Get complete RPSC Vice Principal ITI Information Technology Engineering (ITE) solved questions with detailed explanations. Practice previous year papers, boost your subject knowledge, and prepare effectively for the RPSC ITI Vice Principal exam with authentic and accurate solutions.
In addition, this solution guide is not just about answers, it is designed as a learning companion. By studying these explanations, students can strengthen their problem-solving skills and approach future exams with greater clarity and confidence.
| Unit | Unit Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Unit 1 | Computer Organization & Architecture (COA) | Digital Logic Family: Logic Gates, Logic functions, Boolean Algebra, Map Simplifications, Design of Sequential and Combinational Logic Circuits, Number System and data representation, Logic Gates, Flip-Flops, Integrated Circuits, Decoders, Multiplexers, Memory Organization, DMA. |
| Unit 2 | Programming and Data Structures (DSA) | Programming in C: Tokens, Identifiers, Data Types, Sequence Control, Loops, Array, Function, Recursion, Structure, File.Data Structure: Stack, Queue, Linked List, Binary and Linear Search, Tree, Graph, Sorting (Bubble, Heap, Quick, Insertion, Selection sort). |
| Unit 3 | Operating System (OS) | Processes, Threads, Inter Process Communication, Semaphores, Concurrency, Synchronization, Deadlock, CPU Scheduling, Memory Management and Virtual Memory, File System.Linux Operating Systems: Design Principles, Kernel Modules, Process Management, Scheduling, Memory Management, File Systems, Input and Output; Inter-process Communication, Network Structure. |
| Unit 4 | Computer Networks (CN) | Data Communication Model, Data Transmission (analog and digital), modulation, multiplexing., Wired and Wireless Transmission Media, LAN, MAN, WAN, Routing Protocols, Network Technologies (ATM, Frame Relay, DSL, ISDN), MANET, Wireless network and technologies.IPv4 Structure and Address Space. Classful and Classless Addressing. Datagram, Fragmentation and Checksum; IPv6 Packet Format, Mapping Logical to Physical Address (ARP), Routing Algorithms, TCP and UDP Protocols; Flow Control, Error Control and Congestion Control in TCP. |
| Unit 5 | Database Management System (DBMS) | Basic DBMS Terminology, Database System versus File System, Keys, Entity Relationship Model, Relational Model, Distributed Database System.SQL: Data Definition and Data Types. Constraints, Queries, Insert, Delete, and Update Statements. Views, Stored Procedures and Functions; Database Triggers, SQL Injection.Normalization for Relational Databases: Functional Dependencies and Normalization. Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization. Transaction Processing, Concurrency Control Techniques, Database Recovery Techniques. Database Security and Authorization. |
| Unit 6 | Information Security | Network Attacks, IPSec, Network Scanning, Security of web Browsers and Servers, Firewalls and Intrusion Detection System. Malwares, Cryptography and Steganography, Encryption Algorithms (DES & RSA), Secret-Key Algorithms, Public-Key Algorithms, Digital Signature, Virtual Private Networks. |
| Unit 7 | Software Engineering (SE) | Software Requirement Specification, Software Process and Design Models, Modularity, Information Hiding, Functional Independence, Cohesion and Coupling. Object-Oriented Design, Data Design, Architectural Design, User Interface Design, Component Level Design.Software Testing: Verification and Validation. Error, Fault, Bug and Failure. Unit and Integration Tesing. White-box and Black-box Testing. Basis Path Testing, Control Structure Testing, Deriving Test Cases, Alpha and Beta Testing. Regression Testing, Performance Testing, Stress Testing. |
| Unit 8 | Data Warehousing & Mining | Data Warehousing: Introduction, Architecture, Implementation, OLAP, Data Cleaning, Data Reduction, Data Integration and Transformation, Data Compression.Data Mining: Data Mining Concepts, Architecture of Data Mining System, Mining Class Comparison, Mining Descriptive Statistical Measures, Associative Rule Mining, Apriori algorithm, Supervised and Un-supervised algorithms related to datamining, Classification and Prediction. |
| Unit 9 | Web Design and Development | World Wide Web (WWW): Uniform Resource Locator (URL), Domain Name Service (DNS), Resolution - Mapping Names to Addresses and Addresses to Names. Electronic Mail Architecture, SMTP, POP and IMAP; TELNET and FTP, HTML, DHTML, XHTML, Java Script, Python and PHP. |
| Unit 10 | Emerging Technologies in the field of IT | Fundamentals and Applications of AI, E-Commerce, Multimedia, Expert Systems, Digital marketing, Introduction to mobile application development, Concept of Cyber security, Basics of IoT. |
| Exam Name | RPSC Vice Principal (Superintendent) ITI Exam ITE (Information Technology Engineering) Paper : 2024 | |
|---|---|---|
| Exam Date | 30th July 2025 | |
| S.N. | Name of Subjects | No. of Questions Asked |
| 01. | Web Design and Development | 20 |
| 02. | Programming and Data Structure (DSA) | 16 |
| 03. | Computer Organization & Architecture (Digital Logic Family) | 10 |
| 04. | Operating System (OS) | 19 |
| 05. | Computer Network (CN) | 10 |
| 06. | Database Management System (DBMS) and Structured Query Language (SQL) | 20 |
| 07. | Network Security and Cryptography / Information Security | 10 |
| 08. | System Analysis and Design (SAD) & Software Engineering (SE) | 20 |
| 09. | Data Warehousing & Mining | 20 |
| 10. | Emerging Technologies in the field of IT | 05 |
Q: Suppose X is a composite attribute of an entity type and has three components, A1, A2 and A3, where only A2 is multi-valued and can be NULL. If domain sets of A1, A2 and A3 have 5, 3, and 4 elements respectively, what is the size of the domain of X?
60
12
120
160
[ Option D ]
The attribute X is a composite attribute made up of three components, A1, A2, and A3, whose domain sizes are 5, 3, and 4 respectively. Since A2 is a multi-valued attribute, it can take multiple values from its domain or even be NULL.
If the domain of A2 has 3 elements, then the number of possible subsets of A2 is 23 = 8, because each element may be either included or not.
Now, the total number of possible combinations for X is calculated as:
Domain size of X = (Domain of A1) × (Domain of A2) × (Domain of A3)
Domain size of X = 5 × 8 × 4 = 160
Q: What will be the output of the following C code in GCC compiler?
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 5, i = 0;
for(;i<3;a++,i++){}
printf(“%d”,a++);
return 0;
}
5
6
7
8
[ Option D ]
The loop executes 3 times, incrementing both a and i in each iteration. After the loop ends, the value of a becomes 8. The statement printf("%d", a++); prints the current value of a, which is 8. Since it is a post-increment, a is increased to 9 after printing, but this updated value is not displayed.
Q: Output of 2-inputs NAND gate if one of its input is permanently connected to ‘0’ is :
0
1
High Impedance state
Not Defined
[ Option B ]
A NAND gate produces the output as the negation of the AND operation, i.e., Y=(A⋅B)’. If one of its inputs is permanently connected to 0, then the AND operation becomes 0⋅B=0. So, Y=(0⋅B)′=0′=1. This means the output of the NAND gate will always be 1 regardless of the other input. Hence, the correct answer is 1.
Q: Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched:
Co-incidental cohesion – unplanned and random cohesion.
Temporal cohesion – elements of module are processed at different points of time.
Sequential cohesion – output of one element serves as input to another.
Procedural cohesion – elements of module are grouped together, which are executed sequentially in order to perform a task.
[ Option B ]
Cohesion refers to how closely the elements within a single module of a program are related to one another. The higher the cohesion, the better the design, as the module performs a single, well-defined task. Different types of cohesion describe different levels of relationship among module elements.
| TYPE OF COHESION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Co-incidental Cohesion | The elements inside the module are unrelated and are put together without any specific reason or purpose. Such grouping usually happens by accident or poor design decisions, making maintenance and understanding very difficult. |
| Logical Cohesion | Elements are grouped because they perform similar types of activities. However, which operation is executed depends on a control flag or parameter. |
| Temporal Cohesion | Elements of the module are grouped together because they are executed at the same time, such as during system startup, initialization, or shutdown. These operations are related by their timing rather than their function. |
| Procedural Cohesion | Elements are grouped because they are part of the same procedure or control sequence. |
| Communicational Cohesion | The elements of the module are grouped because they operate on the same data set. |
| Sequential Cohesion | This occurs when the output of one element becomes the input of the next. |
| Functional Cohesion | Every element in the module contributes to a single, well-defined purpose or function. The module performs exactly one task and nothing else, making it easy to test, reuse, and maintain. |
Q: Choose the correct output of the following code when executed in GCC compiler:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
printf(“%c”,*(arr+3)+65);
}
69
68
D
E
[ Option D ]
The expression *(arr+3) accesses the 4th element of the array (4). Adding 65 gives 69. Since %c is used, ASCII 69 is printed, which is E.
Q: Which of the following represents the two approaches to store a relation in the distributed database?
Replication and Fragmentation
Biasing and Quorum
Indexing and Partitioning
Propagation and Bullying
[ Option A ]
In a distributed database system, data is stored across multiple sites or nodes, and there are two main approaches to store relations.
Replication involves storing copies of the same data at multiple sites to increase availability and allow parallel query processing. However, replication requires synchronizing updates across copies to maintain consistency, which adds overhead.
Fragmentation involves dividing a relation into smaller parts called fragments, and storing each fragment at a site where it is most needed.
Q: The most common technique used for protecting a critical section in Linux is:
Critical lock protocol
Spinlock
Critical Spinning
Mutex interlocking
[ Option B ]
In Linux, a critical section is a part of the code that accesses shared resources, such as variables, files, or hardware, that must not be used by more than one process or thread at a time. To prevent data corruption or race conditions, Linux uses synchronization mechanisms to protect these critical sections. The most common technique used in the Linux kernel for this purpose is the spinlock.
A spinlock is a lightweight lock used in Linux to protect a critical section. It makes a process “spin” in a loop until it can enter the section, ensuring that only one process accesses the shared resource at a time without using heavy context switching.
Q: At the architectural design level, a software architect uses an _________ to model the manner in which software interacts with entities external to its boundaries.
Architectural Activity Diagram (AAD)
Architectural Context Diagram (ACD)
Architectural State Diagram (ASD)
Architectural Design Diagram (ADD)
[ Option B ]
An ACD (Architectural Context Diagram) provides a high-level view of the system and shows how it fits into its environment. It illustrates the system boundary and depicts all external interfaces through which the system communicates with other entities.
This helps designers and stakeholders understand what lies inside and outside the system’s scope, ensuring that all necessary interactions are properly identified and managed.
Q: What will be the output of the following Python code?
a = True
b = False
c = False
if not a or b:
print(1)
elif not a or not b and c:
print(2)
elif not a or b or not b and a:
print(3)
else:
print(4)
1
2
3
4
[ Option C ]
The precedence of logical operator in Python is:
Q: Which of the following domains is NOT typically part of a requirements (analysis) model?
Information domain
Functional domain
Behavioral domain
Architectural domain
[ Option D ]
During the requirements analysis phase of software engineering, the main goal is to understand what the system should do, not how it will be built. The requirements analysis focuses on describing the system in terms of information, functions, and behavior.
However, the Architectural Domain is not part of the requirements model. It comes later in the design phase, where the system overall structure and organization are defined.
Q: Which of following is not a data classification technique?
Bayesian belief networks
Support Vector Machine
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbours)
Principal component analysis
[ Option D ]
Data classification is a type of supervised learning where the goal is to assign data points to predefined classes based on training data.
| TECHNIQUE NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Bayesian Belief Networks | Probabilistic models that classify data based on conditional dependencies between variables; useful for uncertain or probabilistic scenarios. |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Finds the optimal hyperplane that separates data points into different classes, works well for high-dimensional data. |
| K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) | Classifies a data point based on the majority class of its nearest neighbors in the feature space, simple and intuitive. |
| Decision Trees | Builds a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences to classify data, interpretable and widely used. |
| Random Forest | An ensemble of decision trees that improves classification accuracy by aggregating multiple trees' predictions. |
| Neural Networks | Model’s complex relationships using layers of interconnected nodes, suitable for large and complex datasets. |
Principal Component Analysis (PCA), is not a classification technique. PCA is a dimensionality reduction technique used to reduce the number of features while preserving variance.
Q: In SQL triggers, the action part can be executed in which of the following ways?
Only once for all affected tuples
Only once per transaction
Either once for each modified tuple or once for all tuples changed in the operation
Only before an update operation
[ Option C ]
A Trigger in SQL is a set of actions automatically executed by the database in response to a specific event, such as an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE on a table. Triggers are often used for tasks like maintaining audit logs, enforcing business rules, or validating data automatically.
The action part of a trigger (the code that gets executed) can be performed in two ways:
Row-Level Trigger: The trigger is executed once for every row (tuple) that is modified by the operation.
Statement-Level Trigger: The trigger is executed only once, regardless of how many tuples are affected by the operation.
Q: A is a supplementary protocol that allows non-ASCII data to be sent through e-mail.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME)
IMAP (Internet Mail Access Protocol)
POP (Post Office Protocol)
[ Option B ]
Emails were originally designed to send only ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) text, meaning simple English letters, digits, and symbols. But over time, people needed to send images, audio, video, documents, and text in other languages (Non-ASCII).
To solve this, an additional standard was developed called MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions). It works with existing email protocols like SMTP, POP, or IMAP and allows emails to carry different types of content.
Besides supporting non-ASCII text, MIME also allows multiple parts in a single email, enabling attachments and formatted text. When we attach a photo or a PDF in an email, MIME encodes that file into a format (like Base64) that can be sent as plain text through SMTP. The receiver’s email client then decodes it back to the original file.
Q: SHA-2 algorithm generate ____________ length of hash value.
128 bits
512 bits
256 bits
1024 bits
[ Option B ]
The SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) family is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed to provide secure hashing for data integrity and digital signatures.
SHA-2 includes variants such as SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512, where the number in the name indicates the length of the hash output in bits.
SHA-256, the most commonly used variant, produces a 256-bit (32-Byte) hash value.
Q: Which of the following is not true about IMAP4 protocol?
A user can check the e-mail header prior to downloading.
A user can search the contents of the e-mail for a specific string of characters prior to downloading.
A user can create, delete, or rename mailboxes on the mail server.
A user cannot create a hierarchy of mailboxes in a folder for e-mail storage.
[ Option D ]
When we use email, different protocols handle the sending and receiving of messages. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used for sending emails from one server to another, while POP (Post Office Protocol) is designed to download emails from the server to a single device, usually removing them from the server afterward.
In contrast, IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows users to access, manage, and organize their emails directly on the mail server, keeping messages synchronized across multiple devices such as phones, laptops, and tablets.
| FEATURE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| View headers before download | You can preview sender, subject, and date without downloading the full email. |
| Search emails on server | You can search for specific words or phrases in emails directly on the mail server. |
| Create/manage mailboxes | You can create, delete, or rename mail folders. |
| Organize in hierarchy | IMAP allows a hierarchy (folder and subfolder system) for better organization. |
Q: In the context of basis path testing, let the flow graph G (V, E) is drawn using the procedural design or source code. If graph G have 17 edges and 13 nodes, what is cyclomatic complexity of G?
Five
Four
Six
Three
[ Option C ]
Cyclomatic complexity tells us how many independent paths exist in a program. Here, graph has 17 edges and 13 nodes, there are 6 independent paths that must be tested to cover all possible branches in the logic.
Cyclomatic Complexity (V(G)) :
V(G)=E−N+2
Where:
E is number of edges given as 17.
N is number of nodes given as 13.
So,
V(G) = 17−13+2
V(G) = 6
Q: HTTPS uses __________ port number.
80
51
443
25
[ Option C ]
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is the secure version of HTTP, which is used for communication between a web browser and a web server.
Unlike regular HTTP, HTTPS provides encryption and security using the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols. This ensures that any data exchanged, such as passwords, card details, or personal details is protected from unauthorized access.
Every network service on the internet uses a specific port number to communicate. By default, HTTP uses port 80, while HTTPs uses port 443.
Q: What is the total number of non-empty subsets of a 100-item frequent itemset?
100
2100
2100 – 1
100!
[ Option C ]
For a set containing n items, the total number of subsets is given by 2n. This includes the empty set. To find the number of non-empty subsets, we subtract the empty set, i.e., 2n−1.
Here, the itemset has 100 items, so the total number of non-empty subsets is 2100−1.
Q: In case of flow-oriented requirement modeling, context diagram is also known as
Level 0 DFD
Level 1 DFD
Level 2 DFD
Level 3 DFD
[ Option A ]
Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are used to represent how data moves through a system. A Context Diagram is the highest-level view of a DFD, which provides an overview of the entire system as a single process.
Because it gives this top-level, overall picture without showing internal details, the Context Diagram is also called a Level 0 DFD.
Lower-level DFDs such as Level 1, Level 2, and so on, break this single process into smaller sub-processes, showing more internal details of how the system functions.
Q:
Match the following List – 1 with the List – 2:
| List – 1 | List – 2 |
|---|---|
| (i) Unit Testing | (a) It is concerned with scheduling and resourcing all of the activities in the testing process. It involves defining the testing process, taking into account the people and the time available. |
| (ii) Test Planning | (b) This testing should focus on testing component interactions. Where some or all of the components in a system are integrated and the system is tested as a whole. |
| (iii) Component Testing | (c) This type of testing should focus on testing the functionality of objects or methods. |
| (iv) System Testing | (d) This type of testing should focus on testing component interfaces. |
(i) – a, (ii) – b, (iii) –c, (iv) –d
(i) – c, (ii) – a, (iii) – d, (iv) – b
(i) – c, (ii) – a, (iii) – b, (iv) – d
(i) – a, (ii) – c, (iii) – d, (iv) – b
[ Option B ]
| LIST – I | (LIST – II) | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Testing the functionality of objects or methods. | Tests individual program units or functions. |
| Test Planning | Scheduling and resourcing the testing process. | Defines the testing strategy, schedule, and resources. |
| Component Testing | Testing component interfaces. | Verifies interactions between connected modules. |
| System Testing | Testing component interactions in a complete system. | Checks overall system behavior and performance. |
Q: Which of the following testing techniques does not come under control structure testing?
Condition testing
Data flow testing
Loop testing
Graph-based testing
[ Option D ]
Control structure testing is a type of White-Box testing that focuses on the logical control structures of a program, such as decisions, loops, and conditions, to ensure that all possible execution paths are tested. It includes techniques like, condition testing, data flow testing, Loop testing etc.
The Graph-Based Testing does not belong to control structure testing. It falls under Black-Box testing techniques, where the focus is on relationships between inputs, outputs, and modules rather than internal control flow.
Q: Which of the following statement is incorrect?
OLTP adopts Entity-Relationship model
OLAP adopts star or snowflake model
OLTP consists of read-only operations
OLTP consists of short, atomic transactions
[ Option C ]
OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) and OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) serve different purposes in database systems:
OLTP:
OLAP:
Q: In context of transactions in DBMS, S is a schedule having T1, T2, T3 and T4 as participant transactions. A precedence graph (G) is constructed from S to determine its conflict serializability. Consider the following facts:
I. T1 executes write(Q) before T2 executes read(Q).
II. T2 executes read(Q) before T3 executes write(Q).
III. T3 executes write(Q) before T4 executes write(Q).
Which of the following statements is not true?
The graph G contains a directed edge from T1 to T2.
The graph G contains a directed edge from T2 to T3.
The graph G contains a directed edge from T3 to T4.
The schedule S is not conflict serializable
[ Option D ]
In the given schedule, we have the following operations, T1 writes Q before T2 reads Q, T2 reads Q before T3 writes Q, and T3 writes Q before T4 writes Q. These create directed edges T1 → T2, T2 → T3, and T3 → T4 in the precedence graph. Since this graph has no cycles (acyclic), the schedule is conflict serializable and equivalent to the serial order T1 → T2 → T3 → T4.
Q: Let R1 and R2 be two relations with different attributes. What is the output of R1 U R2?
A relation with a combined schema of R1 and R2
Syntax error due to mismatched attributes
A Cartesian product
A view of all tuples from both
[ Option B ]
In relational algebra and SQL, the Union (U) operation combines tuples from two relations and removes duplicates. However, for a union operation to be valid, both relations must be Union-Compatible. Two relations are said to be union-compatible if they satisfy the following conditions:
If these conditions are not met, the union operation cannot be performed, and the system produces a Syntax Error.
Q: Consider the following relation R and the set of all functional dependencies that hold on it :
R(A,B,C,D,E,F)
AB→C
C→ABDE
ADE→F
Which of the following statements is true about R?
It is not in 2NF
It is in 2NF, but not in 3NF
It is in 3NF, but not in BCNF
It is in BCNF
[ Option B ]
In the context of database design, Normalization is a process used to organize data efficiently within a database, reducing redundancy and improving data integrity.
For the given relation R(A,B,C,D,E,F) with functional dependencies AB→C, C→ABDE, and ADE→F. We first identify the candidate keys. Here, C and AB are candidate keys because each can uniquely identify all attributes.
The prime attributes (part of key) are A, B, and C, while D, E, and F are non-prime.
To check which normal form the relation satisfies, we start with 2NF (Second Normal Form), which requires that all non-key (non-prime) attributes are fully functionally dependent on the entire primary key. Since no partial dependency exists here, the relation is in 2NF.
For 3NF, every functional dependency X→Y must satisfy means X is a superkey or Y is a prime attribute.
However, the dependency ADE→F violates this because ADE is not a superkey, and F is not a prime attribute. This means the relation does not satisfy 3NF.
Finally, since the relation is not in 3NF, it also is not in BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form), which is stricter than 3NF.
Q: In the context of data warehousing, the semantic heterogeneity and structure of data, are challenges in which of following?
Data reduction
Data integration
Data cleaning
Data transformation
[ Option B ]
In a Data Warehouse, data comes from multiple heterogeneous sources, such as different databases, formats, and structures. The process of combining this data into a single, consistent view is known as Data Integration.
Q: Which of the following is a scheme for deadlock avoidance?
Manipulate to find at least one safe path
Requesting all resources at once and keep other task waiting
Pre-emption
Resource ordering
[ Option A ]
Deadlock Avoidance is a method used by an operating system to ensure that a system never enters a deadlock state. In deadlock avoidance, the OS makes decisions dynamically by checking whether allocating a requested resource will keep the system in a safe state.
A safe state means that there is at least one sequence in which all processes can complete their execution without getting stuck waiting for each other. The Banker’s Algorithm is a well-known example of deadlock avoidance that works by finding at least one safe sequence before granting a request.
Q: Which of the following does NOT characterize an executing process?
Program counter
Context Data
Priority
Source Code Length
[ Option D ]
A Process is a program in execution. When a program is loaded into memory for execution, the OS assigns it various attributes to help manage and control it effectively. These attributes are part of the Process Control Block (PCB), which contains all the important information about a running process.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Process ID (PID) | Unique identifier assigned to each process. |
| Process State | Shows the current status, New, Ready, Running, Waiting, or Terminated. |
| Program Counter (PC) | Holds the address of the next instruction to be executed. |
| CPU Registers | Store temporary data and intermediate results during execution. |
| Context Data | Contains saved information when a process is switched out, used to restore the process later. |
| Memory Management Information | Includes base and limit registers or page table references for memory allocation. |
| Priority | Defines the scheduling order of processes based on importance. |
| Accounting Information | Keeps track of CPU usage time and other resource statistics. |
| I/O Status Information | Lists the files opened or I/O devices currently used by the process. |
Q: Which of the following statements is true regarding classful and classless routing protocols?
RIPv1 and OSPF are both classless routing protocols that support variable-length subnet masking (VLSM).
Classful routing protocols allow different subnet masks on each router interface.
RIPv1 and IGRP are classful protocols and do not support classless addressing or VLSM.
Classless routing protocols discard subnet mask information to reduce routing table size.
[ Option C ]
In computer networks, routing protocols are used by routers to share information about available paths so data can reach its destination efficiently. These routing protocols are broadly classified into classful and classless types.
Classful routing protocols like RIPv1 and IGRP were introduced early in networking when IP addressing followed fixed class boundaries, Class A, B, and C networks. These protocols do not include subnet mask information in their routing updates. As a result, all subnets within the same major network must use the same subnet mask. This limitation makes them incompatible with Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM), where different subnets can have different mask lengths to optimize IP address usage.
In contrast, classless routing protocols like RIPv2, OSPF, and EIGRP, include the subnet mask information in every routing update. This allows routers to support VLSM and CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing), providing better flexibility and efficient use of IP addresses.
Q: What will be the output of the following PHP code?
<?php
$x = 5;
$y = 10;
function fun()
{
$y = $GLOBALS[‘x’] + $GLOBALS[‘y’];
}
Fun();
echo $y;
?>
5
10
15
25
[ Option B ]
In this PHP code, the variables $x = 5 and $y = 10 are defined globally. Inside the function fun(), a new local variable $y is created and assigned the value of $GLOBALS['x'] + $GLOBALS['y'], which is 15.
However, since no global $y; keyword is used, this local $y does not affect the global $y. After the function call, the global $y still holds the value 10, so the output is 10.
Q: In Data Encryption Standard (DES), the number of rounds is _________.
8
16
24
56
[ Option B ]
Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a Symmetric Key block cipher algorithm that uses the same secret key for both encryption and decryption.
The encryption process in DES consists of a series of operations known as rounds. In DES total 16 rounds are performed, making the encryption much stronger and harder to break through Brute-Force or Statistical Attacks.
Q: The characteristic equation of the T flip-flop is
T̅·Q + Q·T̅
T̅·Q + T·Q̅
TQ
T·Q̅
[ Option B ]
The characteristic equation of a flip-flop defines the next state Q(n+1) in terms of the present state Q(n) and the input. In the case of a T flip-flop, when T = 0, the output remains unchanged, meaning the next state is the same as the present state. When T = 1, the flip-flop toggles, so the next state becomes the complement of the present state.
This behavior can be expressed mathematically as: Q(n+1) = T ⊕ Q(n) which is equivalent to Q(n+1) = T·Q̅(n) + T̅·Q(n).
Q: The number of select inputs required for a 8:1 multiplexer are
2
4
3
1
[ Option C ]
For a multiplexer, the number of select inputs is decided by the relation,
Select Inputs=log2(Number of Data Inputs)
An 8:1 multiplexer has 8 data inputs and only one output, which means we need enough select lines to uniquely choose one of the 8 inputs. Since log2(8) = 3, three select inputs are required.
Q: Consider the resource allocation graph. “This system is always in deadlock state.” This remark is :
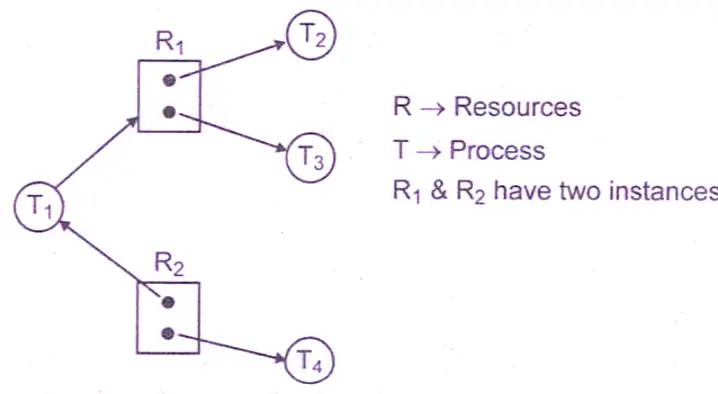
True
False
Unpredictable
Impossible to determine
[ Option B ]
The given resource allocation graph shows two resources, R₁ and R₂, each having two instances, and four processes, T₁, T₂, T₃, and T₄. In this graph, T₁ is waiting for an instance of R₁, while T₂ and T₃ are already holding instances of R₁. Similarly, T₄ is holding an instance of R₂, and T₁ is requesting it.
Since both resources have multiple instances available, all processes can still be allocated resources without creating a circular wait. Therefore, the system is not always in a deadlock state, and the statement that it is always in deadlock is false.
Q: Which of the following best describes the Open-Closed Principle (OCP) in object-oriented component-level design?
A component should be either open or closed for both modification and extension.
A component should be open for extension and closed for modification.
A component should be open for modification and closed for extension.
A component should be neither open nor closed for both modification and extension.
[ Option B ]
The Open-Closed Principle (OCP) is one of the key object-oriented design principles. It states that a software component such as a class, module, or function should be open for extension but closed for modification. This means that the behavior of a component can be extended without altering its existing source code.
Q: If software is developed as a product to be used by many customers, most software product builders use a process called __________ to uncover errors that only the end user seems able to find.
Alpha and beta testing
Integration testing
Recovery testing
System testing
[ Option A ]
When software is developed as a product for many users, developers use Alpha and Beta Testing to find errors that only real users can detect. These tests are performed after internal testing to ensure the software works well in real-world conditions.
Q: Which of the following is NOT a typical or emerging application of multimedia technologies in the field of Information Technology?
Video teleconferencing and distributed lectures for remote education
Telemedicine systems supporting patient consultations over networks
Voice-controlled interactive environments like kitchen-wall web browsers
Static text-based documentation systems with no interactivity or media integration
[ Option D ]
Multimedia technology involves the integration of multiple forms of media such as text, audio, images, video, graphics, and animation to present information in an interactive and engaging way. In Information Technology (IT), Multimedia is used to enhance communication, learning, and user experience.
Static text-based systems are not considered multimedia applications because they contain only plain text and no interactive or visual elements.
Q: In context of mining descriptive statistical measures of data, which of the following sets represents measures of the central tendency and measures of the dispersion of data respectively?
{Mean, Mode, Range}, {Median, Variance, Standard Deviation}
{Mean, Mode, Median}, {Range, Variance, Standard Deviation}
{Median, Variance, Standard Deviation}, {Mean, Mode, Range}
{Mean, Range, Variance}, {Mode, Median, Standard Deviation}
[ Option B ]
In descriptive statistics, data is analyzed using two main types of measures, measures of central tendency and measures of dispersion.
Measures of Central Tendency describe the center or average of a data set. They indicate where most of the data values lie.
Measures of Dispersion describe the spread or variability of data. They show how much the data values differ from the central value. Common examples include:
Q: In context of multidimensional data models for a data warehouse, the fact table contains:
Names of the facts as well as keys to each of the related dimension tables.
List of dimensions.
List of users or expert.
Fact table is abstract and it remains empty.
[ Option A ]
In a multidimensional data model used in a data warehouse, data is organized into fact tables and dimension tables.
The Fact Table is the central table that contains quantitative data, also called measures or facts such as sales amount, quantity, or profit.
In addition to the facts, the fact table contains foreign keys that link it to the associated dimension tables.
Dimension Tables provide descriptive context for the facts, such as time, product, customer, or location.
Q: If a decision tree classifier keeps expanding until every training instance is correctly classified but test error rate begin to increase what is the most likely outcome?
Underfitting
Generalization
Overfitting
Cross-validation error minimized
[ Option C ]
When a decision tree is grown to perfectly classify every training instance, it may start capturing noise and random fluctuations in the training data rather than just the underlying patterns. This results in a phenomenon called overfitting, where the model performs exceptionally well on the training set but fails to generalize to new, unseen data.
Q: In a particular database system, it is estimated that on an average (across many system crashes) the number of committed transactions is almost 5 times the number of uncommitted transactions in the log at the time of restart after the crash. In which of the following logging mechanisms, the recovery manager attends to the least number of transactions, after being given control after a crash?
REDO
UNDO
UNDO-REDO
Equal in all logging mechanisms
[ Option B ]
The number of uncommitted transactions is the smallest, the UNDO mechanism requires the recovery manager to attend to the least number of transactions.
Q: In data warehouse technology, a multiple dimensional view can be implemented using different OLAP storage models. Which of the following correctly distinguishes between ROLAP, MOLAP, and HOLAP?
ROLAP uses multidimensional arrays.
MOLAP uses relational tables.
HOLAP uses only materialized views.
ROLAP use a relational or extended-relational DBMS to store and manage warehouse data.
MOLAP uses array-based multidimensional storage engines.
HOLAP combines ROLAP and MOLAP technology.
ROLAP is faster than MOLAP in indexing of summarized data.
MOLAP supports sparse data better than ROLAP.
HOLAP doesn't support drill-down operations.
ROLAP can only co support numeric data types.
MOLAP supports single-level storage.
HOLAP requires columnar storage engines.
[ Option B ]
In Data Warehouse technology, OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems provide multidimensional views of data for fast analysis. There are three main OLAP storage models.
| OLAP TYPE | STORAGE | DATA REPRESENTATION | ADVANTAGES | REMARK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROLAP (Relational OLAP) | Relational or extended-relational databases | Data stored in tables;. Multidimensional views generated using SQL. | Scales well for large datasets, supports detailed data | Slower query performance on aggregated data. |
| MOLAP (Multidimensional OLAP) | Specialized multidimensional storage engines. | Data stored in arrays / cubes. | Fast query performance, efficient aggregation, and summary. | Handles sparse data well using compression. |
| HOLAP (Hybrid OLAP) | Combines relational tables and multidimensional cubes. | Detailed data in ROLAP, aggregated data in MOLAP. | Balances storage efficiency and query performance. | Provides both scalability and speed. |
Q: Which of the following attack is used for identity theft?
Phishing attack
TCP flooding attack
Virus infection
DNS amplification attack
[ Option A ]
Phishing is when someone tricks you to give your personal information like passwords, bank details, or ID numbers by sending fake emails, messages, or websites that look real. Hackers use this stolen information to steal your identity, make purchases, or commit fraud.
Q: Which of the following is the role of pickle module in Python?
Convert objects into an ordered sequence of bytes
Convert Python objects into JSON notation
Convert a byte stream into Python object hierarchy
Covert a list into a data table
[ Option A ]
The pickle module in Python is used for serializing and deserializing Python objects.
Q: The number of unused states in a 4-bit switch tail ring counter, (Johnson Counter) are
2
4
8
12
[ Option C ]
In a 4-bit Johnson counter (also called a switch-tail ring counter), the total number of possible states is 24=16. However, a Johnson counter produces only 2n unique states, where n is the number of flip-flops. For n=4, the number of valid states is 2×4=8. Therefore, the number of unused or invalid states is 16−8=8.
Q: Which of the statement is correct in JavaScript regarding var and let keywords?
var has global scope, and let has block scope
var has block scope, and let has global scope
var has local scope, and let has global scope
var has global scope, and let also has global scope
[ Option A ]
In JavaScript, the main difference between var and let lies in their scope. A variable declared with var has either global scope (if declared outside a function) or function scope (if declared inside a function). It does not follow block scope, meaning it can still be accessed outside the block { } in which it is defined.
On the other hand, a variable declared with let is block scoped, which means it is only accessible within the block { } where it is declared.
// Using var
if (true) {
var x = 10;
}
console.log(x); // No Error, print 10 (var is not block scoped).
// Using let
if (true) {
let y = 20;
}
console.log(y); // Error, y is not defined (let is block scoped).
Q: Full form TIFF image file format is
Targeted Image File Format
Tagged Image File Format
Tuned Image File Format
Tilted Image File Format
[ Option B ]
TIFF stands for Tagged Image File Format. It is a flexible and high-quality image format used for storing photographs and scanned images.
Q: What is the role of content Providers in Android?
Controls the life cycle of activities
Provides a consistent and non-intrusive mechanism for signaling to users
Share data between applications
Supports non-code resources like strings and graphics
[ Option C ]
In Android, Content Providers are mainly used to share data between applications in a secure and structured way. They provide a standard interface for accessing and managing data like contacts, images, videos, etc., and apps can query or modify this data using URIs.
Q: What will be the output of the following code?
#include<stdio.h>
void modify(int a, int b)
{
a += 10;
b += 20;
printf(“Inside modify: %d%d\n”,a,b);
}
int main()
{
int x =5, y = 7;
modify(x,y);
printf(“Inside main : %d%d\n”,x,y);
return 0;
}
Inside modify : 15 27
Inside main : 5 7
Inside modify : 15 27
Inside main : 15 27
Inside modify : 5 7
Inside main : 5 7
Inside modify : 5 7
Inside main : 15 27
[ Option A ]
This program demonstrates call by value in C. When modify(x,y) is called, the values of x and y are copied into local variables a and b. Inside the function, a becomes 15 and b becomes 27, which are printed. However, changes to a and b do not affect the original variables in main, so x and y remain 5 and 7.
Q: Consider the code segment:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int i,n;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(fork() == 0)
printf(“CHILD\n”);
}
printf(“OS\n”);
return 0;
}
Number of times CHILD and OS are printed?
2^n and 2^n
2^(n-1) and 2^(n-1)
2^(n-1)-1 and 2^(n-1)
2^n and 2^(n-1)
[ Option C ]
Q: Which of the following statement(s) is/are true about OLAP?
I. These systems have very large number of users than that of database systems.
II. Accesses to these systems are mostly read-only operations.
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
[ Option B ]
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems are designed for complex analysis of large volumes of data. They are optimized for query performance and analytical operations, rather than for handling large numbers of concurrent users.
OLAP systems primarily involve read-only operations, such as slicing, dicing, and aggregating data, rather than frequent updates or inserts.
Q: What is the recurrence relation of the best case in quick sort?
T(n) = 2T(n/2)+Ө(n)
T(n) = T(n-1)+ Ө(n)
T(n) = T(n/2)+ Ө(n2)
T(n) = 2T(n/2)+ Ө(n2)
[ Option A ]
A recurrence relation is an equation that expresses the running time of a problem in terms of smaller instances of the same problem. It is used in the analysis of recursive algorithms because recursion naturally breaks a large problem into smaller subproblems.
By writing and solving the recurrence relation, we can calculate the overall time complexity of the algorithm in an exact and systematic way.
In the best case of Quick Sort, each partition splits the array into two equal halves. The partitioning step itself requires scanning the entire array once, which takes Θ(n) time. After this step, two recursive calls are made on subarrays of size n/2 each, giving 2T(n/2). Therefore, the recurrence relation can be expressed as T(n) = 2T(n/2) + Θ(n). By applying the Master Theorem to this recurrence, we find that the solution is T(n) = Θ(n log n).
Q: Which of the following techniques cannot be used for removal of noise from data?
Smoothing by bin means
Smoothing by bin medians
Smoothing by bin compliment
Smoothing by bin boundariesSmoothing by bin boundaries
[ Option C ]
Noise removal in data preprocessing aims to reduce errors or random variations in datasets.
SMOOTHING BY BIN MEANS: Replaces each value in a bin with the mean of the bin to reduce variability.
SMOOTHING BY BIN MEDIANS: Replaces each value with the median of the bin, which is robust to outliers.
SMOOTHING BY BIN BOUNDARIES: Replaces values with the closest boundary (min or max) of the bin to limit extreme values.
Q: What is the “Convoy effect” in CPU scheduling?
A situation where multiple processes arrive at the CPU at the same time.
A condition where all I/O-bound processes are executed before CPU-bound processes.
A scenario in which one long CPU-bound process delays many shorter I/O-bound processes, reducing overall system utilization.
A technique used to prioritize processes with the shortest burst time.
[ Option C ]
The Convoy Effect is a performance problem that occurs in CPU scheduling, especially in algorithms like First-Come, First-Served (FCFS). In this situation, a long CPU-Bound process gets the CPU first. Meanwhile, several I/O-Bound processes have to wait in the Ready Queue.
Since the CPU is busy executing the long process, the shorter I/O-bound processes are delayed. As a result, the CPU stays idle when those I/O-bound processes later perform I/O operations, and overall system utilization drops.
| TYPE OF PROCESS | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|
| CPU-Bound | Uses the CPU heavily with few I/O operations. When it runs first, it keeps the CPU busy for a long time, delaying other processes waiting in the queue. |
| I/O-Bound | Performs frequent I/O operations with short CPU bursts. These processes must wait for the long CPU-bound process to finish, leading to poor CPU and I/O utilization. |
Q: Which of the following is not a component of NTFS volume layout?
Partition boot sector
Master bytes
File area
System files
[ Option B ]
NTFS (New Technology File System) is the main file system used by Windows operating systems to store and organize data on hard drives. It is more advanced than FAT and FAT32 because it supports features like file permissions, encryption, compression, and large storage sizes.
An NTFS volume layout is divided into several main components that define how data is stored and accessed:
| COMPONENT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Partition Boot Sector | Contains information needed to start the operating system and details about the NTFS structure. |
| System Files | Includes essential metadata files like the Master File Table (MFT), which keeps records of all files and directories. |
| File Area | The space where the actual data and files created by users are stored. |
There is no component called “Master bytes” in the NTFS layout.
Q: What is the worst-case complexity of selection sort?
O(n log n)
O(log n)
O(n)
O(n2)
[ Option D ]
The worst-case time complexity of Selection Sort is O(n²). This is because, in every pass of the algorithm, the smallest (if sort in ascending order) or largest (if sort in descending order) element is selected from the unsorted portion of the array by scanning all remaining elements. This requires (n−1) comparisons in the first pass, (n−2) in the second pass, and so on, until only one element is left.
The total number of comparisons becomes (n−1)+(n−2)+...+1=n(n−1)/2, which simplifies to O(n²).
Q: In the given key pattern:
1 → 4, 2 → 8, 3 → 1, 4 → 5, 5 → 7, 6→2, 7→6, 8→3
The first bit of plaintext moves to the fourth position of ciphertext and so on.
What would be the cipher text in transposition cipher for the following plaintext ?
Plaintext : SACKGAUL
(Note: above plaintext should be read from right to left)
UKAGLSCA
KUCGASLA
SCAUKAGL
SAUKCALG
[ Option A ]
Given, Plaintext = SACKGAUL, but it says read from right to left, so we reverse it: LUAGKCAS. Now, the positions are:
| POSITION | LETTER |
|---|---|
| 1 | L |
| 2 | U |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | K |
| 6 | C |
| 7 | A |
| 8 | S |
The given key pattern:
1 → 4
2 → 8
3 → 1
4 → 5
5 → 7
6 → 2
7 → 6
8 → 3
This means:
The 1st plaintext letter goes to 4th position in ciphertext.
The 2nd plaintext letter goes to 8th position in ciphertext.
The 3rd plaintext letter goes to 1st position and so on. So,
| PLAINTEXT LETTER | GOES TO POSITION | CIPHERTEXT POSITION |
|---|---|---|
| L (1) | 4 | 4th = L |
| U (2) | 8 | 8th = U |
| A (3) | 1 | 1st = A |
| G (4) | 5 | 5th = G |
| K (5) | 7 | 7th = K |
| C (6) | 2 | 2nd = C |
| A (7) | 6 | 6th = A |
| S (8) | 3 | 3rd = S |
Now after arranging ciphertext in order 1 to 8, ACSLGAKU. Since plaintext was read right to left, the ciphertext is also read from right to left, i.e., UKAGLSCA.
Q: Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
I. Keywords are those words whose meaning is already defined by Compiler.
II. Keywords cannot be used as variable name.
III. There are 32 keywords in ANSI C.
IV. C keywords are also called as reserved words.
I and II only
II and III only
I, II and IV only
I, II, III and IV
[ Option D ]
Must Know:
| Keyword | Description |
| _Bool | Represents Boolean data type. In C, 0 (zero) is treated as false and any non-zero value is treated as true. |
| _Complex | Represents complex numbers (real + imaginary). |
| _Imaginary | Represents imaginary numbers (pure imaginary part). |
| inline | Suggests the compiler to expand the function inline to reduce call overhead. |
| restrict | A pointer qualifier that tells compiler the pointer is the only way to access data. |
Q: Which of the following is NOT a condition for deadlock to be possible?
Mutual Exclusion
Hold and Wait
Pre-emption
No resources can be forcibly removed from a process holding it.
[ Option C ]
A Deadlock is a situation in an operating system where two or more processes are waiting for each other indefinitely to release resources. For a deadlock to occur, four necessary conditions (Coffman’s conditions) must hold simultaneously.
| CONDITION | MEANING |
|---|---|
| Mutual Exclusion | At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode, only one process can use it at a time. |
| Hold and Wait | A process is holding at least one resource and is waiting for another that is currently held by another process. |
| No Pre-emption | A resource cannot be forcibly taken away from a process. It must be released voluntarily. |
| Circular Wait | A circular chain of processes exists, where each process holds one resource and waits for the next process resource. |
Deadlock happens only when resources cannot be pre-empted. Therefore, Pre-emption itself is not a condition for deadlock. In fact, it helps prevent deadlock.
Q: Output of the linked list node access in the following code:
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
int main()
{
struct node n1 = {10,NULL};
struct node n2 = {20,NULL};
n1.next = &n2;
printf(“%d”, n1.data+n1.next->data);
}
10
20
NULL
30
[ Option D ]
In this program, n1 is initialized with data 10 and n2 with data 20. Then n1.next is set to point to n2. In the printf statement, n1.data gives 10 and n1.next->data accesses the data of n2, which is 20. Their sum is 30, so the output is 30.
Q: What is the purpose of swapping in an operating system?
To permanently terminate long-running processes.
To move processes between different CPU cores for load balancing.
To increase the CPU's clock speed during peak usage.
To temporarily remove a process from memory and resume it later.
[ Option D ]
Swapping is a memory management technique used when the system’s main memory (RAM) becomes full.
In a multitasking environment, several processes are loaded into memory, but sometimes there is not enough space for all of them. To handle this, the operating system temporarily moves some inactive processes from main memory to the hard disk (swap space). This process is called swapping out.
When the process is needed again, it is swapped back into memory, called swapping in. This allows the OS to manage limited memory more efficiently and ensures that active processes get enough memory to run.
| TERM | MEANING |
|---|---|
| Swapping Out | Moving a process from main memory to disk. |
| Swapping In | Bringing the process back from disk to main memory when needed. |
Q: One’s complement representation of (-8)10 is :
(01000)2
(10111)2
(11000)2
(00111)2
[ Option B ]
In one’s complement representation, a negative number is obtained by inverting all the bits of its positive binary form. For (−8)10, we first write +8 in 5-bit binary, which is (01000)2. Now, by inverting each bit (all 0s become 1s and all 1s become 0s), we get (10111)2. Hence, the one’s complement representation of (−8)10 is (10111)2.
Q: Which of the following can work as error detecting and correcting code?
Cyclic Redundancy Checks
Hamming codes
Checksum
1D parity
[ Option B ]
In data communication, error detection and correction are essential for ensuring that transmitted data reaches the destination accurately. Most error control methods can only detect errors, while some can also correct them.
Hamming Code is a special type of code that can both detect and correct single-bit errors. It adds redundant bits called parity bits at specific positions in the data.
| CODE TYPE | PURPOSE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Parity Bit / 1D Parity | Error Detection. | Detects single-bit errors only. |
| Checksum | Error Detection. | Detects most errors in blocks of data. |
| Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) | Error Detection. | Detects burst errors effectively. |
| Hamming Code | Error Detection & Correction. | Detects and corrects single-bit errors. |
Q: What would be an appropriate call to action for a digital marketing campaign in the awareness stage of the customer journey?
Asking the audience to purchase a product
Encouraging the audience to subscribe to a newsletter
Inviting the audience to listen to a podcast episode or read a blog post
Recommending the audience to download a whitepaper
[ Option C ]
In the Awareness Stage of the customer journey, the goal is to introduce your brand or product to potential customers and provide educational or engaging content. At this stage, the audience is not yet ready to make a purchase, so hard-sell actions like buying a product or downloading detailed whitepapers are less effective.
Q: Which of the following is not an example of Open-Loop Congestion Control?
Window Policy
Discarding Policy
Admission Policy
Choke Packet
[ Option D ]
In network congestion control, there are two main approaches, Open-Loop and Closed-Loop control.
Open-Loop Congestion Control tries to prevent congestion before it happens. It uses policies set at the design or setup stage rather than reacting to network conditions. The Admission Policy, Discarding Policy, and Window Policy are example of open-loop control.
Closed-Loop Congestion Control, is reactive, it monitors the network and takes action when congestion is detected. The Choke Packet is an example of closed-loop control. It is a signal sent by the router to the source to slow down transmission when congestion occurs.
Q: What is an infrastructure network as per IEEE 802.11 standard?
A basic service set without an access point.
A basic service set with an access point.
Two or more basic service sets without access point.
Only access points but no basic service set.
[ Option B ]
In wireless networking, IEEE 802.11 is the standard that defines Wi-Fi networks. Under this standard, a Basic Service Set (BSS) is the fundamental building block of a wireless LAN. There are two primary types of network configurations:
Infrastructure Mode : This setup includes a central Access Point (AP) that coordinates communication between wireless devices (stations). Multiple BSS can be interconnected via access points.
Ad hoc Mode (Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS)) :This setup does not have an access point. Wireless devices communicate directly with each other, forming a temporary or decentralized network.
| Network Type | Access Point Present | Communication Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Network | Yes | Through Access Point. | Home Wi-Fi, Office Wi-Fi. |
| Ad hoc (IBSS) | No | Direct (Peer-to-Peer) | Temporary device-to-device sharing. |
Q: A functional dependency of the form X → Y is trivial if
X ⊆ Y
Y ⊆ X
Χ = ϕ
X ⊂ Y
[ Option B ]
In DBMS, a Functional Dependency (FD) represents a relationship between two sets of attributes in a relation. It is written as X → Y, meaning that the value of attribute set X uniquely determines the value of attribute set Y.
A Trivial functional dependency is one that always holds true and does not provide any new information about the data. It occurs when the dependent attributes (Y) are already included in the determinant (X). In other words, if Y is a subset of X (Y ⊆ X), the dependency is called trivial.
Q: The minimized expression for a 4-variables logic function, f(A, B, C, D) = Σm(0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14) , using K-Map is
(Ā + B + C̅ + D) (Ā + B̅ + C) (Ā + B̅ + D̅) (A + B̅ + D)
ABCD̅ + B̅C̅ + B̅D + A̅D + A̅B̅
B̅ + A C̅ + A̅ C D
A̅B̅C̅D + BC + BD̅ + AD̅ + AB̅
[ Option B ]
Q: In context of expression equivalence rules used for query optimization in DBMS, choose the false statement.
The set operations union and intersection are commutative.
The set operations union and intersection are not associative.
The projection operation distributes over the union operation.
The set difference operation is not commutative.
[ Option B ]
In query optimization, expression equivalence rules help the DBMS simplify queries without changing their final result. Some operations like union (∪) and intersection (∩) are both commutative and associative.
The Projection (π) operation distributes over union, meaning π(A ∪ B) = π(A) ∪ π(B).
The Set Difference (−) is not commutative because A − B ≠ B − A.
Q: What is the key difference between user-level threads and kernel-level threads?
User threads are created by the hardware, while kernel threads are created by the user.
Kernel threads can run without an operating system, while user threads cannot.
User threads are managed without kernel support, while kernel threads are managed by the operating system.
There is no relationship between kernel threads and user threads.
[ Option C ]
A Thread is a lightweight unit of a process that allows multiple parts of a program to execute concurrently. There are two main types of threads.
User-Level Threads (ULTs):
Kernel-Level Threads (KLTs):
Q: What will be the output of the following Python script?
>>>L=[‘spam’, ‘Spam’, ‘SPAM!’]
>>>L[-2]
‘Spam’
‘spam’
‘SPAM!’
‘SP!’
[ Option A ]
In Python, negative indexes count from the end of the list.
Positive Indexing starts from left to right:
Index: 0 1 2
Value: 'spam' 'Spam' 'SPAM!'
Negative Indexing start from right to left:
Index: -3 -2 -1
Value: 'spam' 'Spam' 'SPAM!'
Q: Which of the following is true for adjacency matrix representation of a graph with n vertices?
Space complexity is O(n)
Can not be used for directed graph
Space complexity is O(n2)
Can not be used for weighted graphs
[ Option C ]
In an adjacency matrix, we represent a graph using a two-dimensional array of size n×n, where n is the number of vertices. Each row and column correspond to a vertex, and the value stored in a cell tells us whether an edge exists between two vertices.
If the graph is weighted, the cell stores the weight instead of just 0 or 1. Since the matrix always needs space for n2 entries, the space complexity is O(n2). This representation can be used for directed or undirected graphs as well as weighted or unweighted graphs.
The only drawback is that it uses more memory for sparse graphs, but it provides quick access to check if an edge exists between two vertices.
Q: In a 4-stage ripple counter, the propagation delay of a flip-flop is 50ns. If the pulse width of the strobe is 30ns, find the maximum frequency at which the counter operates reliably.
10.0 MHz
20.0 MHz
7.5 MHz
4.35 MHz
[ Option D ]
Q: _________ is a collection of programs written to service other programs.
System software
Application software
Both System software & Application software
Neither System software Nor Application software
[ Option A ]
System Software is a collection of programs designed to manage and support the operation of a computer system and to service other programs. It acts as a interface between the hardware and application software.
Examples of system software include the Operating System like Windows, Linux, macOS, Device Drivers, Utility Programs, and Language Translator like compiler, assembler, and interpreter.
Q:
Match the clustering approach (Column 1) with its correct description (Column 2):
| Column 1 (Clustering Approach) | Column 2 (Description) |
|---|---|
| 1. Agglomerative Method | A. Begins with each data object as its own cluster and merges them iteratively. |
| 2. Divisive Method | B. Uses density rather than distance to form clusters, enabling discovery of arbitrary shapes. |
| 3. Density Based Method | C. Starts with all data in one cluster and then recursively splits into smaller clusters. |
1 – A, 2 – C, 3 – B
1 – C, 2 – A, 3 – B
1 – B, 2 – C, 3 – A
1 – C, 2 – B, 3 – A
[ Option A ]
Clustering approaches can be categorized based on how they form groups of data.
| CLUSTERING APPROACH | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Agglomerative Method | Bottom-up hierarchical approach, begins with each data object as its own cluster and merges them iteratively. |
| Divisive Method | Top-down hierarchical approach, starts with all data in one cluster and recursively splits into smaller clusters. |
| Density-Based Method | Forms clusters based on density rather than distance, allowing discovery of arbitrarily shaped clusters and handling noise. |
Q: To verify a digital signature, we need the _____________.
Sender's private key
Sender's public key
Receiver's private key
Receiver's public key
[ Option B ]
In public key cryptography, a Digital Signature is created by the sender using their private key (Sender Private Key). To verify that the signature is authentic and that the message has not been altered, the receiver uses the Sender’s Public Key. This ensures the signature was indeed generated by the sender and provides authentication and integrity.
Q: In context of transactions in DBMS, choose a valid statement about deadlock prevention schemes.
wait-die is a nonpreemptive and wound-wait is a preemptive technique.
wait-die is a preemptive and wound-wait is a nonpreemptive technique.
Both wait-die and wound-wait schemes are nonpreemptive techniques.
Both wait-die and wound-wait schemes are preemptive techniques.
[ Option A ]
Deadlock prevention schemes in databases use timestamp ordering to avoid cyclic waiting. Two popular timestamp-based methods are wait-die and wound-wait schemes.
In the wait-die scheme (non-preemptive), if an older transaction requests a resource held by a younger one, it is allowed to wait, otherwise, the younger transaction is rolled back.
The wound-wait scheme (preemptive) allows the older transaction to “wound” the younger one by forcing it to roll back immediately and release the resource. Because wait-die involves waiting (non-preemptive) and wound-wait involves forced rollback (preemptive).
Q: Which of the following statements are true regarding firewalls?
A. Only the packets from trusted source address can enter the organization's network.
B. It is important to have firewalls to prevent the network from unauthorized access.
C. A firewall can be implemented using hardware or software or the combination of both.
D. A firewall can not be implemented using software.
A, B, C are correct.
A, B, D are correct.
A and C are correct.
A and B are correct.
[ Option A ]
A Firewall is a network security device or software that acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and an untrusted external network, like the internet.
Its main purpose is to monitor data packets entering or leaving the network and decide whether to allow or block them based on predefined security rules.
Firewalls help protect systems from hackers, viruses, and unauthorized access. They can be implemented using hardware, software, or both, depending on the system’s security needs.
Firewalls ensure that only packets from trusted source addresses are allowed to enter the organization’s network.
Q: Consider the following SQL query to retrieve Cust_ID of the customers from CUSTOMER table, whose name contains P as second character and ends with A
SELECT Cust_ID
FROM CUSTOMER
WHERE _________;
Which of the following is most suitable to complete the query?
name like '_P%A'
name like '$P%A'
name like '2P$A'
name like '%P_A'
[ Option A ]
In SQL, the LIKE operator is used with wildcard characters to match patterns in string data. The two main wildcards are:
| WILDCARD CHARACTER | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE | RESULT |
|---|---|---|---|
| _ (Underscore) | Represents exactly one character. | 'A_P' | ACP, ABP, A2P |
| % (Percent) | Represents zero or more characters. | 'A%P' | AP, ABP, ABBP, APQRP |
In the given query, we need to find customer names where the second character is ‘P’ and the name ends with ‘A’.
Thus, the correct pattern is '_P%A', which means, any first character (_), followed by ‘P’, then any number of characters (%), and ending with ‘A’.
Q: Which of the following SQL statements is a DDL command?
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
ALTER
[ Option D ]
In SQL, commands are categorized into DDL, DML, DQL, DCL and TCL based on their purpose.
| Category | Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
DDL (Data Definition Language) Defines and manages the structure of the database and its objects. | CREATE | Creates a new database, table, or other database object. | CREATE TABLE Students (Rollno INT, Name VARCHAR(50)); |
| ALTER | Modifies the structure of an existing database object (add/drop column, change datatype). | ALTER TABLE Students ADD Age INT; | |
| DROP | Deletes a database, table, or object permanently. | DROP TABLE Students; | |
| TRUNCATE | Deletes all rows from a table but keeps the table structure. | TRUNCATE TABLE Students; | |
| RENAME | Renames a table or database object. | ALTER TABLE Students RENAME TO PGStudent; | |
DML (Data Manipulation Language) Used to manipulate or modify data stored in the database tables. | INSERT | Adds new rows (tuples) to a table. | INSERT INTO Students VALUES (1001, 'Suresh'); |
| UPDATE | Modifies existing rows in a table. | UPDATE Students SET Age = 31 WHERE Rollno = 1001; | |
| DELETE | Removes specific rows from a table. | DELETE FROM Students WHERE Rollno= 1001; | |
DCL (Data Control Language) Controls access and permissions to the database. | GRANT | Gives privileges/permissions to users. | GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON Students TO User1; |
| REVOKE | Removes privileges/permissions from users. | REVOKE INSERT ON Students FROM User1; | |
DQL (Data Query Language) Used to retrieve data from the database. | SELECT | Retrieves data from one or more tables. | SELECT Name, Age FROM Students; |
TCL (Transaction Control Language) Manages transactions to ensure data integrity and consistency. | COMMIT | Saves all changes made in the current transaction permanently. | COMMIT; |
| ROLLBACK | Undoes all changes made in the current transaction. | ROLLBACK; | |
| SAVEPOINT | Sets a point within a transaction to which you can roll back. | SAVEPOINT sp1; |
Q: Which of the following are represented by the box icons divided into horizontal parts in UML class diagrams?
classes only
interfaces only
neither a class nor an interface
classes, abstract classes and interfaces
[ Option D ]
In Unified Modeling Language (UML), classes, abstract classes, and interfaces are depicted using Rectangular Boxes divided into three horizontally into compartments.
This standardized box notation applies to classes, abstract classes (often italicized names), and interfaces (sometimes labeled with «interface»).
| Student |
| name : String rollno : int |
| setDetails() : void getDetails() : void updateRecord() : void |
| Employee |
| empID: int salary: float |
| calculateBonus() : void |
| «interface» Drawable |
| Interfaces typically do not have attributes. |
| draw() : void resize() : void |
Q: Which of the following is a disk scheduling policy ensuring selection of the disk I/O request that requires the least movement of the disk arm from its current position?
Shortest-service-time-first (SSTF)
First In First Out (FIFO)
SCAN algorithm
Back and forth over disk
[ Option A ]
In an operating system, multiple processes often request disk I/O operations at the same time. To manage these requests efficiently, the OS uses Disk Scheduling Algorithms, which decide the order in which the disk head (arm) moves to service requests. The main goal is to reduce Seek Time, which is the time taken by the disk arm to move to the track where data is located.
Among the given options, the Shortest-Service-Time-First (SSTF) algorithm selects the disk I/O request that is closest to the current position of the disk arm. This means the arm moves the least possible distance, which minimizes seek time and improves performance.
| ALGORITHM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| FIFO (First In First Out) | Serves requests in the order they arrive. Simple but may cause long seek times. |
| SSTF (Shortest-Service-Time-First) | Chooses the request nearest to the current head position. It reduces seek time but may cause starvation. |
| SCAN (Elevator Algorithm) | Moves arm in one direction, serving requests, then reverses. It provides fairness and reduces variance. |
Q:
Which of the following statements are correct with respect to the given system call?
| System Call | Statement |
|---|---|
| A. fork() | Creates a new process that starts from the main() function again. |
| B. wait() | Waits for the child process to terminate and retrieves its exit status. |
| C. exec() | Replaces the current process image with a new program executable. |
Options B, C are correct.
Options A, C are correct.
Options A, B are correct.
Options A, B, C are correct.
[ Option A ]
System Calls are special functions provided by the OS that allow user programs to request services from the kernel, such as process creation, file handling, or communication.
In process management, three important system calls are fork(), wait(), and exec(), each serving a specific purpose in process control.
| System Call | Used For |
|---|---|
| fork() | Creates a new process, called the child process, which is a copy of the parent process. The child process starts execution from the next instruction after fork(), not from the main() function again. |
| wait() | Makes the parent process wait until its child process finishes. It also retrieves the exit status of the child process. |
| exec() | Replaces the current process image with a new program executable, allowing a process to run a different program in the same process ID. |
Q: The 0-D cuboid, which holds the highest level of summarization is also known as:
Base cuboid
Apex cuboid
Intermediate cuboid
Multi-dimensional cube
[ Option B ]
In data warehousing and OLAP, a cuboid represents a specific level of aggregation in a multidimensional cube.
The 0-D cuboid is the highest level of summarization, meaning it aggregates data across all dimensions, providing only a single summarized value for the entire dataset. This cuboid is also called the Apex Cuboid because it sits at the top of the aggregation lattice.
Q: In the context of data warehousing, let 'smoothing by bin boundaries' is applied for data cleaning on the data [4, 8, 15, 21, 21, 24, 25, 28, 34] with equal-frequency bins of size 3 (namely bin1, bin2 and bin3). After smoothing bin2 data is given by:
21, 21, 24
22, 22, 22
21, 24, 24
21, 22.5, 24
[ Option A ]
Smoothing by bin boundaries is a data cleaning technique used to reduce the effect of noise or outliers in a dataset. The process involves dividing data into bins and then replacing each value in a bin with the closest bin boundary value either minimum or maximum of the bin.
Given the data [4, 8, 15, 21, 21, 24, 25, 28, 34] and equal-frequency bins of size 3:
Smoothing by bin boundaries for Bin2:
Bin boundaries: Min = 21, Max = 24
Replace each value in Bin2 with the nearest boundary:
Finally, the smoothed Bin2 is [21,21,24].
Q: Which is true about OSPF Routing protocol?
It is based on Distance Vector routing
It is an exterior routing protocol
It does not have authentication capability
It is an interior routing protocol
[ Option D ]
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a link-state Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) used for routing within a single Autonomous System (AS), such as an organization or a campus network. It uses the link-state routing algorithm.
Q: Which of the following statements are true regarding fragmentation and reassembly in IPv6?
A. IPv6 allows for fragmentation and reassembly at intermediate routers.
B. IPv6 allows for fragmentation and reassembly only at the source and destination.
C. IPv6 allows to intermediate routers forward the oversized packets.
D. IPv6 sends ICMP error message for oversized packets to the sender.
A and C
B and D
A and D
A and B
[ Option B ]
In IPv4, fragmentation could occur at both source and intermediate routers, meaning routers could break large packets into smaller fragments to fit the network’s Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU).
The IPv6 changed the approach to make packet handling faster and simpler. In IPv6, only the source node is allowed to perform fragmentation, and reassembly is done only at the destination, not at intermediate routers.
If a router receives a packet larger than the MTU, it does not fragment the packet. Instead, it drops the packet and sends an ICMPv6 “Packet Too Big” error message back to the sender.
Q: In context of Intrusion Detection Systems, which of the following is not true about honeypots?
Divert attention of a potential intruder from critical systems.
Collect information about the intruder's actions.
Look like real-life systems.
Allow legitimate users to know about or access honeypots.
[ Option D ]
A Honeypot is a security mechanism used in Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to attract attackers and study their behavior. It is designed to look like a real system containing valuable data or services, but it is actually a Decoy that isolates and monitors malicious activities.
Honeypots help in diverting attackers’ attention away from critical systems and collecting information about their methods, tools, and intentions.
However, Legitimate Users are not supposed to know about or access honeypots, as their purpose is purely for monitoring and deception.
Q: What is the difference between && and & operator in C?
No difference; both are logical AND
&& is logical AND, & is bitwise AND
&& is a syntax error
& is a syntax error
[ Option B ]
Q: What will be the output of the following code?
#include<stdio.h>
struct info
{
int x;
};
int main()
{
struct info a = {10};
struct info b = a;
b.x = 20;
printf(“%d %d”, a.x,b.x);
return 0;
}
10 10
20 20
10 20
20 10
[ Option C ]
As we know, structure variables in C are copied by value, not by reference. When struct info b = a; is executed, the value of a.x (10) is copied into b.x. Later, changing b.x = 20 does not affect a.x, which remains 10. Therefore, the output of the program is 10 20.
Q: The levels of granularity in software testing include all of the following except __________.
Unit Testing
Segment Testing
Component Testing
System Testing
[ Option B ]
In software testing, the term Granularity refers to the level of detail or scope at which the software is tested. There are several recognized levels of testing techniques like unit testing, component testing, and system testing, each focusing on different parts of the system.
The Segment Testing is not a standard level of software testing. It is not formally recognized in the software testing process hierarchy.
Q: Which of the following defines the measure 'precision' in the context of metrics for evaluating classifier performance, if TP, TN, FP, FN refer to the number of true positive, true negative, false positive and false negative respectively?
TP/(TP+FP)
TN/(TN+FN)
TP/(TN+FN)
TN/(TP+FP)
[ Option A ]
In classification problems, evaluating the performance of a classifier involves several metrics, one of which is Precision. Precision measures the accuracy of positive predictions.
Mathematically, precision is defined as TP/(TP+FP).
Where:
Q: Consider the following memory map using multiprogram with partition model. Dark represent memory in use while white represent free memory as shown in the figure below:
| 65k | 125k | 150k | 175k | 150k |
Request for memory follows the following order : 100k, 25k, 125k, 50k. which of the following allocation satisfies the above request? [8]
(A) Best Fit
(B) First Fit
(C) Worst Fit
A, B, C
A, B
B, C
A, C
[ Option B ]
Q: According to the Bell-LaPadula security model, a subject S is permitted to write to an object O only if the security classification of S satisfies which of the following conditions with respect to O?
class (S) ≥ class(O)
class (S) > class(O)
class(S) ≤ class (O)
class (S) < class (O)
[ Option C ]
According to the Bell-LaPadula security model, a subject S is permitted to write to an object O only if the security classification of the subject satisfies the condition:
class(S)≤class(O)
This is known as the "No Write Down" or Star (*) Property rule, which prevents a subject from writing information to a lower security level object, thereby preventing potential information leakage from higher classified data to lower classification levels.
Q: Act of listening to a private conversation between hosts in a network is called ___________.
Spoofing
Tampering
Eavesdropping
Repudiation
[ Option C ]
Eavesdropping is the act of secretly listening to or capturing private communication between two parties over a network.
It is a type of network attack where an unauthorized person monitors data that is being transmitted between hosts. This can include listening to phone calls, reading emails, or intercepting messages exchanged over the internet.
Q: Consider a system using 2-level paging and the virtual address is 38 bits. The most significant 10 bits are used to index the page directory and next 16 bits index the page table. Each entry in both levels is 4 bytes. What is the maximum size of a page table in KB?
4 KB
16 KB
256 KB
None of these
[ Option C ]
The virtual address is 38 bits long, where 10 bits are for the page directory and 16 bits for the page table. Each page table entry is 4 bytes. So, the number of entries in a page table is 216. Multiplying by 4 bytes gives 218 bytes, which is equal to 256 KB. Hence, the maximum size of a page table is 256 KB.
Q: Amazon.com provides what kind of E-Com services?
B2G
C2B
C2G
B2C
[ Option D ]
E-commerce (Electronic Commerce) refers to buying and selling goods or services over the Internet. Depending on who is involved in the transaction, businesses, consumers, or governments, e-commerce can be divided into several types or models.
| TYPE | FULL FORM | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2C | Business to Consumer | A business sells products or services directly to consumers. | Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra |
| B2B | Business to Business | Transactions between two businesses. | Alibaba, IndiaMART |
| C2B | Consumer to Business | Consumers offer products or services to businesses. | Freelancing platforms. |
| C2C | Consumer to Consumer | Consumers sell directly to other consumers. | OLX, eBay |
| B2G | Business to Government | Businesses provide products or services to government agencies. | Government procurement portals |
| C2G | Consumer to Government | Consumers interact or make payments to the government. | Paying taxes or utility bills online |
Amazon.com provides B2C E-commerce services, where businesses sell products directly to individual customers through an online marketplace.
Q: In context of software design, choose the correct option for the following Assertion and Reason:
Assertion (A) : It is desirable to have the lowest possible coupling between modules.
Reason (R) : Simple connectivity among modules results in software that is easier to understand and less prone to a "ripple effect" of errors across the system.
Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
[ Option A ]
In software design, Coupling refers to the degree of interdependence between software modules. Means, how closely connected or dependent one module is on another. It is desirable to have the lowest possible coupling because loosely coupled modules can function independently, are easier to Test, Maintain, and Modify without affecting other parts of the system.
Q: What will be the output of the following PHP program?
<?php
$fruits = array(“apple”, “orange”, array (“pear”, “mango”), “banana”);
print (count($fruits,1));
?>
6
5
4
3
[ Option A ]
In this PHP program, the array $fruits contains four elements: "apple", "orange", a nested array ["pear", "mango"], and "banana".
By default, the count() function in PHP counts only the top-level elements, which would give 4. However, since the program uses count($fruits, 1), the second parameter enables recursive counting, meaning elements inside nested arrays are also included in the count.
The nested array ["pear", "mango"] has 2 elements, so the total becomes 4 + 2 = 6. Therefore, the output of the program is 6.
Q: What is the purpose of the valid-invalid bit in a page table entry?
To track page frequency replacement
To distinguish between read and write access
To indicate whether the page is in physical memory
To determine if the page is part of the process's logical address space
[ Option D ]
The Valid-Invalid bit in a page table entry is used to check whether a page belongs to a process’s logical address space. If the bit is valid (1), the page is part of the process and can be accessed. If it is invalid (0), the page does not belong to the process, and any access attempt will cause a memory protection error. This mechanism helps the operating system prevent illegal memory access and ensures safe process isolation.
Q: In context of the major disadvantages of file processing system over database system, consider the following statements :
I. The same information may be duplicated in several files; and this problem is known redundancy.
II. The various copies of the same data may no longer agree; and this problem is known as data inconsistency.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are true?
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
[ Option C ]
In a traditional File Processing system, data is stored in separate files for different applications. Since there is no central control or integration like in a Database Management System (DBMS), several problems can occur.
| DISADVANTAGE | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Data Redundancy | Same data is stored in multiple files, leading to unnecessary duplication. | Student’s name and address stored in both Student and Fee files. |
| Data Inconsistency | Different copies of the same data may not match if one is updated and others are not. | One file shows old mobile number, another shows new. |
| Data Isolation | Data is scattered in separate files and formats, making it hard to access and combine. | The marks data in one file and attendance data in another cannot be easily linked. |
| Lack of Data Security | No centralized control, any user can access or modify files without restrictions. | Unauthorized user changes salary details in an employee file. |
| Difficulty in Data Access | Retrieving specific information often requires writing complex programs. | To find top 3 students, separate programs must be written for each file. |
| Integrity Problems | Rules or constraints are difficult to enforce across files. | Two students may accidentally get the same roll number. |
| Concurrency Issues | Multiple users accessing the same file simultaneously can cause data conflicts. | Two clerks update the same record at the same time, leading to errors. |
| Poor Backup and Recovery | No automatic system for restoring data after crashes or failures. | If a file is deleted, recovery is difficult or impossible. |
Q: Which of the following statement(s) is/are true about schemas for multidimensional data models?
I. The dimension tables of the star schema model is kept in normalized form to reduce redundancies.
II. There are multiple fact tables to share dimension tables in snowflake schema.
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
[ Option D ]
Q: What will the following SQL statement do? SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees;
Count all the employees with NULL values
Count all rows in the employees table
Count only rows with non-NULL values
Return all count column values
[ Option B ]
In SQL, the COUNT() function is an aggregate function used to determine the number of records in a table. It can be used in different forms, such as COUNT(*), COUNT(Column_Name), and COUNT(DISTINCT Column_Name).
When we use COUNT(*), it counts all rows in the specified table, regardless of whether any column contains a NULL value. This means it simply counts the total number of entries present.
In the query SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees;, the database counts all the rows in the employees table, including those having NULL values in one or more columns.
| FUNCTION | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE | OUTPUT |
|---|---|---|---|
| COUNT(*) | Counts all rows in a table, regardless of NULL values in any column. | SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees; | If the table has 10 rows, including some with NULL, the result is 10. |
| COUNT (Column_Name) | Counts the number of Non-NULL values in a specific column. | SELECT COUNT(salary) FROM employees; | If 2 employees have NULL salaries out of 10, the result is 8. |
| COUNT(DISTINCT Column_Name) | Counts the number of unique (Non-NULL) values in a column. | SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT department) FROM employees; | If there are 10 rows but only 4 unique departments, the result is 4. |
Q:
Match List — I with List — II and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
| List — I | List — II |
|---|---|
| (i) Boot Virus | A. The attacker sends a large number of connection or information requests to a target. |
| (ii) Worm | B. Infects the key operating system files located in a computer. |
| (iii) Zombies | C. Malicious program that replicates itself constantly until they completely fill available resources. |
| (iv) Denial-of-service attack | D. Machines directed remotely. |
(i) – A, (ii) – B, (iii) – C, (iv) – D
(i) – B, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – A
(i) – C, (ii) – D, (iii) – A, (iv) – B
(i) – D, (ii) – A, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
[ Option B ]
A Boot Virus is a type of computer virus that infects the boot sector of a storage device or the key operating system files that help a computer start. When the infected computer is turned on, the virus is automatically loaded into memory before the operating system starts.
A Worm is a self-replicating malicious program that spreads without needing to attach itself to any file or program. Unlike ordinary viruses, worms can travel automatically through networks and the internet.
Zombies are computers that have been secretly infected with malicious software and are controlled remotely by a hacker, often without the owner’s knowledge. These compromised machines are used to perform tasks such as sending spam emails, spreading viruses, or participating in large-scale network attacks.
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attempt by an attacker to make a computer or network service unavailable to its users. In this attack, the hacker sends a massive number of requests or data packets to a target server or website.
Q: If there are 3 inputs of a logic gate, A, B, C with the output (A'+B'+C') then the logic gate is:
NOR
Ex-OR
OR
NAND
[ Option D ]
The given output expression is Y=A′+B′+C′. By applying De Morgan’s law, this can be rewritten as Y=(A⋅B⋅C)′. This form directly represents the operation of a NAND gate, since a NAND gate produces the complement of the AND operation.
Q: ___________ testing executes a system in a manner that demands resources in abnormal quantity, frequency, or volume. Which of the following correctly fill in the blank?
Performance
Stress
Recovery
Theta
[ Option B ]
Stress Testing is a type of non-functional testing that evaluates how a system behaves under extreme or abnormal conditions.
Q: If a signal consists of V discrete levels and channel bandwidth is B, then according to Nyquist's theorem, the maximum data rate is:
4B log2V bits/sec
2V log2B bits/sec
2B log2V bits/sec
V log2B bits/sec
[ Option C ]
According to Nyquist’s theorem, the maximum data rate of a noiseless channel depends on its bandwidth (B) and the number of discrete signal levels (V) used in transmission.
Maximum Data Rate = 2B log2V bits per second
Q: In the context of data warehousing, which of the following is not a data transformation strategy?
Normalization
Discretization
Attribute construction
Wavelet transforms
[ Option D ]
In data warehousing, data transformation is the process of converting data from its original form into a format suitable for analysis.
Q: Which of the following sorting algorithm have a worst-case time complexity of O(n log n)?
A1. Bubble Sort
A2. Heap Sort
A3. Quick Sort
A4. Insertion Sort
A5. Selection Sort
A2 only
A2 and A3 only
A1, A2 and A3 only
A2 and A5 only
[ Option A ]
Must Know:
| Algorithm | Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | Space Complexity | Stable? |
| Bubble Sort | O(n) (if already sorted) | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | Yes |
| Insertion Sort | O(n) (if already sorted) | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | Yes |
| Selection Sort | O(n) (if already sorted) | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | No |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n) | Yes |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n2) | O(log n) | No |
| Heap Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(1) | No |
Q: Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
TELNET-logon to a remote machine
MIME-transfer multimedia messages
SMTP-Email Services
NVT-Name Server
[ Option D ]
In Internet communication, different protocols and standards are used for specific purposes.
| TERM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| TELNET – logon to a remote machine | TELNET (TELecommunication NETwork) is a protocol used to remotely log in to another computer and execute commands as if you were directly connected to it. |
| MIME – transfer multimedia messages | MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) allows sending non-ASCII data such as images, audio, and video through email. It extends the basic email format. |
| SMTP – Email services | SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the main protocol used for sending emails from client to server or between mail servers. |
| NVT – Name Server | NVT (Network Virtual Terminal) is not a name server. It is a standard interface used in TELNET that allows different computer systems to communicate in a common text format. The protocol related to name servers is DNS (Domain Name System), not NVT. |
Q: Which element is used to embed a multimedia object in an HTML document?
<em> tag
<embed> tag
<emb> tag
<embedded> tag
[ Option B ]
The <embed> tag in HTML is used to embed multimedia content such as audio, video, or interactive applications. It is a self-closing tag and requires attributes like src, type, width, and height to define the media.
<embed src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4" width="400" height="300">
The <embed> tag differs from <audio> and <video> tags in modern HTML5.
Q: Which of the following is the correct sequence of software testing process?
Prepare test data → Design test cases → Run program with test data → Compare results to test cases
Design test cases → Prepare test data → Run program with test data → Compare results to test cases
Design test cases → Run test cases → Prepare test data → Compare results
Design test cases → Prepare test data → Compare results
[ Option B ]
The software testing process follows a logical and structured sequence to ensure that the program is tested accurately and efficiently.
| ACTIVITY | DESCRIPTION | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| Design Test Cases | Identify and document test scenarios, input conditions, and expected results based on software requirements. | To ensure all functionalities are covered before testing begins. |
| Prepare Test Data | Create or collect the input data needed to execute the test cases, including valid and invalid values. | To simulate real-world usage and check how the program handles different inputs. |
| Run Program with Test Data | Execute the software using the prepared test data to observe the actual output. | To check if the software behaves as expected under test conditions. |
| Compare Results to Test Cases | Compare the actual output with the expected output defined in the test cases. | To determine whether each test case passes or fails. |
| Report and Fix Defects (Optional) | Record any mismatches, communicate to developers, and retest after fixes. | To ensure that all errors are resolved and the software meets quality standards. |
Q: The most obvious difference between frame relay and ATM is that frame relay uses packets, called frames, and ATM uses packets, called cells.
variable-length, fixed-length
fixed-length, variable-length
variable-length, variable-length
fixed-length, fixed-length
[ Option A ]
Frame Relay and ATM both are data communication technologies used for transferring data across networks.
Frame Relay sends data in the form of frames, which are variable-length packets. This means the size of the frame can change depending on the amount of data being transmitted.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode), on the other hand, transmits data in fixed-size packets called cells. Each cell is 53 bytes long (48 bytes of data + 5 bytes of header).
Q: How does the time complexity of the K-means algorithm change as the number of clusters K increases?
Time complexity decreases linearly with K.
Time complexity remains constant with respect to K.
Time complexity increases linearly with K.
Time complexity increases exponentially with K.
[ Option C ]
The K-Means algorithm works by repeatedly assigning data points to clusters and updating the cluster centroids until convergence. The time complexity of K-Means is approximately, O(n × K × I × d).
Where,
n = number of data points.
K = number of clusters.
I = number of iterations.
d = number of dimensions.
Q: Match memory management techniques in Column – I to their description in Column – II.
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| a. Simple Segmentation | i. it is not necessary to load all of the segments of a process. Non- resident segments that are needed are brought in later automatically. |
| b. Virtual Memory Paging | ii. A process is loaded by loading all of its pages into available, not necessarily contiguous, frames. |
| c. Virtual Memory Segmentation | iii. It is not necessary to load all of the pages of a process. Non-resident pages that are needed are brought in later automatically. |
| d. Simple Paging | iv. A process is loaded by loading all of its segments into dynamic partitions that need not be contiguous. |
Choose the correct option:
a – ii, b – i, c – iii, d – iv
a – iv, b – i, c – iii, d – ii
a – ii, b – iii, c – i, d – iv
a – iv, b – iii, c – i, d – ii
[ Option D ]
In memory management, different techniques are used to load and manage processes in main memory.
Q: Which one is the Unipolar logic family?
RTL
DTL
TTL
NMOS
[ Option D ]
Note:
Bipolar families use BJTs (Bipolar Junction Transistors), while unipolar families use MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide Semiconductor FETs) as switching devices.
Q: In TCP header, if the value of HLEN field is 0111 then how many bytes of options will be included in the segment?
16
8
20
40
[ Option B ]
In the TCP header, the HLEN (Header Length) field indicates the length of the TCP header. The minimum header length is 20 bytes when no options are used. The HLEN field is 4 bits long, and its value tells how many 4-byte words are in the header.
Now,
HLEN = 0111 (binary) = 7 (decimal)
So, total TCP header length = 7 × 4 = 28 bytes
Since the standard TCP header (without options) is 20 bytes, the extra part = 28 – 20 = 8 bytes, which corresponds to the options field.
Q: Which of the following techniques is NOT used to improve the efficiency of the Apriori algorithm?
Hash-based technique
Transaction reduction
Partitioning
Selection
[ Option D ]
The Apriori algorithm is a popular method for mining frequent itemsets in a dataset. Since generating candidate itemsets and scanning the database repeatedly can be computationally expensive, several techniques are used to improve its efficiency:
| TECHNIQUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Hash-based technique | Uses hash tables to reduce the number of candidate itemsets counted. |
| Transaction reduction | Removes transactions that do not contain frequent items to reduce database scans. |
| Partitioning | Divides the dataset into smaller partitions to find local frequent itemsets and merge them. |
Q: What is the primary purpose of using Intents in Android?
To manage the app’s memory allocation
To execute background threads
Message passing framework
To compile and build the Android project
[ Option C ]
In Android, Intents are used as a messaging object that allows communication between different components of an app such as Activities, Services, and Broadcast Receivers, or even between different apps.
Intents can be used to start a new activity, launch a service, deliver a broadcast, or request an action like opening a web page or sharing content.
Q: The decimal number represented by the binary number (0.10101) is :
(0.56)10
(0.6875)10
(0.3125)10
(0.65625)10
[ Option D ]
The binary fraction (0.10101)2 is converted to decimal by multiplying each digit with 2−n, where n is the position after the decimal point. Thus, it becomes 1×2−1 + 0×2−2 + 1×2−3 + 0×2−4 + 1×2−5. This equals 0.5 + 0 + 0.125 + 0 + 0.03125 = 0.65625. Therefore, the decimal equivalent of (0.10101)2 is (0.65625)10.
Q: Complete the following loop to print even numbers from 2 to 10:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=10;____)
printf(“%d”,i);
return 0;
}
i+=1
i+=2
i++
i+2
[ Option B ]
The loop starts with i = 2 and should print even numbers up to 10. To achieve this, we need to increase i by 2 in every iteration. Hence, using i+=2 ensures the loop prints 2 4 6 8 10.
Q: Which of the following is a valid value that can be stored in a variable of type NUMERIC (3,1) in SQL?
444.5
4.45
44.5
4.445
[ Option C ]
In SQL, a column defined as NUMERIC(3, 1) can store a total of three digits, out of which one digit is reserved for the decimal part and the remaining two for the integer part. Hence, valid numbers range approximately from –99.9 to 99.9. Among the given options, only 44.5 satisfies these conditions.
So, in SQL,
So, for NUMERIC(3, 1):
Q: The Kernel dispatcher keeps track of all _________ threads and schedules them in priority order.
Ready
Standby
Running
Waiting
[ Option A ]
In an Operating System (OS), the kernel dispatcher (scheduler) is responsible for managing CPU time among different threads or processes. It decides which thread should run next based on their state and priority.
Threads in an OS can be in different states such as Ready, Running, Waiting (Blocked), or Terminated. The Ready state means that the thread is prepared to run and is waiting for CPU allocation.
The Kernel dispatcher maintains a Ready Queue, which contains all the ready threads. It selects one thread from this queue based on priority and assigns it the CPU.
Q: A view in SQL is defined by using the ____________ command. To define a view, the view is given a name and must state the ___________ that computes the view.
create view, query
define view, trigger
make view, trigger
show view, query
[ Option A ]
In SQL (Structured Query Language), a view is a virtual table that is created based on the result of a query. It does not store data physically.
To create a view, we use the CREATE VIEW command followed by the view name and a SELECT query that determines the view's contents.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Q: What does a quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plot display?
It displays all of the data for the given attribute and it plot quantile information.
It is a graphical method for summarizing the distribution of a given attribute.
The quantiles of one univariate distribution against the corresponding quantiles of another.
It is a useful method for providing a first look at bivariate data to see clusters of points and outliers.
[ Option C ]
A Q-Q plot is used to compare two distributions by plotting the quantiles of one distribution against the corresponding quantiles of another. If the points fall roughly along a straight line, the distributions are similar. Q-Q plots are commonly used to check whether data follows a theoretical distribution or to compare two datasets.
Q: Consider Column – I and Column – II in the context of various activities of a generic process framework for software engineering.
| Column – I | Column – II |
|---|---|
| a. Communication | i. Coding and Testing |
| b. Planning | ii. Requirement Gathering |
| c. Construction | iii. Delivery and Feedback |
| d. Deployment | iv. Risk, Resources and Schedules |
Which of the following is the most suitable match of Column – I and Column – II?
a – ii , b – iv, c – i, d – iii
a – ii, b – iii, c – iv, d – i
a – iii, b – iv, c – i, d – ii
a – iv, b – i, c – ii, d – iii
[ Option A ]
In the generic process framework for software engineering, the software development process is divided into several important activities, each having a specific purpose.
Communication : This is the first step of software development where interaction takes place between developers and customers. The goal is to understand what the customer needs. Therefore, it involves requirement gathering and analysis.
Planning : After gathering requirements, the next step is to plan the project activities. This includes identifying risks, resources, and schedules to ensure the project is completed on time and within budget.
Construction : This phase involves Coding and Testing of the software. Developers write the actual code and then test it to make sure it functions correctly and meets requirements.
Deployment : After successful testing, the software is delivered to the customer, and feedback is collected for future improvements.
Q: Which best describes how Kruskal’s algorithm constructs a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)?
Adds edges in increasing order of weight while avoiding cycles.
Adds the smallest edge that connects a visited vertex to an unvisited one.
Grows the MST by adding the maximum weight edge from a starting node.
Selects a root and grows the MST by always choosing the closest neighbour.
[ Option A ]
Kruskal’s algorithm is a greedy algorithm used to find the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of a connected, weighted graph. It works by sorting all the edges of the graph in non-decreasing order of their weights. Then, it iteratively adds the smallest edge to the MST, provided that adding the edge does not create a cycle in the growing tree.
The algorithm continues until the MST has exactly V−1 edges, where V is the number of vertices.
Unlike Prim’s algorithm, which grows the MST from a starting vertex, Kruskal’s algorithm builds the MST by focusing on edges first, ensuring the final tree has the minimum total weight.
Must Know:
Non-decreasing order of their weight means the edges are arranged from smallest weight to largest weight, but equal weights are allowed to appear next to each other. For example, if the edge weights are [6, 2, 9, 4, 2], then sorted in non-decreasing order they become [2, 2, 4, 6, 9].
Q: What is the meaning of status code 400 in HTTP?
Accepted
Moved Permanently
Not Found
Bad Request
[ Option D ]
When a client (web browser) sends a request to a web server using the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), the server responds with a status code. These codes tell whether the request was successful, redirected, failed, or caused an error. HTTP status codes are divided into five main categories:
| CATEGORY | CODE RANGE | MEANING |
|---|---|---|
| 1xx | 100–199 | Informational, request received and continuing process. |
| 2xx | 200–299 | Success ,the request was successfully received and processed. Example: 200 OK means everything worked fine, 201 Created means a new resource was successfully created. |
| 3xx | 300–399 | Redirection, further action needs to be taken. Example: 301 Moved Permanently or 302 Found indicate that the resource has a new location. |
| 4xx | 400–499 | Client Error, the request has bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled. Example: 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, or 404 Not Found. |
| 5xx | 500–599 | Server Error, the server failed to fulfill a valid request. Example: 500 Internal Server Error, 502 Bad Gateway, or 503 Service Unavailable. |
Status code 400 in the HTTP protocol means "Bad Request". This error occurs when the server cannot process a request because the client has sent data that is invalid, malformed, or cannot be understood.
Q: Which statement is correct about the /proc file system in Linux?
It is a disk-based file system used to save long-term process logs.
It resides in kernel memory and is used for querying process and kernel statistics.
It contains static information for processes that have already exited.
It is designed to store loadable kernel binaries permanently.
[ Option B ]
The /proc file system in Linux is a virtual file system that provides information about the system’s processes and kernel in real time. It does not exist on the disk like regular files, instead, it resides in kernel memory and is generated dynamically when accessed.
The /proc directory contains files and folders that represent system information such as CPU usage, memory details, running processes, and kernel parameters.
Q: Which of following is a technique that facilitates hiding of a message that is to be kept secret inside an image?
Steganography
Cryptography
Encryption
Calligraphy
[ Option A ]
A plain text message can be hidden or protected in two main ways.
Steganography is a technique used to hide secret messages or data within another file, such as an image, audio, or video, in such a way that its existence is not apparent to others.
For example, a confidential message can be hidden inside the pixel values (modifying the Least Significant Bits (LSBs) of the Pixels) of an image file without noticeably changing the image itself.
Cryptography transforms plaintext into ciphertext via encryption, rendering the content unintelligible to outsiders without the decryption key.
Q: Which of the following correctly explains why DNS uses both UDP and TCP?
DNS uses UDP only for all types of data transfer.
DNS uses only UDP because it is faster and always reliable.
DNS uses TCP for tasks like zone transfers or large responses.
DNS switches from TCP to UDP when data exceeds 512 bytes.
[ Option C ]
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to convert domain names (www.surakuacademy.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand. DNS mainly communicates over the Internet using two transport layer protocols:
For most regular DNS queries, UDP is used because it is fast and efficient. Since DNS requests and responses are usually small (less than 512 bytes), using UDP avoids the extra time needed to establish a connection, making it ideal for quick lookups such as finding the IP address of a website.
DNS also uses TCP in specific cases where reliability is required. When a DNS response exceeds 512 bytes, during zone transfers between servers, or if a UDP query fails, TCP provides a reliable, connection-oriented transfer.
In short, DNS uses UDP for speed and TCP for reliability and large data transfers, ensuring both efficiency and accuracy.
Q: How many subnets and valid hosts are provided by network address 172.16.0.0/19?
7 subnets, 2,046 hosts each
7 subnets, 8,190 hosts each
8 subnets, 2,046 hosts each
8 subnets, 8,190 hosts each
[ Option D ]
The IP address 172.16.0.0/19 belongs to Class B, where the default subnet mask is /16 (255.255.0.0). Here, /19 means 3 extra bits are borrowed for subnetting (19 − 16 = 3).
Number of subnets = 23 = 8 subnets
Number of host bits = 32 − 19 = 13 bits
Therefore, the number of valid hosts per subnet is 213 − 2 = 8190, where 2 is subtracted for the network and broadcast addresses. Hence, the network 172.16.0.0/19 provides 8 subnets, each containing 8190 valid hosts.
Q: Complete the following code to get sum of array elements:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int A[] = {1,2,3,4,5},i,sum = 0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
_____________;
}
printf(“%d”,sum);
return 0;
}
A[i]
sum = sum+i
sum +=A[i]
sum[i]
[ Option C ]
Q: In RSA, let the two prime numbers are P = 7, Q = 17 and public key e = 5. Find the Cipher text for the plain text 10.
40
77
96
119
[ Option A ]
In RSA encryption, we are given P = 7, Q = 17, public key e = 5, and plaintext M = 10.
First, calculate n = P × Q = 7 × 17 = 119 and φ(n) = (P - 1) × (Q - 1) = 6 × 16 = 96.
The public key pair is therefore (5, 119). Using the encryption formula C = Me mod n, we get C = 105 mod 119 = 40.
Q: What will be the output of following code?
int main()
{
int i = 1;
printf(“%d”, i);
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++);
if (i == 1)
printf(“%d”, i);
return 0;
}
13
11
1
112
[ Option C ]
Q: Consider set F of functional dependencies A → B, ABCD → E, EF → G, EF → H, and ACDF → EG. Which of these correctly represents the correct minimal cover for F?
A→B, ACD → E, EF → G, and EF → H.
A → B, ACD → E, EF → G, and EF → C.
A→ B, ABD → E, EF → G, and EF → H.
A→ B, ACE → D, EF → G, and EF → C.
[ Option A ]
A Minimal Cover or Canonical Cover for a set of functional dependencies is an equivalent set where every dependency has a single attribute on the right-hand side, every left-hand side has no extraneous attribute, and no dependency is redundant.
Q: The maximum number of levels in the inverted tree structure of Domain Name Space can be:
64
128
256
192
[ Option B ]
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to translate human-readable website names (www.surakuacademy.com) into IP addresses that computers use to communicate. The Domain Name Space is organized like an inverted tree structure, where:
| STRUCTURE ELEMENT | EXAMPLE | LEVEL |
|---|---|---|
| Root | . | Level 0 |
| Top-Level Domain | .com | Level 1 |
| Second-Level Domain | surakuacademy.com | Level 2 |
| Subdomain | testseries.surakuacademy.com | Level 3 |
The Domain Name Space allows multiple levels in this hierarchy, each level represents one “LABEL” (a part between dots). According to DNS standards (RFC 1035), the maximum number of levels allowed in a domain name is 128 including the root.
Q: ___________ is the process of fixing errors and problems that have been discovered by testing.
Validation
Verification
Debugging
Refutation
[ Option C ]
Debugging is the process of finding and fixing errors or defects in a program after they have been discovered during testing. It is different from Testing, because testing helps detect the presence of errors, while debugging helps locate and remove them.
Q: The intent of __________ is to conceal the details of data structures and procedural processing behind a module interface.
Modularity
Information hiding
Coupling
Exposing
[ Option B ]
The main intent of information hiding is to protect the internal details of a module, such as data structures and algorithms.
By hiding the internal implementation, changes made inside a module do not affect other modules that depend on it. This leads to better modularity, maintainability, and security of the software.
Q: Which of the following statement(s) is/are true in the context of software testing?
I. Verification is to ensure that software correctly implements a specific function.
II. Validation is to ensure that the software that has been built is traceable to customer requirements.
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
[ Option C ]
Verification is the process of checking whether the software is being built correctly according to design documents, specifications, and plans. It focuses on ensuring that each function, logic, and module is correctly implemented before the product is completed.
Validation is the process of checking whether the final software product meets customer needs and expectations. It ensures that the system performs the intended functions in the actual working environment and satisfies all user requirements.
| VERIFICATION | VALIDATION |
|---|---|
| Ensures the product is built according to specifications and design. | Ensures the final product meets customer requirements. |
| Focus on the process of development. | Focus on the final product and its usefulness. |
| We are building the product right. | We are building the right product. |
| Performed by developers, quality assurance team. | Performed by end users, testers, and clients. |
| Reviews, inspections, walkthroughs. | Functional testing, system testing, acceptance testing. |
Q: Suppose the original training set contains 100 positive and 1000 negative tuples. After under sampling, the new training set will contain:
1000 positive and 1000 negative tuples
100 positive and 100 negative tuples
550 positive and 550 negative tuples
All positive tuples only
[ Option B ]
Under-sampling is a technique used to address class imbalance in a training dataset. When one class significantly outnumbers the other class, under-sampling reduces the number of instances in the majority class to match the number of instances in the minority class.
In this case:
Q: What is the purpose of the free-frame list in an operating system?
To track which processes are currently running
To store page tables for each process
To keep a list of active I/O operations
To manage frames available for allocation when a page fault occurs
[ Option D ]
In an Operating System (OS) that uses virtual memory, physical memory (RAM) is divided into fixed-size blocks called frames, and logical memory is divided into pages. When a program tries to access a page that is not currently in memory, a page fault occurs.
At this time, the OS needs to bring the required page from the disk into main memory. To do this efficiently, the OS maintains a Free-Frame List, which is a list of all the empty frames available in physical memory.
When a page fault happens, the OS selects a free frame from this list, loads the required page into it, and updates the page table.
So, the free-frame list helps the operating system know which parts of memory are empty so it can quickly allocate space whenever a new page needs to be loaded due to a page fault.
Q: Find an AI agent that evaluates different actions based on a function and it measures the "value" or "satisfaction" of achieving a goal in different ways.
Model-based Reflex Agent
Goal-based Agent
Utility based Agent
Simple Reflex Agent
[ Option C ]
A Utility-Based Agent in AI (Artificial Intelligence) goes beyond just achieving a goal. Unlike a Goal-Based Agent, which only decides whether a goal is achieved, a utility-based agent evaluates multiple possible actions using a utility function.
The utility function assigns a numeric value to each possible state, reflecting how “Good” or “Satisfactory” that state is.
Q: Which standard is used to define protocol, host computer, port and path on the Internet?
IP address
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
MAC address
POP address
[ Option B ]
When we access a webpage or any resource on the Internet, we use an address that tells the computer where to find it. This address is called a URL (Uniform Resource Locator). It includes several parts such as the protocol, host computer, port, and path.
URL example, https://www.surakuacademy.com/rpsc-vice-principal-iti-information-technology-paper-solution
| PART | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Communication method such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP. | https |
| Host | Domain name or IP address of the server. | www.surakuacademy.com |
| Port | Connection port, optional, tells which service or connection point to use. Common default ports are 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS. | 443 |
| Path | The specific file or page inside the website. Specifies the exact location or file on the host server. | /rpsc-vice-principal-iti-information-technology-paper-solution |
Q: Which of the following is not an element of interface design?
the user interface (UI)
external interfaces to other systems, devices, networks, or other producers or consumers of information
internal interfaces between various design components
Modularity
[ Option D ]
In software engineering, interface design focuses on defining how different parts of a system interact with each other and with external entities. It ensures smooth communication between components, users, and external systems. The main elements of interface design include, User Interface (UI), External Interfaces, and Internal Interfaces.
The Modularity refers to the division of a system into smaller, independent components or modules to improve maintainability, reusability, and clarity.
Q: The total participation of an entity in a relationship is represented by:
Double Rectangle
Double Ellipse
Double Line
Dashed Line
[ Option C ]
In an Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagram, Total Participation means that every entity in an entity set must participate in a given relationship.
To represent this, we use a Double Line between the entity set and the relationship set. This indicates that the participation of the entity is mandatory or required or total.
Q: Which of the following is a Linux System Call for Interprocess Communication (IPC)?
semctl
bind
sched_yield
link
[ Option A ]
In Linux, processes often need to communicate and share data with each other, this is called Interprocess Communication (IPC). Linux provides several IPC mechanisms like pipes, message queues, shared memory, and semaphores.
The semctl system call is used to control and manage semaphores, which are synchronization tools that help processes coordinate access to shared resources.
| IPC MECHANISM | SYSTEM CALL | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| Pipes | pipe() | Communicate between parent and child processes. |
| Message Queues | msgsnd(), msgrcv() | Send and receive messages between processes. |
| Shared Memory | shmget(), shmat() | Allow processes to access common memory space. |
| Semaphores | semctl(), semget() | Synchronize process execution and resource access. |
Q:
Match the following URL Schemes with their uses:
| URL Scheme Name | Used For |
|---|---|
| a. mailto | i. Streaming media |
| b. rtsp | ii. Browser information |
| c. https | iii. Sending email |
| d. about | iv. Hypertext with security |
a – i, b – iii, c – iv, d – ii
a – iii, b – i, c – iv, d – ii
a – ii, b – i, c – iv , d – iii
a – iii, b – ii, c – iv, d – i
[ Option B ]
Each URL starts with a scheme name (like http, https, mailto, ftp, etc.), which defines the protocol or method used to handle the request. Different schemes are used for different purposes, such as opening a web page, sending an email, or streaming a video.
| URL SCHEME | USED FOR | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| mailto | Sending email | This scheme is used to create a link that opens the default email client. Example: mailto:info@surakuacademy.com opens your email app with the address filled in. |
| rtsp | Streaming media | RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) is used to stream audio or video over the Internet in real time. Example: rtsp://media.example.com/movie |
| https | Hypertext with security | HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure version of HTTP that uses encryption (SSL/TLS) for safe data transfer. Example: https://www.surakuacademy.com |
| about | Browser information | The about: scheme is used internally by browsers to show built-in pages like about:blank, about:settings, etc. |
Q: In which of the following problem areas expert system does not provide real assistance?
Weather forecasting
Medical diagnosis
Legal reasoning
Decoupling
[ Option D ]
An Expert System is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) program designed to mimic human expert reasoning in a specific domain. It uses a knowledge base (containing expert facts and rules) and an inference engine (which applies logic to that knowledge) to solve complex problems that normally require human expertise.
Expert systems are most useful in areas that involve logical reasoning, pattern recognition, and decision-making based on well-defined rules.
However, Decoupling is not a problem area where expert systems provide assistance. Decoupling refers to separating interconnected components or systems to reduce dependency, commonly used in engineering, programming, or system design, not in reasoning-based problem solving.
Q: In context of keys of a relation in DBMS, choose the true statements:
I. A superkey of a relation is a set of one or more attributes whose values are guaranteed to identify tuples in the relation uniquely.
II. A candidate key is a minimal superkey, that is, a set of attributes that forms a superkey, but none of whose subsets is a superkey.
III. One of the candidate keys of a relation, containing highest number of attributes, is chosen as its primary key.
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
[ Option A ]
In a Database Management System (DBMS), Keys are attributes or sets of attributes used to uniquely identify each tuples (rows) in a table (relation).
In a relational database, a Super Key is any set of attributes that uniquely identifies tuples, but it may contain extra attributes.
A Candidate Key is a minimal super key, meaning no subset of it can be a super key.
Among candidate keys, one is chosen as the Primary Key to uniquely identify tuples but it is not chosen based on the number of attributes. It is usually selected for simplicity, stability, and efficiency, not because it has the highest number of attributes.
So, statements I and II correctly describe Super Key and Candidate Key, while III is incorrect because the primary key is not selected based on attribute count.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.