version."; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
void display() { cout << "Derived Class Version."; }
};| OOP’S FEATURE | MEANING | REAL-LIFE ANALOGY |
|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation | Wrapping data and functions into a single unit (class). Protects data from outside interference. It ensures data security and prevents unauthorized access. | A capsule that keeps medicine (data) safe inside. |
| Abstraction | Hiding unnecessary implementation details and showing only essential features. It provides simplicity by focusing on what an object does, not how it does it. | Driving a car without knowing the inner mechanics of the engine. |
| Inheritance | One class acquires the properties and behaviors of another. It promotes code reusability and establishes relationships. | A child inheriting traits from parents. |
| Polymorphism | Ability of the same entity (method/operator) to behave differently based on context. It provides flexibility and reduces code complexity. | A person acting as a teacher for student, a husband for wife, a father for children and son for parents. |
Q: IPv4 address has a size of –
32 bit
64 bit
128 bit
256 bit
[ Option A ]
An IPv4 address is a 32-bit number used to uniquely identify a device on a network. It is usually represented in dotted decimal notation as four decimal numbers separated by dots, e.g., 192.248.0.1, where each number represents 8 bits.
| Feature | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address Size | 32-bit. | 128-bit. |
| Address Format | Dotted decimal notation. | Hexadecimal, colon-separated. |
| Address Classes | Classful addressing with classes A, B, C, D, E. | No concept of address classes. |
| Checksum | Present in header. | Not present. |
| Header Size | 20–60 bytes. | Fixed 40 bytes. |
| Configuration | Manual or DHCP. | Auto-configuration (SLAAC) and DHCPv6. |
| Security | IPSec optional. | IPSec mandatory. |
| Broadcast Support | Supports broadcast. | No broadcast (uses multicast and anycast). |
| Routing Efficiency | Less efficient due to large routing tables. | More efficient with hierarchical addressing. |
| NAT (Network Address Translation) | Widely used due to address shortage. | Not required because of large address space. |
| Subnet Mask | Supports CIDR and VLSM. | Supports CIDR but not VLSM. |
Q:
In context of network security match the following –
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| (P) Fabrication | 1. Message Confidentiality |
| (Q) Modification | 2. Message Integrity |
| (R) Interception | 3. Authentication |
P-1, Q-3, R-2
P-2, Q-1, R-3
P-3, Q-1, R-2
P-3, Q-2, R-1
[ Option D ]
Fabrication refers to creating fake messages or data, so authentication mechanisms are used to detect and prevent this.
Modification means altering messages during transmission. Ensuring message integrity detects such tampering.
Interception refers to unauthorized access or eavesdropping. Confidentiality (encryption) protects the message content.
Q: Which of the following document contains the user system requirement?
SRD
DDD
SDD
SRS
[ Option D ]
The document that contains the user system requirements is the SRS (Software Requirements Specification) document. The SRS document details the functional and non-functional requirements of the system from the user's perspective. It serves as a contract between the client and the developers, outlining what the software should do and how it should perform.
DDD (Detailed Design Document), contains detailed design of modules, algorithms, and data structures.
SDD (Software Design Document), Provides high-level and low-level design details.
Q: Let relation R2 has a 'foreign key' that refers to the primary key of relation R1. Which of the following operation may cause violation of referential integrity constraints?
Insertion of new tuple into R2
Deletion of tuple from R1
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
[ Option C ]
Referential integrity constraint ensures that a Foreign Key in one relation (R2) must always refer to an existing Primary Key in another relation (R1).
If we insert a tuple in R2 with a foreign key value that does not exist as a primary key in R1, it violates referential integrity.
If a tuple in R1 is deleted but there are still tuples in R2 that reference it, the relationship becomes invalid, causing a referential integrity violation.
| Operation | Reason for Violation | Possible SQL Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion in R2 | Foreign key in R2 points to a non-existent primary key in R1. |
|
| Deletion from R1 | R2 has orphan references after deletion in R1. |
|
| Update in R1 | Violation occurs because foreign key values in R2 no longer match R1. |
|
| Update in R2 | Violation occurs because foreign key values in R2 no longer match R1. |
|
Q: Choose the correct statements—
(i) Simplex reflex agents take decisions on the basis of the current percepts and past history.
(ii) When uniqueness in the agent’s current state completely determines the next state of the agent, the environment is said to be deterministic.
(iii) The environment is semi-dynamic if the environment itself does not change with the passage of time but agent's performance score does.
(i) and (iii)
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
All of the above
[ Option C ]
The first statement is incorrect because the simple reflex agents act only on the current percept using condition-action rules. They do not consider past history.
The second statement is correct because in a deterministic environment, the next state is completely determined by the current state and action.
The third statement is correct because in AI terminology, a semi-dynamic environment means the environment state is static, but the agent’s performance score can change, reflecting the passage of time or other external evaluation factors.
Q: Children are usually egocentric during ______ and ________ stages.
Sensorimotor, Preoperational
Formal operational, Sensorimotor
Preoperational, Concrete operational
Concrete operational, Formal operational
[ Option A ]
Q: What is the another name for the circular queue among the following options?
Square buffer
Rectangle buffer
Ring buffer
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A Circular Queue is also commonly known as a Ring Buffer. It is a data structure that connects the last position back to the first, forming a circle, which allows efficient reuse of buffer space.
Same as queue the circular queue data structure follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle and is widely used in scenarios where fixed size buffer management is needed.
The circular queue is empty (underflow) when front == -1 and full (overflow) when (rear + 1) % capacity == front.
Q: Which of the following is an example of effective motivational strategy to encourage students to learn?
Giving opportunities for competition to students in class
Providing scaffolding specially, when students learn a new skill
Emphasis on competition of work rather than learning
To dictate the answers of questions to students
[ Option B ]
Q: When a process is in a "Blocked" state it waits for some I/O service. When the service is completed it goes to the-
Terminated state
Suspended state
Running state
Ready state
[ Option D ]
When a process is in the Blocked State, it is waiting for some I/O service or resource to become available. Once the I/O operation or the required event is completed, the process cannot immediately start executing because the CPU may currently be busy with other processes. Therefore, it transitions to the Ready State.
Q: Secure Hash Algorithm-1 (SHA-1) has a message digest of –
160 bits
512 bits
628 bits
820 bits
[ Option A ]
Secure Hash Algorithm-1 (SHA-1) produces a message digest of 160 bits (20 bytes). SHA-1 takes an input of any length (less than 264 bits) and outputs a fixed-length hash value of 160 bits. This hash value, called the message digest, is used for data integrity verification, digital signatures, and other cryptographic applications.
Q: Who is known as the father of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Ada Fisher
Alan Turing
John McCarthy
Allen Newell
[ Option C ]
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science that deals with creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
John McCarthy, an American computer scientist, is recognized as the “Father of Artificial Intelligence” because he both coined the term "Artificial Intelligence" in 1955 and organized the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, which is widely considered the birth of AI as an academic field.
| Year | Scientist | Contribution & Relevance to AI |
|---|---|---|
| 1830 | Ada Lovelace | Wrote the first algorithm for Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine. Considered the FIRST COMPUTER PROGRAMMER. |
| 1936–1950 | Alan Turing | Proposed the Turing Machine (foundation of computation) and the Turing Test (to measure machine intelligence); called the Father of Theoretical Computer Science and AI Concepts. |
| 1955–1956 | John McCarthy | Coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” organized the Dartmouth Conference, and developed LISP, the first AI programming language. Known as the Father of AI. |
| 1956 | Allen Newell & Herbert A. Simon | Created the Logic Theorist (first AI program) and the General Problem Solver (GPS); contributed to early AI system design and problem-solving models. |
| 1960–1970 | Marvin Minsky | Co-founded the MIT AI Laboratory, advanced AI in robotics and cognitive simulation, and popularized AI research globally. |
Q: Ethernet uses ________ physical address that is imprinted on the Network Interface Card (NIC).
48-bits
48-bytes
4-bytes
128-bits
[ Option A ]
Ethernet networks use MAC (Media Access Control) addresses as their physical addresses, which are permanently imprinted on the Network Interface Card (NIC) by the manufacturer. A MAC address is 48 bits long, equivalent to 6 bytes, and is usually represented in hexadecimal notation.
This unique identifier ensures that devices within the same local network can correctly recognize and communicate with each other.
Q: If the channel band is limited to 6 kHz and signal to noise ratio is 16, what would be the capacity of the channel?
15.15 kbps
24.74 kbps
30.12 kbps
52.18 kbps
[ Option B ]
Q:
In context of internet consider the following –
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| (P) DuckDuckGo | 1. Browser |
| (Q) Firefox | 2. Video Conferencing |
| (R) Skype | 3. Search Engine |
Which of the following is correct match of Column – I and Column – II?
P-1, Q-3, R-2
P-2, Q-1, R-3
P-3, Q-1, R-2
P-3, Q-2, R-1
[ Option C ]
Q: Which type of channel does not represent any correlation between input and output symbols?
Noiseless channel
Lossless channel
Useless channel
Deterministic channel
[ Option C ]
A Useless Channel is a communication channel where there is no correlation between input and output symbols. This means the output is completely independent of the input, the received symbol gives no information about what was sent. In this, the channel capacity is zero because the output does not carry any meaningful information about the input.
A noiseless channel, output is exactly the same as input, so there is a perfect correlation between input and output.
A lossless channel, input can be uniquely determined from the output, so correlation still exists.
A deterministic channel, each input symbol corresponds to exactly one output symbol, hence strong correlation.
Q: The word which describes the importance of software design is –
Complexity
Quality
Efficiency
Accuracy
[ Option B ]
Software design plays a crucial role in ensuring the Quality of software systems. A good design makes software more understandable, maintainable, reliable, and reusable. It reduces development time and effort by providing a clear blueprint before coding begins.
Software design is the foundation of software quality. It influences not only the immediate development but also the long-term success of the system by affecting maintainability, usability, performance, reliability, scalability, and reusability.
| Quality Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintainability | The ease with which software can be modified to fix bugs, add features, or adapt to new requirements. |
| Usability | How simple and intuitive the software is for end-users to learn and operate effectively. |
| Performance (Efficiency) | The ability of the software to execute quickly and use system resources optimally. |
| Reliability | The consistency of the software in producing correct outputs and operating without failures. |
| Scalability | The capability of the software to handle growth, such as more users, data, or workload, without performance issues. |
| Reusability | The extent to which software components can be used in other systems or projects, reducing duplication of effort. |
Q: ARP stands for –
Address Routing Protocol
Address Routing Packet
Address Resolution Protocol
Address Routing Program
[ Option C ]
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to map an IP Address (Logical Address) to a physical MAC Address (Physical Address) in a network.
For example, when a computer wants to send data to another device on the same network, it first uses ARP to find out the MAC address corresponding to the known IP address. This ensures that the data packets are delivered to the correct device.
Q: To match specific XML elements child like of parent element is the syntax will be –
<xsl:template match="PLANET_NAME">
<xsl:template match="PLANET/NAME">
<xsl:template match="NAME">
<xsl:template match="//">
[ Option B ]
In XSLT, the match attribute of the <xsl:template> element uses an XPath expression to specify which XML elements the template applies to.
<xsl:template match="XPath">
<!-- Template content -->
</xsl:template>To match a specific child element (like NAME) of a parent element (like PLANET), the syntax is "PARENT/CHILD", i.e., "PLANET/NAME".
<xsl:template match="PLANET/NAME">
Q: Which one of the following errors will be handled by the operating system?
Lack of paper in printer
Connection failure in the network
Power failure
All of the above
[ Option D ]
Operating systems handle a variety of errors that may arise during process execution or hardware interaction.
Lack of paper in printer, the OS detects and handles this by notifying the user or pausing the printing process until paper is available.
Connection failure in the network, the OS manages network errors by detecting connection failures, reporting issues, and attempting reconnections or switching to backup networks.
Power failure, the OS can handle power failures by initiating safe shutdown procedures, saving unsaved data, and preserving system integrity through battery backups or power management features.
Q: Which of the following statements are true?
I. Shortest Remaining Time First (SRTF) scheduling may cause starvation.
II. Preemptive scheduling may cause starvation.
III. Round robin is better than FCFS in terms of response time.
I only
I & III only
II and III only
I, II and III
[ Option D ]
SRTF (Shortest Remaining Time First) is a Preemptive Scheduling algorithm where the process with the shortest remaining execution time is given the CPU. A long-running process might never get to execute if there is a continuous stream of new, short-burst processes arriving in the ready queue. The long-running process would always have a longer remaining time and would be repeatedly preempted, leading to starvation.
Preemptive scheduling may cause starvation, this is a general statement that is true. Starvation is a common problem in any Preemptive Scheduling algorithm that uses a priority or time-based approach, like SRTF or a Priority-Based Scheduler where low-priority processes might never get to run if there is a constant flow of high-priority processes.
Round Robin (RR) scheduling allocates CPU time in small time slices (quantum) to each process fairly, leading to better responsiveness compared to FCFS (First-Come, First-Serve), where a process waits (even short-burst ones) until the previous one completes because its Non-Preemptive Scheduling algorithm.
Q: GSM technology was a standard developed by –
United Kingdom
United States
Europe
Australia
[ Option C ]
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) was developed by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) in the late 1980s. It originated in Europe to standardize mobile communication systems.
| Standard | Full Form | Developed By | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMPS | Advanced Mobile Phone System | United States (AT&T Bell Labs) | 1G analog mobile standard. |
| GSM | Global System for Mobile Communications | Europe (ETSI – European Telecommunications Standards Institute) | 2G technology, digital voice, SMS, international roaming support. |
| TDMA | Time Division Multiple Access | United States (ANSI/IS-54 standard) | Digital 2G standard, basis for GSM in some regions. |
| CDMA | Code Division Multiple Access | United States (Qualcomm, TIA – Telecommunications Industry Association) | 2G/3G, multiple users share the same frequency using unique codes. |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution | 3GPP | 4G technology, high-speed mobile broadband, low latency. |
| 5G NR | 5th Generation – New Radio | 3GPP | Ultra-fast internet, low latency, IoT, massive connectivity. |
| WiMAX | Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access | IEEE (USA) | Wireless broadband standard. |
Q: What does DDoS stand for?
Data Denial-of-Service
Distributed Denial-of-Service
Distributed Data of Server
Distribution of Data Service
[ Option B ]
DDoS stands for Distributed Denial-of-Service. It is a type of cyberattack where multiple compromised systems flood the bandwidth or resources of a targeted system, usually one or more web servers.
The goal of a DDoS attack is to make the targeted online service or resource unavailable to legitimate users by overwhelming it with a massive volume of traffic or requests. This attack originates from multiple sources, making it more difficult to defend against than a single-source DoS attack.
Q: Select the false statement about CDMA technology –
(I) CDMA technology optimizes the use of available bandwidth as it transmits over the entire frequency range.
(II) Each user in a CDMA system uses a different code to modulate their signal.
(III) CDMA technology offers less security as compared to the GSM technology.
(IV) A SIM card is always required for the working of a CDMA device.
Only (I)
Only (II)
(I) and (II)
(III) and (IV)
[ Option D ]
The statement (I) is true, CDMA spreads the signal over the entire available spectrum using spread-spectrum technology.
The statement (II) is true, every user has a unique pseudo-random code, which allows multiple users to share the same frequency simultaneously.
The statement (III) is false, CDMA technology offers more security compared to GSM because it uses spread spectrum technology and encryption, making signal interception and detection harder.
The statement (IV) is false, A SIM card is not always required for CDMA devices. CDMA phones traditionally do not rely on SIM cards, unlike GSM phones.
Q: Which protocol layer uses the protocol SMTP, HTTP, FTP?
Application layer
Transport layer
Internal layer
Hardware layer
[ Option A ]
Protocols such as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), and FTP (File Transfer Protocol) operate at the Application Layer of the OSI and TCP/IP models. The application layer provides network services directly to end-user applications and manages communication between users and networks.
SMTP is responsible for email transmission, HTTP is used for accessing and transferring web pages, and FTP allows file transfers between systems.
Q: Which one of the following is an application of queue data structure?
When a resource is shared among multiple consumers.
When data is transferred asynchronously between two processes.
Load balancing
All of the above
[ Option D ]
A queue data structure has several important applications in the real world. It is commonly used when a resource is shared among multiple consumers, as it manages access by processing requests in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner. This ensures fairness by servicing requests in the order they arrive.
Queues are also used when data is transferred asynchronously between two processes, acting as a buffer to hold data until the receiving process is ready, as seen in the producer-consumer problem with message queues.
Another significant use of queues is in load balancing, where tasks or workloads are distributed evenly across multiple servers or systems by holding tasks in a queue until resources are available to process them.
Overall, queues play a vital role in managing resource sharing, buffering asynchronous data transfer, and balancing workload efficiently in computing systems.
Q: Which of the following is the first computer virus?
Sasser
Blaster
Creeper
Both (a) and (c)
[ Option C ]
The Creeper virus, created in 1970s by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies, is considered the first computer virus. It was an experimental self-replicating program that moved across ARPANET and displayed the message: "I'M THE CREEPER, CATCH ME IF YOU CAN!".
Q: Which of the following is not a symmetric key cryptography algorithm?
RC4
Blowfish
Diffie-Hellman
DES
[ Option C ]
Symmetric key algorithms use the same key for encryption and decryption. RC4, Blowfish, and DES (Data Encryption Standard) are examples of symmetric key cryptography algorithms.
Diffie-Hellman is a key exchange algorithm and is part of asymmetric key cryptography, used to securely exchange cryptographic keys over a public channel. It is not an encryption algorithm itself.
Q: Consider the following statement –
(i) A child process that remains running even after its parent process is terminated or completed without waiting for the child process execution is called an orphan.
(ii) A process that has completed its task but still, it shows an entry in a process table is called a zombie process.
Both are True
Both are False
Only I is True
Only II is True
[ Option A ]
Orphan Process:
In operating systems, when a parent process terminates before its child process completes, the child process is still running. Such a child process is called an orphan. Typically, the orphan process is adopted by the init process, ensuring proper cleanup when it finishes.
Zombie Process:
A zombie process is a process that has finished execution but still appears in the process table because its parent process has not yet collected its exit status via the wait() system call. Zombie processes do not consume CPU resources but occupy a slot in the process table until the parent collects the exit information.
Q: Register is a group of –
Flip-Flop
OR gate
AND gate
None of these
[ Option A ]
A register in digital electronics is a group of flip-flops used together to store multiple bits of data. Each flip-flop typically stores one bit, so a register consisting of multiple flip-flops can hold multi-bit binary data. Registers are used for temporary data storage.
Q: Which of the following events is/are exposed by the Data table object?
RowChanged
ColumnChanged
RowChanging
All of the above
[ Option D ]
In ADO.NET, the DataTable object represents an in-memory table of data. One of its powerful features is that it exposes events which allow you to monitor and respond to changes in its data. The main events include:
| EVENT NAME | TRIGGERED WHEN | USED FOR |
|---|---|---|
| RowChanging | Before a row is changed (added, modified, or deleted). | Allows validation or cancellation of changes before they are applied. |
| RowChanged | After a row has been successfully changed. | Perform tasks like logging or updating related data after a change. |
| RowDeleting | Before a row is deleted. | Allows checking or preventing deletion before it happens. |
| RowDeleted | After a row has been deleted. | Take actions after a row is removed. |
| ColumnChanging | Before a column value in a row is modified. | Allows validation or cancellation of the column change. |
| ColumnChanged | After a column value in a row has been modified. | Perform tasks after a column value is updated. |
| TableNewRow | When a new row is created in the table. | Initialize default values or perform setup when a new row is added. |
Q: A proxy firewall filter works at –
Physical Layer
Data link Layer
Network Layer
Application Layer
[ Option D ]
A Proxy Firewall filter works at the Application Layer of the OSI model. It acts as an intermediary between a client and a server, intercepting all requests and responses.
| Firewall Type | OSI Layer | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Packet-Filtering Firewall | Network Layer | Filters packets based on IP address, protocol, and port. Fast but limited visibility. |
| Stateful Inspection Firewall | Network & Transport Layer | Tracks the state of active connections, allows or blocks packets based on state, port, and protocol. |
| Proxy Firewall | Application Layer | Acts as an intermediary, inspects application data, supports HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc. Provides deep packet inspection. |
| Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) | Network to Application Layer | Combines traditional firewall capabilities with deep packet inspection and application awareness. |
| Circuit-Level Gateway | Session Layer | Monitors TCP handshakes and sessions without inspecting packet contents deeply. |
Q: Machine learning is a field of artificial intelligence consisting of learning algorithms that -
Improve their performance
At executing some task
Over time with experience
All of the above
[ Option D ]
Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing algorithms and systems which can learn from data and improve their performance automatically without explicit programming.
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
|---|---|---|
| Broad field of computer science aimed at making machines think and act like humans. | Subset of AI that uses algorithms to learn patterns from data and improve automatically. | Subset of ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to learn complex patterns. |
| Enable machines to perform intelligent tasks (reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making). | Improve performance on a specific task through experience (data). | Mimic the human brain’s neural structure for advanced learning. |
| Rule-based systems, knowledge representation, search algorithms, ML, DL. | Algorithms like regression, decision trees, SVM (Support Vector Machine), clustering, etc. | Deep neural networks (CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), Transformers, etc.). |
| Can work with smaller or symbolic data. | Needs structured data in moderate amount. | Needs huge volumes of data to perform well. |
| Expert Systems, Robotics, Natural Language Processing (NLP). | Spam Detection, Recommendation Systems, Fraud Detection. | Image Recognition, Speech Recognition, Autonomous Vehicles. |
Q: Which feature of OOP boosts code reusability?
Encapsulation
Polymorphism
Inheritance
Abstraction
[ Option C ]
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is built on PIE principles, Polymorphism, Inheritance and Encapsulation. Among these, inheritance is the key feature that significantly boosts code reusability.
Inheritance allows a new class (subclass or derived or child class) to acquire the properties and behavior (data and methods) of an existing class (superclass or base or parent class). This means that the subclass reuses the code already written in the parent class without needing to rewrite it.
Q: The postfix form of the expression
(A+B)*(C*D-E)*F/G, is –
AB+CD*E-FG/**
AB+CD*E-F**G/
AB+CD*E-*F*G/
AB+CDE*-*F*G/
[ Option C ]
Expression: ( A + B ) * ( C * D - E ) * F / G
| Scanned Symbol | Action | Stack Status (Top → Bottom) | Output (Postfix P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ( | Push ( | ( | P : |
| A | Operand (Add to P) | ( | P : A |
| + | Push + | + ( | P : A |
| B | Operand (Add to P) | + ( | P : AB |
| ) | Pop until ( | # (Empty) | P : AB+ |
| * | Push * | * | P : AB+ |
| ( | Push ( | (* | P : AB+ |
| C | Operand (Add to P) | (* | P : AB+C |
| * | Push * | *(* | P : AB+C |
| D | Operand (Add to P) | *(* | P : AB+CD |
| - | Pop Higher or Equal Precedence | -(* | P : AB+CD* |
| E | Operand (Add to P) | -(* | P : AB+CD*E |
| ) | Pop until ( | * | P : AB+CD*E- |
| * | Push * | * | P : AB+CD*E-* |
| F | Operand (Add to P) | * | P : AB+CD*E-*F |
| / | Pop Higher or Equal Precedence | / | P : AB+CD*E-*F* |
| G | Operand (Add to P) | / | P : AB+CD*E-*F*G |
| End | Pop Remaining. | # (Empty) | P : AB+CD*E-*F*G/ |
Q: If a process fails, most operating systems write the error information to a -
New file
Another running process
Log file
None of the mentioned
[ Option C ]
When a process fails, most operating systems record the error information in a log file. This log file serves as a permanent record to help system administrators, developers, and support personnel diagnose and troubleshoot problems.
By recording details such as the time of failure, type of error, and sometimes even a memory dump, log files help developers and administrators trace the cause of the failure. This approach provides a reliable and centralized way to analyze problems and ensure system stability.
| Operating System | Log File | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Linux / Unix | /var/log/syslog | Stores general system messages and errors. |
| Linux / Unix | /var/log/messages | Contains kernel and system-level messages, including startup logs. |
| Linux / Unix | /var/log/auth.log | Records authentication attempts such as login successes and failures. |
| Linux / Unix | /var/log/dmesg | Contains boot-time kernel messages and hardware detection logs. |
| Windows | Event Viewer – System Log | Stores system-level events such as driver failures, shutdowns, and reboots. |
| Windows | Event Viewer – Application Log | Contains error and status information from user applications. |
| Windows | Event Viewer – Security Log | Records login attempts, account management, and security-related events. |
Q: If (146)x + (313)x-2 = (246)8, then the value of base x is –
5
6
7
9
[ Option C ]
To solve this base arithmetic problem, we first understand that numbers in different bases can be converted to decimal (base 10) to simplify calculations. By converting each term to decimal, we can form an algebraic equation in terms of the unknown base x and then solve for it using standard algebraic methods.
Alternatively, since the bases involved are small integers, a trial-and-error method can be used to test reasonable values of x until the sum matches the decimal equivalent of the right-hand side.
Method 1: Algebraic / Decimal Conversion Method:
Convert each number to decimal:
Form the equation in decimal:
(x2 + 4x + 6) + (3x2 − 11x + 13) = 166
4x2 − 7x + 19 = 166
4x2 − 7x − 147 = 0
When solving this quadratic equation, we found value of x is 7.
Method 2: Trial-and-Error
Understand the Base Involved:
Check possible integer values for x:
From the given option 5,6,7,9, try only x=7,9 (because x must be >6), by converting each term to decimal and verify if the sum equals the decimal value of (246)8 (which is 166).
Q: Sequence of 5 E's in Roger Bybee's 5 'E' model—
Explore, Elaborate, Evaluate, Engage, Explain
Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, Evaluate
Evaluate, Elaborate, Engage, Explore, Explain
Elaborate, Engage, Evaluate, Explore, Explain
[ Option B ]
Q: An entity is represented by a set of –
Attributes
Relationship
Model
None
[ Option A ]
An entity in a database or data modeling context is a real-world object or concept that can be uniquely identified and about which data can be stored.
Entities are represented by a set of attributes, which describe the characteristics or properties of that entity. For example, a Student entity may have attributes like Rollno, Name, Class, Age, and Address. These attributes provide information about the entity and are used to uniquely distinguish one entity instance from another.
Q: Which of the following is not a type of constructor?
Copy constructor
Friend constructor
Default constructor
Parameterized constructor
[ Option B ]
In Object-Oriented Programming System (OOPS), a constructor is a special member function that automatically gets called when an object of a class is created. Its main purpose is to initialize newly created objects. There are several types of constructors, each serving a distinct purpose in object initialization.
Default Constructor: This is a constructor that takes no arguments and initializes objects with default values.
class Demo {
int x;
public:
Demo() { x = 0; } // Default Constructor.
};Parameterized Constructor: It takes one or more parameters, allowing the object’s data members to be initialized with user-defined values at the time of object creation.
class Demo {
int x;
public:
Demo(int a) { x = a; } // Parameterized Constructor.
};Copy Constructor: The constructor which takes object as an argument of its own types, called copy constructor. It creates a new object as a copy of an existing object.
class Demo {
int x;
public:
Demo(int a) { x = a; } // Parameterized Constructor.
Demo(Demo &obj) { x = obj.x; } // Copy Constructor.
};There is no such thing as a 'friend constructor' in mainstream object-oriented programming languages like C++, Java. We can have friend functions or friend classes in C++, but constructors cannot be declared as friend.
Q: Which of the following principle does queue use?
LIFO principle
FIFO principle
Linear tree
Ordered array
[ Option B ]
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. This means the first added element to the queue will be the first one to be removed. There are mainly two operations enqueue (adding an element at the rear end) and dequeue (removing an element from the front end).
Q: The knapsack problem where the objective function is to minimize the profit is-
Greedy
Dynamic 0/1
Back Tracking
Branch & Bound 0/1
[ Option D ]
The 0/1 Knapsack problem is a classic combinatorial optimization problem where each item must be either included or excluded from the knapsack. In this version, the objective is to minimize the profit (or cost), rather than maximize it. Simple greedy methods are not suitable here because they do not always guarantee an optimal solution for 0/1 decisions.
To handle minimization effectively, the Branch & Bound (0/1) technique is used. This method systematically explores all possible combinations of items while using bounds to prune suboptimal branches, which reduces unnecessary computations. While dynamic programming or backtracking can also solve the problem.
Q:
Consider the following in the context of internet—
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| (P) Vint Cerf | 1. Facebook |
| (Q) Mark Zuckerberg | 2. Google |
| (R) Larry Page | 3. Internet |
Match Column—I and Column—II .
P-2, Q-1, R-3
P-1, Q-3, R-2
P-3, Q-2, R-1
P-3, Q-1, R-2
[ Option D ]
Vint Cerf, along with Robert Kahn, is regarded as the “Father of the Internet.” He played a key role in designing the TCP/IP protocols, which are the foundation of modern internet communication.
Mark Zuckerberg co-founded Facebook in 2004 while studying at Harvard University. He later became the CEO of Facebook (Meta).
Larry Page, along with Sergey Brin, co-founders of Google, the search engine and technology company.
Q: 8's complement of (7650) is –
0230
0130
1230
3450
[ Option B ]
To compute the 8’s complement of a number, we use the (r−1)’s complement method, where r is the base. First, we find the (r−1)’s complement by subtracting each digit of the number from (r−1), and then we add 1 to the result to get the r’s complement.
For example, consider the octal number (7650)8. Here, the base r=8, so r−1=7. To find the 7’s complement of 7650, we subtract each digit from 7 individually.
Thus, the 7’s complement of (7650)8 is 0127. Next, to obtain the 8’s complement, we add 1 to the 7’s complement, 0127+1= 0130.
Note: The addition is performed according to the base. Here, since it is base 8 (octal), each digit is added modulo 8, and any carry is handled within octal arithmetic.
Q: In which step of SDLC is actual programming of software code done?
Development and documentation
Maintenance and evaluation
Design
Analysis
[ Option A ]
In the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), the actual programming or coding of the software is done during the development phase, which is often referred to as the "development and documentation" phase.
This phase follows the design and analysis phases and involves writing the source code based on detailed design specifications.
| SDLC Phase | Activities | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Requirement Analysis | Collect and analyze requirements from stakeholders, identify system goals, and feasibility study. | Software Requirement Specification (SRS) document. |
| System Design | Create system architecture, data flow, database design, and UI design based on SRS. | Design Document, Data Models, System Architecture. |
| Development (Implementation) & Documentation | Actual programming of software code is done, modules are built, and internal documentation is prepared. | Source Code, Technical Documentation. |
| Testing | Verify and validate the software, perform unit, integration, system, and user acceptance testing. | Test Cases, Test Reports, Bug Fixes. |
| Deployment | Release the software into production environment, install and configure the system for users. | Deployed Software, User Manuals. |
| Maintenance | Fix bugs, update features, improve performance, and ensure software continues to meet user needs. | Patches, Updates, Maintenance Reports. |
Q: Which method is used for both error detection and error correction method in computer networking?
Single Parity Check
Hamming Distance
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
Checksum
[ Option B ]
Single Parity Check, Checksum, and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) are primarily error detection methods. They detect if an error has occurred in the transmitted data but do not necessarily correct the errors.
Hamming Distance refers to Hamming Code, which is a method used for both error detection and error correction. It can detect and correct single-bit errors by adding redundant bits to the data.
Q: What is the correct HTML for creating a hyperlink?
<a name= : "">A</a>
<a> B </a>
<a href="http://www.example.com">example</a>
<a url= "http://www.example.com">example</a>
[ Option C ]
In HTML, a hyperlink is created using the <a> (anchor) tag. The href attribute specifies the URL of the page the link goes to. The text between the opening <a> and closing </a> tags is the clickable part that the user sees.
<a href="https://www.surakuacademy.com">Suraku Academy</a>
Q: DHTML is not a standardized language for which company?
Microsoft
Oracle
W3 Schools
[ Option B ]
Q: For defining the best time complexity, let f(n) = log(n) and g(n) = √n, ……..
f(n) ∈ Ω(g(n)), but g(n) ∉ Ω(f(n))
f(n) ∉ Ω(g(n)), but g(n) ∈ Ω(f(n))
f(n) ∉ Ω(g(n)), and g(n) ∉ Ω(f(n))
f(n) ∈ Ω(g(n)), and g(n) ∈ Ω(f(n))
[ Option B ]
Q: Quantizing noise occurs in–
PCM
TDM
FDM
PPM
[ Option A ]
Quantizing noise occurs during the quantization process in Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). PCM converts an analog signal into a digital signal by sampling the amplitude of the analog signal at regular intervals and then quantizing these samples to the nearest value among a finite set of levels. The difference between the actual analog value and the quantized digital value is called quantization error or quantizing noise.
Q: Which one of the following is the process of inserting an element in the stack?
Insert
Add
Push
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle, where elements are added or removed only from one end called TOP of the stack.
The process of adding or inserting new element at the top of stack is called Push Operation. The process of deleting or removing an existing element from top of stack is called Pop Operation.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.