Get complete RPSC Programmer Exam Paper-2 solved questions with detailed explanations. Practice previous year papers, boost your subject knowledge, and prepare effectively for the RPSC Programmer exam with authentic and accurate solutions.
In addition, this solution guide is not just about answers, it is designed as a learning companion. By studying these explanations, students can strengthen their problem-solving skills and approach future exams with greater clarity and confidence.
| Unit | Unit Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Unit 1 | System Analysis and Design |
|
| Unit 2 | Programming Concepts |
|
| Exam Name | RPSC Programmer Exam Paper-1 : 2024 | |
|---|---|---|
| Exam Date | 27th October 2024 | |
| S.N. | Name of Subjects | No. of Questions Asked |
| 01. | System Analysis and Design | 48 |
| 02. | Programming Concepts | 52 |
Q: Fact Finding Technique through ___________ enables the analysts to collect a large amount of data through a variety of users quickly.
Interviews
Documents
Observations
Questionnaires
[ Option D ]
A questionnaire is a fact-finding technique where the analyst prepares a set of structured questions and distributes them to many users. Because users can fill them out independently, this technique allows analysts to:
This is why questionnaires are preferred when the analyst needs large-scale data collection in less time.
| TECHNIQUE | DESCRIPTION | ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interview | Direct, face-to-face or group discussion with users to gather detailed information. | Very detailed information. Can clarify doubts instantly. Helps understand user feelings and attitudes. | Time-consuming. Requires good interviewer skills. |
| Questionnaire | A written set of questions distributed to many users to collect data quickly. | Collects data from a large number of users. Fast and cost-effective. Responses are easy to analyze. | Limited depth of answers. Sometimes low response rate. Cannot clarify users doubts immediately. |
| Observation | Analyst watches users perform tasks in real working conditions. | Shows actual workflow. Helps identify hidden problems. Useful when tasks are hard to explain. | Time-consuming. Users may change behavior while being observed. |
| Document Review | Studying existing reports, forms, files, manuals, logs, and records of the current system. | Provides historical and backup data. Saves time by showing existing problems and patterns. | Documents may be outdated. Missing or incomplete documents reduce effectiveness. |
| Joint Application Development (JAD) | Structured workshop with users, analysts, and managers to discuss requirements. | Fast decision-making. Encourages teamwork and shared understanding. Reduces follow-up meetings. | Requires experienced facilitator. Scheduling all participants is difficult. |
| Prototyping | Building a small model of the system to get user feedback and refine requirements. | Helps users visualize the system. Early error detection. Improves final system quality. | May increase time and cost. |
Q: Which of the following is true about JSP?
JSP pages are interpreted at runtime.
JSP pages are compiled into servlets.
JSP is not used to make interactive web pages.
JSP pages cannot use Java code.
[ Option B ]
In JSP (Java Server Pages) technology, JSP pages are first translated into Java servlets. These servlets are then compiled and executed by the web server. This allows JSP to create dynamic and interactive web pages.
<%@ page language="java" %>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello, JSP Example</h1>
<%
String name = "Suresh";
out.println("Welcome, " + name);
%>
</body>
</html>
When you save this file as myfile.jsp and run it on a server like Tomcat, the server automatically converts it into a servlet like this:
public final class myfile_jsp extends HttpJspBase {
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
JspWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.write("<html><body>");
out.write("<h1>Hello, JSP!</h1>");
String name = "Suresh";
out.write("Welcome, " + name);
out.write("</body></html>");
}
}
Q: _________ are conceptual and non-physical entities that may be formulas, representation or model of a real system.
Physical Systems
Abstract Systems
Deterministic Systems
Probabilistic Systems
[ Option B ]
Abstract Systems are conceptual and non-physical entities that represent ideas, models, or formulas of real systems. They do not exist physically but serve as representations or theoretical constructs to study, analyze, or simulate how a real system functions.
Abstract Systems are conceptual, meaning they do not have a physical form. They exist as ideas, models, formulas, diagrams, or representations of a real system. Examples included, mathematical formulas, economic models, organizational charts, logical flow diagrams, theoretical computer models etc.
| TYPE OF SYSTEM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Physical Systems | Tangible and material systems that exist in reality. |
| Abstract Systems | Conceptual or non-physical models or representations of real systems. |
| Deterministic Systems | Systems where outputs are precisely determined by inputs without randomness. |
| Probabilistic Systems | Systems with inherent randomness or uncertainty in outputs. |
| Open Systems | Systems that interact with their environment and exchange matter, energy, or information. |
| Closed Systems | Systems that do not interact with their environment. |
| Static Systems | Systems with outputs dependent only on current inputs, not time or past states. |
| Dynamic Systems | Systems where outputs depend on time and history of inputs, exhibiting behavior over time. |
Q: Which of the following is the most important feature that makes Java suitable for Internet applications?
Faster Execution
Object oriented and Robust
Portable and Distributed
Simple and Secure
[ Option C ]
Java is widely used for Internet and web-based applications because of several important features. One of the key requirements for Internet applications is that programs must run on different platforms without modification and support networked or distributed computing.
Java fulfills these requirements through its Portability, meaning compiled Java bytecode can run on any system with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), and its ability to work in a Distributed environment, allowing objects and programs to communicate over networks.
Q: __________ is a structured repository of data about data.
Data Flow Diagram
System Components Matrix
Data Dictionary
Decision Table
[ Option C ]
A Data Dictionary is a centralized, structured repository that contains metadata, information about the data used in a system, such as:
Q: ______________, a program development tool, shows how the program has been partitioned into smaller more manageable modules, the hierarchy and organization of those modules and the communication interfaces between modules.
Structure Chart
Fourth Generation Language Tools (4GL Tools)
Object-Oriented Programming and Design Tools
Program Flow Chart
[ Option A ]
When a big program becomes too large to understand, we divide it into small manageable modules. To show how these modules are arranged and how they communicate, we use a special tool called a Structure Chart.
It looks like a Tree Diagram where the top represents the main module and the bottom branches represent submodules.
| STRUCTURE CHART | PROGRAM FLOWCHART |
|---|---|
| Shows module hierarchy. | Shows step-by-step logic of a program or process. |
| Focuses on how the program is divided into smaller modules. | Focuses on how the program flows from start to end. |
| Represents modular design. | Represents program logic or algorithm. |
| Modules are arranged in levels like parent–child relationship. | Statements are arranged in sequence, decision, and loops. |
| Used during the system design phase. | Used during program development and algorithm design. |
| Does not show internal logic of modules. | Shows the internal working of the program in detail. |
| Looks like a tree structure. | Looks like a flow diagram with symbols like oval, diamond, rectangle, parallelogram. |
Q: What will be the output of the following program?
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {120, 200, 016};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); }
}
}
120 200 14
120 200 016
Compilation Error
120 200 16
[ Option A ]
In Java, numbers can be represented in different formats, such as decimal, octal, hexadecimal, and binary. By default, numbers written without any prefix are decimal numbers (base 10).
However, if a number starts with a 0, Java treats it as an octal number (base 8). Octal numbers use digits from 0 to 7 only.
If a number starts with 0x, Java treats it as an hexadecimal number (base 16). Hexadecimal numbers use digits from 0 to 9 and a to f.
In the given program, the array is declared as int[] arr = {120, 200, 016};. Here, 120 and 200 are standard decimal numbers. The third element, 016, starts with a 0, so Java interprets it as an octal number. To understand its decimal value, we convert octal 16 to decimal, 1×81+6×80 = 8+6 = 14. Therefore, the array actually contains the values {120, 200, 14}.
The for loop then iterates through this array and prints each element followed by a space. As a result, the output of the program is 120 200 14.
Q: What do you mean by Method Overloading in Java?
Having two methods with the same name in different packages.
Having two methods with the same name and same parameters.
Having two methods with the same name but different parameters.
Having two methods with the same name in different classes.
[ Option C ]
In Java, a method is a block of code that performs a specific task. One of the core features of Java is Polymorphism, which allows objects or methods to take multiple forms.
Method overloading is a type of compile-time polymorphism where a class has two or more methods with the same name but different parameter lists.
It allows programmers to use the same method name for related actions, improving readability and organization.
class Calculator {
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int add(int a, int b, int c) {
return a + b + c;
}
double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
System.out.println(calc.add(15, 25));
System.out.println(calc.add(15, 12, 30));
System.out.println(calc.add(2.5, 7.5));
}
}
Q: What does the following code do?
public class Example {
private int var;
public Example(int var) { this.var = var; }
}
Creates a new instance of the class Example.
Throws an error because 'this' cannot be used.
Assigns the parameter var to the instance variable var.
Compilation Error.
[ Option C ]
In this code, the class Example has a private instance variable named var. The constructor Example(int var) receives a parameter with the same name. Inside the constructor, the statement this.var = var; is used to distinguish between the instance variable and the constructor parameter.
Here, this.var refers to the instance variable of the current object, while var refers to the parameter. Therefore, the code simply assigns the value passed into the constructor to the object's own variable.
Q: What is the main role of Java Development Kit (JDK)?
To provide only runtime environment for Java Applications
To provide a Graphical User Interface
To only compile and run Java Applications
To create, compile and execute Java Applications
[ Option D ]
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development kit provided by Java to help programmers develop Java applications. It contains tools for writing, compiling, and running Java programs.
The JDK includes the Java Compiler (javac) to convert source code into bytecode, the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) to execute Java programs, and other development tools such as debuggers and documentation generators.
Q: Which of the following is a commonly used Object-Oriented Programming Language?
PROLOG
C Language
JAVA
COBOL
[ Option C ]
Java is a widely used Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language that supports core OOP principles such as classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation.
Q: Which of the following correctly declares a method that accepts one dimensional array of double as a parameter?
public void fun(double *arr[])
public void fun(double[] arr)
public void fun(arr double[])
public void fun(double arr)
[ Option B ]
When a method needs to accept an array as a parameter, the arrays type must be specified correctly. For a one-dimensional array of double, the syntax is double[] arr, where double[] indicates an array of double values and arr is the name of the parameter.
Q: Which of the following is false about Vector class in Java?
It is part of java.util package.
It is synchronized.
It can grow or shrink as needed.
It is part of java.io package.
[ Option D ]
In Java, a Vector is a class that implements a dynamic array, which means it can grow or shrink automatically as elements are added or removed.
Q: What will be the value of ‘val’ displayed when JSP page is accessed for the third time since server startup?
<%! int val = 0; %>
<% val++; %>
<html><body><p>val : <% = val %></p></body></html>
1
2
3
The value of val will remain 0
[ Option C ]
In JSP (Java Server Pages), understanding how variables behave across multiple requests is essential. JSP provides different scripting elements such as declarations <%! %>, scriptlets <% %>, and expressions <%= %>, each with a specific role and scope.
Declarations <%! %>
Scriptlets <% %>
| Request Number | Initial val | Operation (val++) | Value Displayed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Request | 0 | 0 to 1 | 1 |
| 2nd Request | 1 | 1 to 2 | 2 |
| 3rd Request | 2 | 2 to 3 | 3 |
Q: _____________ is an indication of the relative functional strength of a module.
Aversion
Cohesion
Ripple Effect
Coupling
[ Option B ]
Cohesion refers to the degree of relatedness and functional strength of the elements within a single module. It indicates how well the parts of a module work together to achieve a specific purpose.
High cohesion means that all parts of the module are closely related and focused on a single task, which leads to more maintainable, understandable, and reliable software.
Q: __________ approach of system development is easy to accommodate product changes, but not suitable for large, high-risk, or mission-critical projects?
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Spiral
Agile
Prototype
[ Option C ]
Q: Which of the following statement is true about public and private members in Java?
Private members can be accessed from any other class.
Private members can be accessed from subclasses.
Public members can only be accessed within the same class.
Public members can be accessed from any other class.
[ Option D ]
In Java, access modifiers determine the visibility of class members. The two commonly used modifiers are public and private.
Private members are accessible only within the same class in which they are declared, they cannot be accessed from subclasses or other classes.
Public members are accessible from any other class, regardless of the package or subclass relationship.
MEMBER ACCESS RULE TABLE:
| ACCESS MODIFIER → ACCESS LOCATION ↓ | PUBLIC | PROTECTED | DEFAULT | PRIVATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Same class. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Subclass in same package. | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Other classes in same package. | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Subclass in others package. | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Non-subclasses in others package. | Yes | No | No | No |
Q: “System Requirements Specification (SRS)” document is prepared by the System Analyst at the end of ________________ phase of System Development Life Cycle.
Systems Design
Systems Implementation
Preliminary Investigation
Systems Requirement Analysis
[ Option D ]
The System Requirements Specification (SRS) document is prepared by the System Analyst at the end of the Systems Requirement Analysis phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). This phase involves:
Q: Project requests are evaluated in the ______________ phase of System Development Life Cycle.
Preliminary Investigation
System Testing
System Design
Requirement Analysis
[ Option A ]
The Preliminary Investigation phase is the first step in the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). This phase acts like a screening process to decide if a project should move forward. During this phase, the system analyst evaluates:
Q: What will be the output of the following code?
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = “Hello”;
str = str+”World”;
str = str.substring(5,10);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Hello
Hello World
ello
World
[ Option D ]
The initial string str is assigned the value "Hello". Then, str is concatenated with "World" resulting in the string "HelloWorld". Next, the substring(5, 10) method extracts characters starting at index 5 to index 9 (10 is excluded).
The string str = "HelloWorld" has indices:
| Index | str[0] | str[1] | str[2] | str[3] | str[4] | str[5] | str[6] | str[7] | str[8] | str[9] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | H | e | l | l | o | W | o | r | l | d |
So, in "HelloWorld", index 5 corresponds to the character 'W' and index 9 corresponds to 'd'. Thus, the substring "World" is extracted and printed.
Q: In the statement ‘System.out.println("Hello World!")’, the keyword 'out' stands for the following—
Static member of the ‘System’ class
An interface in the Java standard library
A method in the ‘System’ class
Class in the Java standard library
[ Option A ]
In Java, System.out.println("Hello World!") is used to print messages to the console.
| COMPONENT | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| System | System is a class, defined in java.lang package. | Provides access to standard input, output, and error streams; part of Java core library. |
| out | public static member of System class. | The out is an instance of the PrintStream class, which provides methods like println() to display output. |
| println() | Method of PrintStream class. | Prints the given message or value to the console and moves to the next line. |
Q: What will be the result of following Java code?
public class MyString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = “Program”;
String s2 = “Program”;
System.out.println(s1==s2);
}
}
True
Compilation Error
Runtime Error
False
[ Option A ]
In Java, string literals are stored in a special memory area called the String Constant Pool (SCP). When we create two strings using literals like
Java checks the pool first. Since the literal "Program" already exists, s2 does not create a new object and both s1 and s2 point to the same memory location.
The expression s1 == s2 compares references, not string content. Because both variables refer to the same object in the pool, the result is true.
If the strings were created using new String("Program"), then == would return false because two different objects would be created.
Q: A generic process framework for software engineering defines five framework activities. A ______________ executes each of these five framework activities in sequence.
evolutionary flow
parallel process flow
linear process flow
iterative flow
[ Option C ]
A generic process framework in software engineering consists of five main framework activities, usually, Communication, Planning, Modeling, Construction, Deployment. When these activities are carried out one after another in a strict sequence, it is called a Linear Process Flow.
The linear process flow means, no overlaps, one activity must finish before the next begins, follows a straight, step-by-step path. This is very similar to the Waterfall Model.
Q: _____________ is a visual representation that depicts the information flow and the transformation that are applied to data as data moves from input to output.
Data Flow Diagram
System Flow Chart
Layout Form
Hierarchy Chart
[ Option A ]
A Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a visual representation that depicts the flow of information and the transformations applied to data as it moves from input to output in a system. It graphically shows how data enters the system, the processes that act on the data, where the data is stored, and how it exits the system.
Q: What is Encapsulation in Java?
The ability of one class to inherit the properties of another class.
The ability of an object to take many forms.
Integrating data (variables) and code (methods) into a single unit.
The ability to overload methods.
[ Option C ]
Encapsulation in Java is one of the fundamental principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). An act of combining data (variables) and the methods that operate on that data into a single unit called a class.
Through encapsulation, the internal details of an object are hidden from the outside world, allowing controlled access via getter and setter methods. This helps maintain data security, ensures better control over the data, and prevents unintended modification.
| CONCEPT | DESCRIPTION | KEY FEATURES |
|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation | The OOP principle of combining data (variables) and methods (functions) into a single unit and restricting direct access to it. |
|
| Class | A blueprint or template from which objects are created. It defines properties (variables) and behaviors (methods). |
|
| Object | An instance of a class that has its own identity, state, and behavior. It occupies memory. |
|
Q: If A is a superclass and B is a subclass of it and C is subclass of B, in what order the constructors that make up the classes be called?
A, C, B
A, B, C
C, A, B
C, B, A
[ Option B ]
In Java, constructors are special methods used to initialize objects when they are created. When dealing with inheritance, constructors follow a specific order to ensure that the parent class is properly initialized before the child class.
If a class A is a superclass, B is a subclass of A, and C is a subclass of B, then creating an object of class C triggers constructor calls in a Top-Down order, starting from the highest superclass down to the actual subclass.
This happens because the subclass constructor implicitly calls the constructor of its parent class using the super().
class A {
A() {
System.out.println("Constructor of Class A.");
}
}
class B extends A {
B() {
System.out.println("Constructor of Class B.");
}
}
class C extends B {
C() {
System.out.println("Constructor of Class C.");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
C obj = new C();
}
}
OUTPUT
Constructor of Class A.
Constructor of Class B.
Constructor of Class C.
Q: What is Polymorphism in Java?
The ability of a single method to perform different tasks.
The ability of different methods to perform different tasks.
The ability of a class to inherit properties of another class.
The ability of a single variable to hold multiple values.
[ Option A ]
The word Polymorphism means Many Forms. It allows objects or methods to take multiple forms, enabling flexibility and reusability in code. Polymorphism improves code flexibility, readability, and maintainability. There are two main types of polymorphism in Java:
Compile-Time Polymorphism (Method Overloading):
Runtime Polymorphism (Method Overriding):
Q: Conducting study to find out if the proposed system can be used by the employees or not is covered under the _____________ feasibility.
Technical
Schedule
Economic
Operational
[ Option D ]
Operational Feasibility assesses whether the proposed system can be effectively used by the employees and integrated into the existing organizational environment. It examines how well the solution satisfies the identified requirements, problem-solving ability, user acceptance, and operational workflow compatibility.
| TYPE OF FEASIBILITY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Technical Feasibility | Checks whether the required technology, hardware, software, and technical expertise are available to develop and implement the system. |
| Economic Feasibility | Evaluates whether the benefits of the proposed system outweigh the costs. It is also called cost–benefit analysis. |
| Operational Feasibility | Determines whether the system will work in the real business environment and whether employees and users will accept and use it effectively. |
| Schedule Feasibility | Assesses whether the system can be developed and implemented within the available time frame or deadlines. |
| Legal Feasibility | Ensures that the proposed system complies with relevant laws, regulations, and policies. |
| Behavioral Feasibility | Checks how users will react to the new system and whether they will adapt to the changes introduced. |
| Organizational Feasibility | Verifies whether the system fits within the organizational structure, culture, and business goals. |
| Market Feasibility | Assesses market acceptance and demand for the proposed system or product. |
Q: The process of organizing subsystems so as to reduce the number of interconnections is termed as ________________.
Decomposition
Simplification
Regrouping
Decoupling
[ Option B ]
Simplification is the process of organizing subsystems in such a way that the number of interconnections between them is reduced. In system design, when a large system is broken down into smaller subsystems, each subsystem interacts with others through interfaces.
Simplification aims to minimize these connections, making the system easier to understand, maintain, and modify.
Q: Which of the following is the correct way to create an abstract class in Java?
class Demo { abstract void fun(); }
class abstract Demo { void abstract fun(); }
abstract class Demo { abstract void fun(); }
abstract class Demo { void fun() { abstract; } }
[ Option C ]
In Java, an abstract class must be declared using the abstract keyword before the class name, and any abstract method inside it must also be declared with the abstract keyword and cannot have a method body.
Q: ____________ is a usable system or system component that is built quickly and at lesser cost and with the intention of modifying or replacing it by a full-scale and fully operational system.
Approved system
Increment
Prototype
Spiral
[ Option C ]
When developing a new system, it is often helpful to build a quick, small, and low-cost version of the actual system first. This early version is called a Prototype.
A prototype is working model of the system. It is created with the intention of being modified, refined, or replaced later by a full-scale, fully operational system.
In system or software development, building the full system at once can be costly and risky if requirements are unclear. To address this, a Prototype is made as an early version that may not have all features but represents essential aspects of the system.
Q: What does the .NET framework primarily consist of?
JVM and Web forms
CLR and Web forms
CLR and .NET framework class libraries
JVM and Base class libraries
[ Option C ]
The .NET framework primarily consists of two major components, the Common Language Runtime (CLR) and the .NET Framework Class Libraries.
The CLR is the Execution Engine that runs applications and provides services such as memory management, security, and exception handling.
The Class Libraries provide a rich set of reusable types and APIs for common programming tasks like file handling, database interaction, and user interface creation.
Q: ____________ tests are performed on a program unit to verify the response time, the execution time, the throughput, primary and secondary memory utilization and traffic rates on data channels and communication links.
Performance
Stress
Parallel
Functional
[ Option A ]
Performance Testing is a software testing method used to check how efficiently a program or system works under a given workload. It focuses on basic aspects like how quickly the system responds, how much time it takes to execute functions, how many users or operations it can handle at once (throughput), and how much primary or secondary memory it consumes during execution.
Q: Which software testing is used to check the defects in software without executing the actual code?
Static Testing
Black Box
White Box
Performance Analysis Testing
[ Option A ]
Static Testing is a type of software testing that does not require executing the code. It focuses on reviewing and analyzing the code, documentation, or design to find defects. Examples include:
Q: What output is produced for the command: “java cmd a b c d”, when following code is run?
class cmd {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(args[2]);
}
}
c
cmd
b
a
[ Option A ]
Command Line Argument are parameters that are supplied to the application program at the time of invoking it for execution. We can customize the behavior of the main() method using command-line arguments.
When command line arguments are supplied to JVM, JVM wraps these and supply to args[ ]. It can be confirmed that they are actually wrapped up in args array by checking the length of args using args.length.
For the command java cmd a b c d the arguments are assigned as follows:
The statement System.out.println(args[2]); will print the value stored at index 2, which is "c".
Q: Which of these exceptions is thrown in cases when the file specified for writing is not found?
FileOutputException
FileException
FileNotFoundException
IOException
[ Option C ]
In Java, when a program attempts to open a file for reading or writing and that file does not exist or cannot be located in the specified path, Java throws a FileNotFoundException. This exception is a subclass of IOException and specifically indicates problems related to missing files.
Q: Which syntax is incorrect to initialize a two-dimensional array in Java?
int myarr[][] = new int[3][4];
int[][] myarr = {{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}};
int[][] myarr = new int[3][4];
int myarr = new int[3][4];
[ Option D ]
The incorrect syntax for initializing a two-dimensional array in Java is int myarr = new int[3][4];. This statement is wrong because it declares myarr as a simple integer variable, not as an array.
A two-dimensional (2-D) array must always be declared using two sets of square brackets [ ][ ] to indicate rows and columns.
Q: Which of the following general problem solving step is equivalent to system analysis in the software development process?
Design the chosen problem
Implement the chosen solution
Identify the solution requirements and expectations
Identify the problem
[ Option C ]
In software development, system analysis involves understanding what the system must do by gathering functional and non-functional requirements from users and stakeholders. It focuses on identifying solution requirements and expectations, not on designing or implementing the system.
Q: In Java, what is a Base Class?
A class that is used as a template to create other classes and can be instantiated directly.
A class that is used as a foundation for other classes to inherit properties and methods.
A class that contains only static methods and variables.
A class that cannot be inherited by other classes and is only used for creating objects.
[ Option B ]
In Java, a Base Class (Parent Class or Super Class) is a class whose properties and methods are inherited by other classes. It serves as a foundation from which new classes (derived classes or subclasses) can extend functionality. This helps in reusing common code, reducing duplication, and implementing object-oriented feature like inheritance.
Syntax:
class BaseClass
{
……………..;
……………..;
}
class DerivedClass extends BaseClass
{
……………..;
……………..;
}
Q: In the ‘System Requirements Specification’ document, behavioural description covers ______________.
classes of tests to be performed to validate functions, performance and constraints.
diagrammatic representation of functions, processing narrative for each function, interplay among functions, design constraints.
goals and objectives of the software context of the computer-based system, information description.
response to external events and internal controls.
[ Option D ]
In the System Requirements Specification (SRS) document, the behavioral description details how the system responds to external events and internal controls. This includes system reactions to triggers, user interactions, and control mechanisms that govern system processing.
Q: A class that exhibits a high degree of primitiveness encapsulates only ______________ operations.
Volatility
Primitive
Cohesive
Similarity
[ Option B ]
In object-oriented programming, a class is a blueprint for creating objects and can encapsulate (combine) data (variable) and operations (methods). The degree of primitiveness of a class refers to how basic or elementary its responsibilities are.
Q: _______________ are computerized information systems that were developed to process large amount of data for routine business transactions such as payroll and inventory.
Knowledge Work Systems (KWS)
Group Decision Support System (GDSS)
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
Office Automated System (OAS)
[ Option C ]
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) are computerized information systems designed to process large amounts of data related to routine business transactions such as payroll, inventory management, order processing, and billing.
TPS ensures efficient, reliable, and accurate processing of business transactions in real-time or batch mode. They maintain data integrity, rapid response, and controlled processing.
TPS SYSTEMS FOCUS ON:
Q: Which command is used to convert the code written in Java to bytecode?
javap
java
javadoc
javac
[ Option D ]
Compilation : Converting the Java source code (.java file) into bytecode (.class file) that can run on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The javac command is used to compile Java source code into bytecode.
javac FirstExample.java
Execution : Running the bytecode on the JVM. The java command is used to run the bytecode on the JVM.
java FirstExample
| COMMAND | USED FOR |
|---|---|
| javac | Compiles Java source code (.java) into bytecode (.class). |
| java | Runs the compiled Java bytecode on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). |
| javadoc | Generates HTML documentation from Java source code comments. |
| javap | Disassembles bytecode (.class file) to view class structure, methods, and fields. |
| jar | Creates, views, or extracts Java Archive (.jar) files. |
| jdb | Java debugger. Used to debug Java programs. |
| jconsole | Java monitoring and management console for running Java applications. |
| jshell | Java REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop) for running snippets of Java code interactively. |
Q: The maintenance input of matter and energy required to repair, replenish and maintain the system is termed as _____________.
System Maintenance
Debugging
Positive Entropy
Negative Entropy
[ Option D ]
In systems theory, entropy refers to the natural tendency of a system to move toward disorder or breakdown.
Positive Entropy : System moves toward disorder, decay, or breakdown.
Negative Entropy : System receives inputs of energy or resources that help it stay healthy, organized, and functioning.
Q: Scrum is an agile software development method, in which, within each framework activity, work tasks occur within a process pattern called _____________.
Sprint
Demo
Backlog
Scrum Master
[ Option A ]
In Scrum, which is a popular Agile software development method, the project work is divided into small, time-boxed cycles. These cycles are called Sprints. A Sprint is:
Q: What will be the value of arr[2] in the following code?
String[] arr = new String[3];
arr[0] = “Maths”;
arr[1] = “Science”;
Null
“Science”
“Maths”
“”
[ Option A ]
In the given code, a string array of size 3 is created using new String[3]. In Java, when an array of objects is created, all elements are automatically initialized to null unless explicitly assigned a value.
Here, only arr[0] and arr[1] are assigned the values "Maths" and "Science" respectively. The third element, arr[2], is never given any value. Therefore, it retains its default initialization, which is null.
Q: Which of the following activity is not involved in the design of database during system designing phase of System Development Life Cycle?
Physical Layout Design
Data Modeling
Conceptual Modeling
Input/output Volume
[ Option D ]
During the System Designing phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), the database design focuses on how data will be stored, organized, and structured. This includes creating models that describe data elements, their relationships, and the final physical storage format.
| ACTIVITY | PURPOSE |
|---|---|
| Conceptual Modeling | Defines what data the system needs at a high-level using ER diagrams (entities, attributes, relationships). |
| Data Modeling | Converts the conceptual model into detailed database structures such as tables, fields, keys, and relationships. |
| Physical Layout Design | Decides how the data will be physically stored on disk (indexing, file organization, partitioning, storage formats). |
However, the Input/Output Volume is not part of database design. It relates to system performance and workload analysis.
Q: Which protocol does RMI use to communicate between objects distributed across a network?
HTTP
TCP/IP
SMTP
FTP
[ Option B ]
In Java, RMI (Remote Method Invocation) is a technology that allows an object running in one Java virtual machine (JVM) to invoke methods on an object located in another JVM, possibly on a different machine over a network.
To enable this communication, RMI relies on a network protocol that provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data between applications.
The protocol used for this purpose is TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol), which is a standard suite of communication protocols used for transmitting data over networks, including the Internet.
Q: Which of the following software testing verifies that all elements mesh properly and that overall system function/performance is achieved?
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
Validation Testing
System Testing
[ Option D ]
System Testing checks the complete integrated system to ensure:
| TESTING TYPE | PURPOSE |
|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Tests individual modules or components for correct functionality. |
| Integration Testing | Checks interactions and data flow between combined modules. |
| System Testing | Verifies that the complete system works as intended and meets performance goals. |
| Acceptance Testing | Confirms the system meets user requirements. It is often done by the client. |
| Regression Testing | Ensures new changes do not break existing functionality. |
Q: System Design is carried out __________________.
as soon as system requirements are determined.
whenever the system analyst feels it to be urgent.
after the final system specifications are approved by the management.
whenever the management feels it to be urgent.
[ Option C ]
Before designing a system, we must clearly understand, what the system should do, what features it must have and what limitations and rules apply. These details are called System Requirements.
System Design is the phase in system development that follows requirements analysis. It begins as soon as the system requirements are clearly determined and understood. The purpose of system design is to create the blueprint or architecture of the system that will fulfill those requirements.
Why Design Starts After Final Approval?
Q: Mr. X is a member of System Development Team who visits his client company XYZ Ltd. frequently to interview its employees to gather the details regarding the drawbacks of the existing system in the company XYZ Ltd. and understand their future requirements. Identify the role Mr. X is performing.
Programmer
Project Leader
System Analyst
Project Manager
[ Option C ]
A System Analyst plays a key role in system development. Their primary responsibility is to study the existing system, understand its problems, and gather requirements for the new system.
Q: Technical feasibility is carried out by the System Analysts to evaluate _______________.
that the needed technology is available.
that there will be no resistance for the implementation of the new system.
the cost of converting and preparing data files and the cost of preparing new or expanded computer facilities.
the time within which the new system will become operational.
[ Option A ]
Technical feasibility is carried out by System Analysts to evaluate whether the current technology, tools, and resources are sufficient and suitable for developing and implementing the proposed system.
It assesses the availability, capability, and compatibility of hardware, software, infrastructure, and technical expertise required to build the system.
Q: In testing, along with batch control, which of the following programmed check cannot be used?
Sequence check
Completeness check
Consistency check
Consumable check
[ Option D ]
Programmed checks help detect errors automatically during processing, improving data quality and reducing manual inspection.
In testing, programmed checks are automated controls embedded within software or batch processes to verify data integrity, correctness, and processing order. Common programmed checks include:
| VALID CHECK | WHY USED |
|---|---|
| Sequence Check | Commonly used to verify correct order. |
| Completeness Check | Ensures required data is present. |
| Consistency Check | Ensures logical correctness. |
Q: What is the right syntax to read an integer from the user in Java?
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int num = sc.readInt();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int num = sc.inputInt();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int num = sc.nextInt();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int num = sc.getInt();
[ Option C ]
In Java, to read input from the user, we commonly use the Scanner class, which is part of the java.util package. First, a Scanner object is created using new Scanner(System.in), which connects the scanner to standard input like keyboard.
The Scanner class provides several methods to read different types of data. To read an integer, the correct method is nextInt().
Q: Which symbol in Data Flow Diagrams represents Data Store?
.webp)



[ Option B ]
In a Data Flow Diagram (DFD), different symbols are used to show how data moves within a system. A Data Store is a place where data is kept for later use. It could be a file, a database table, a ledger, or any storage location. To represent this storage in a DFD, we use Two Parallel Horizontal Lines (Open-Ended Rectangle).
| DFD SYMBOL | USE |
|---|---|
| Process (Circle or Rounded Rectangle) | Shows an activity that transforms input data into output data. It represents work being done. |
| Data Flow (Arrow) | Represents the movement of data between entities, processes, and data stores. |
| External Entity (Rectangle / Square) | Represents a person, department, organization, or system outside the boundary of the current system that provides or receives data. |
| Data Store (Two parallel horizontal lines) | Represents a place where data is stored for later use, such as files, databases, or records. |
Q: _________ test is NOT included in unit testing.
Performance
Stress
Security
Structural
[ Option C ]
Security Testing is generally not included in unit testing. Unit testing focuses on verifying the functionality of individual program units or components in isolation. It includes tests related to the internal structure and behavior of the unit, often through techniques like Structural Testing.
Q: Most of the Information Systems require some modification after development. There are different categories of Maintenance which are Scheduled, Adaptive, Corrective, Rescue, Preventive, and Perfective. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about these categories of Maintenance?
Corrective Maintenance deals with fixing bugs in the code or defects found during the executions.
Scheduled Maintenance is anticipated and can be planned in advance.
Adaptive Maintenance mainly deals with accommodating to the new or changed user requirements.
Rescue Maintenance deals with the undetected malfunctions that require immediate troubleshooting solution.
[ Option C ]
Adaptive Maintenance primarily focuses on modifying the system to remain usable in a changed or changing environment, such as new operating systems, hardware, or regulations.
It is not mainly concerned with accommodating new or changed user requirements that aspect is typically covered under Perfective Maintenance.
Q: The goal of requirements _______________ is to collect and document what various stakeholders want from the software that is to be built.
analysis
gathering
list
specification
[ Option B ]
The goal of Requirements Gathering is to collect and document the needs, expectations, and desires of various stakeholders regarding the software to be built. Requirements gathering is a critical early phase in software development focused on understanding what stakeholders want from the system. The collected information forms the basis for analysis, design, and implementation.
Q: Which of the following is correct definition of Coupling in Java language?
Degree to which elements of a module belong together.
The ability of a class to inherit from other classes.
Process of hiding internal details of a module.
Degree of direct knowledge one class has of other.
[ Option D ]
In object-oriented programming, coupling refers to the level of dependency between classes or modules.
High Coupling means a class depends heavily on other classes, which makes the system harder to maintain or modify.
Low Coupling means a class has little knowledge of other classes, leading to more modular and flexible code.
Q: Which of the following is a correct statement about constructors in Java?
Constructors cannot be overloaded.
A constructor can be called directly like a regular method.
A constructor does not have a return type, not even void type.
A class can have only one constructor.
[ Option C ]
In Java, a constructor is a special block of code that is automatically executed when an object of a class is created. Its main purpose is to initialize the object, that is, to assign initial values to variables or run setup code.
class MyClass
{
MyClass() //This is a constructor.
{
System.out.println("Constructor called.");
}
void MyClass() //Not a constructor, this is a method.
{
System.out.println("This is a method.");
}
}
Q: Which of the following is NOT a stage of the agile software development approach?
Documenting
Exploration
Maintenance
Planning
[ Option A ]
Agile emphasizes working software over comprehensive documentation, so while some documentation is done, it is not considered a core stage or main phase of Agile development. Agile development mainly includes stages like:
Q: Which statement is true about an Interface in Java?
An interface cannot extend another interface.
An interface can contain implemented methods.
An interface can contain instance variables.
A class can implement multiple interfaces.
[ Option D ]
The abstract class is used for achieving partial abstraction. Unlike abstract class an interface is used for full abstraction.
Interface looks like a class but it is not a class. An interface can have methods and variables just like the class but the methods declared in interface are by default abstract (only method signature, no body). Also, the variables declared in an interface are public, static and final by default.
A class extends another class, an interface extends another interface, but a class implements an interface.
A class can implement more than one interface which is one of the key features of interfaces in Java.
interface MyInterface1
{
void fun1();
}
interface MyInterface2
{
void fun2();
}
class Demo implements MyInterface1,MyInterface2
{
public void fun1()
{
System.out.println("Inside fun1() Method");
}
public void fun2()
{
System.out.println("Inside fun2() Method");
}
void fun3()
{
System.out.println("Inside fun3() Method");
}
}
class InterfaceExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Demo obj1=new Demo();
obj1.fun1();
obj1.fun2();
obj1.fun3();
MyInterface1 obj2=new Demo();
obj2.fun1();
//obj2.fun2(); Error.
//obj2.fun3(); Error.
MyInterface2 obj3=new Demo();
//obj3.fun1(); Error.
obj3.fun2();
//obj3.fun3(); Error.
}
}
OUTPUT
Inside fun1() Method
Inside fun2() Method
Inside fun3() Method
Inside fun1() Method
Inside fun2() Method
Q: A ___________ is a record of historical data that remains in a file, used for reference and serves as control on key details.
Rewrite form
Report form
Memory form
Record form
[ Option C ]
Q: Which component of Java platform is responsible for converting bytecode into machine-specific code?
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Development Kit (JDK)
Java Compiler
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
[ Option D ]
Java is a platform-independent programming language, which means Java programs can run on any operating system without modification. This is possible because Java does not compile code directly into machine-specific instructions.
Instead, Java source code (.java files) is first compiled by the Java Compiler into an intermediate form called bytecode (.class files). Bytecode is platform-independent and cannot be executed directly by the operating system. To run a Java program, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is used.
The JVM is a part of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and it is responsible for interpreting or converting the bytecode into machine-specific code that the operating system can execute.
Q: The _____________ approach of system development is not suitable for accommodating changes as it follows all sequential steps.
Agile
Prototyping
Waterfall
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
[ Option C ]
The Waterfall approach to system development is sequential and linear, meaning each phase must be completed fully before the next begins. This method follows a strict sequence of steps such as requirement gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Due to its rigid structure, it is not suitable for accommodating changes easily once a phase is completed.
Q: Which of the following is true about Java applets?
No plugin is required to run an applet.
They run within a web browser and work at server side.
Applets are not secured.
They run within a web browser and work at client side.
[ Option D ]
In Java, an applet is a small program designed to be embedded in a web page. The core idea of applets is that they run inside a web browser on the client’s machine, not on the server. This allows interactive features, animations, or graphics to be displayed on the user’s browser.
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.Graphics;
public class MyApplet extends Applet {
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.drawString("Hello, Suraku", 60, 60);
}
}
HTML FILE TO RUN THE APPLET:
<html>
<body>
<applet code="MyApplet.class" width="250" height="100"></applet>
</body>
</html>
Q: System Requirements Specification (SRS) document does NOT include ______________.
Non-Functional Attributes
Design Solutions
Schedule and Budget
Functional Requirements
[ Option B ]
A System Requirements Specification (SRS) document focuses on what the system should do, not how it will do it. It typically includes, functional requirements, non-functional attributes (performance, reliability, security, usability, etc.) and schedule and budget.
Design Solutions, on the other hand, describe how the system will be implemented. This is part of the System Design phase and is not included in SRS.
Q: What is the purpose of the ‘new’ keyword in Java?
Defines a new method
Imports a package
Creates a new object instance
Declares a new variable
[ Option C ]
In Java, the new keyword is used to create new objects at runtime. When a class is defined, it serves as a blueprint, but no memory is allocated until an object of that class is created. The new keyword allocates memory for the object on the heap and calls the constructor of the class to initialize it.
Q: _________ errors occur when the code executes without errors but the output is not what the programmer intended.
Compilation
Logical
Syntax
Semantic
[ Option B ]
Logical Errors (Semantic Errors) occur when the code executes without any syntax or compilation errors, but the output is not what the programmer intended. These errors arise from mistakes in the program's logic, causing it to produce incorrect or unintended results.
Q: Which part of a Decision Table comprehensively lists the comparisons or conditions?
Action Entries
Condition Entries
Condition Stub
Action Stub
[ Option C ]
A Decision Table is a tabular method for representing logical relationships between conditions and actions in a system. It is widely used in software testing, system design, and decision-making.
| Quadrant | Position | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Condition Stub | Top-Left (Upper-Left) | Lists the conditions to be tested. |
| Condition Entry | Top-Right (Upper-Right) | Shows possible values for each condition. |
| Action Stub | Bottom-Left (Lower-Left) | Lists all possible actions. |
| Action Entry | Bottom-Right (Lower-Right) | Specifies the actions to take for each condition combination. |
Q: Financial Feasibility Study is carried out by the System Analysts to evaluate that _____________.
it will be profitable to implement the system.
the proposed system will result in improved operations.
finances are available to implement the proposed system and it will be cost-effective.
implementation will lead to low operating cost.
[ Option C ]
Financial Feasibility Study evaluates whether finances are available to implement the proposed system and whether the project will be cost-effective. A Financial Feasibility Study (Economic Feasibility) answers two main questions:
Q: ____________ refers to the automation of anything that humans do to develop systems and supports virtually all phases of Traditional System Development Process.
Decision Tree
Computer-Aided-Software Engineering (CASE)
System Flow Charts
Data Flow Diagram
[ Option B ]
System Development involved manual processes which were time-consuming and prone to errors. CASE tools provide an environment where activities such as diagramming, code generation, version control, and testing are partially or fully automated.
Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) refers to the use of software tools that automate many activities humans perform during system development.
Compared to a Data Flow Diagram (DFD), which simply shows the movement of data in a system and is used only in the analysis phase, CASE tools work throughout all phases of SDLC.
Q: What is bytecode in Java?
Machine-dependent code in Java.
Source code in Java.
Intermediate machine-independent code generated by Java compiler.
Machine code specified to a processor.
[ Option C ]
In Java, when you compile a .java file using the javac compiler, it does not directly generate machine code. Instead, it produces an intermediate code known as bytecode, stored in .class files.
This bytecode is platform-independent, meaning it can run on any device that has the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM then converts this bytecode into machine-specific instructions depending on the operating system and hardware. This is the main reason Java is called Write Once, Run Anywhere (WORA).
| TYPE OF CODE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Source Code | Human-readable, high-level program written by the developer using programming languages like Java, C, C++, Java, Python. It contains logic, statements, and comments. It cannot be executed directly by the computer and must be compiled or interpreted. |
| Bytecode | Intermediate, platform-independent code generated by the Java compiler. It is stored in .class files. Bytecode is not machine code, but it can run on any system that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which converts bytecode into machine code at runtime. |
| Object Code | Low-level code produced by a compiler. It contains machine instructions plus unresolved references, placeholders, and symbol tables. Object code is not executable on its own and must be linked with other object files and libraries.
|
| Machine Code | The final binary instruction set understood directly by the CPU. Produced after linking all object files. It contains fully resolved addresses and ready-to-execute commands. Represented in 0s and 1s.
|
| Executable Code | The complete, linked, and ready-to-run program created by combining machine code, libraries, and metadata. This is the file that users can double-click or run from the terminal. It loads directly into memory and executes on the operating system.
|
Q: Which of the following is NOT an advantage of Java bytecode?
Portability
Security
Platform Independent
Faster execution than machine code
[ Option D ]
Java programs are compiled into bytecode, which is an intermediate, platform-independent code. This bytecode is executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which interprets [Just-In-Time (JIT)] compiles it for the underlying hardware. The advantages of Java bytecode include:
However, bytecode is generally slower than native machine code because it must be interpreted or compiled at runtime.
Q: Each time a new module is added to the system, new data flow paths are established, new input/output may occur and new control logic is invoked. These changes may cause problems with functions that previously worked flawlessly. ________ tests ensure that changes or corrections have not introduced new errors.
Top-Down Integration
Regression
Bottom-Up Integration
Performance
[ Option B ]
When a new module is added to a system, several things change:
Even if these changes are small, they can accidentally affect older parts of the system that were working perfectly earlier. To ensure that new changes do not break the existing functionality, we perform Regression Testing.
Regression Testing is a type of testing that re-checking everything to confirm nothing got disturbed.
Q: ____________ refers to the set of tasks that ensures that software correctly implements a specific function is called.
Validation
Veracity
Verification
Volume
[ Option C ]
When software is being developed, we must check whether it is being built correctly according to the required functions and design. This checking process is called Verification.
On the other hand, Validation is the process of checking whether the final software product meets customer needs and expectations. It ensures that the system performs the intended functions in the actual working environment and satisfies all user requirements.
| VERIFICATION | VALIDATION |
|---|---|
| Ensures the product is built according to specifications and design. | Ensures the final product meets customer requirements. |
| Focus on the process of development. | Focus on the final product and its usefulness. |
| We are building the product right. | We are building the right product. |
| Performed by developers, quality assurance team. | Performed by end users, testers, and clients. |
| Reviews, inspections, walkthroughs. | Functional testing, system testing, acceptance testing. |
Q: What is the output of the following code?
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
System.out.println(++x*2);
}
}
12
11
10
Compile Time Error
[ Option A ]
In this code, the variable x is initially assigned the value 5. The expression ++x * 2 uses the pre-increment operator, which means x is increased before it is used in the calculation. So, ++x changes the value of x from 5 to 6, and then the multiplication 6 * 2 is performed. Therefore, the output printed by System.out.println(++x * 2); is 12.
Q: A company was recommended to adopt a new Accounting System. The company was advised to use both the old and the new Accounting Systems alongside each other, both being able to operate independently. If all goes well, the old system is discontinued and the new system carries on as the only system. Which of the following new Accounting System implementation strategy was advised to the company?
Phased Implementation
Direct Implementation
Parallel Implementation
Pilot Implementation
[ Option C ]
Parallel Implementation is a strategy where the new system runs alongside the old system for a period of time. Both systems operate independently, and outputs from both are compared to ensure the new system works correctly. Once confident, the old system is discontinued.
Q: Which of the following code gives error of “outofbounds” in array?
int[] a = new int[5]; a[4] = 5;
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; System.out.print(a[2]);
int[] a = new int[10]; for (int I = 0; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = i*2; }
int[] a = new int[3]; a[3] = 9;
[ Option D ]
In Java, an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException occurs when a program tries to access an array index that does not exist. Java arrays always start with index 0, and the last valid index is always length − 1.
So, if you create an array like int[] a = new int[3];. This array has 3 elements, and their valid indexes are a[0], a[1], and a[2]. Any attempt to access a[3], a[4], etc., will cause an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Q: The interconnections and interactions between the sub-systems are termed as ______________.
Connectors
Interfaces
Protocols
Links
[ Option B ]
In a system, you have multiple sub-systems (smaller parts) that work together. For these sub-systems to exchange data, signals, or control information, they must be connected in a meaningful way. This connection is called an Interface. An interface specifies:
Q: ______________ tests on a program unit are performed to check “whether programs do what they are expected to do or not”.
Performance
Structural
Stress
Functional
[ Option D ]
Functional tests on a program unit are performed to check whether programs do what they are expected to do. It focuses on:
Q: Which of the following streams is used to deserialize the primitive data and objects in Java?
PrintWriter
BufferedReader
FileWriter
ObjectInputStream
[ Option D ]
In Java, streams are used to handle input and output of data. The core concept here is serialization and deserialization:
Serialization: Converting an object into a byte stream so it can be saved to a file or sent over a network.
Deserialization: Reconstructing the object from the byte stream back into a Java object.
To handle deserialization of primitive data types and objects, Java provides the ObjectInputStream class.
Q: ____________ is a program development tool used for specifying program logic.
DFD
Structure Chart
Program Flow Chart
Fourth Generation Language Tools (4GL Tools)
[ Option C ]
A program flow chart is a development tool used to visually represent the step-by-step logic of a program. It uses standard symbols to show the flow of control, decisions, loops, inputs, outputs, and processing steps. This helps programmers design, understand, and debug program logic before writing actual code.
Q: Which one of the following correctly defines a System?
System may be defined as a group of two or more interrelated components or sub-systems that serve a common purpose.
System may be defined as a group of two or more interrelated components or sub-systems that function independently of the others and do not contribute to the common goal.
System may be defined as a group of two or more interrelated components or sub-systems that do not serve a common purpose.
System may be defined as a group of elements that operate in a predictable manner.
[ Option A ]
A System is fundamentally a collection of interrelated components working together to achieve a common goal. These components or subsystems interact and depend on each other to produce a unified output or outcome.
Q: Which of the following Java technology is used for server-side programming in Internet applications?
Java Servlet
Java Swing
JavaFX
Java Applets
[ Option A ]
In Java, Java Servlets are used for server-side programming. Servlets run on a web server or application server and generate responses, usually in the form of HTML, to be sent to web browsers.
Java Swing and JavaFX are used for creating desktop GUI applications, and Java Applets are designed for client-side execution within web browsers.
Q: What is the output of following code?
public class ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
printn(a);
}
public static void printn(int[] a){
for(int n : a) {
System.out.print(n+” “);
}
}
}
Compilation error
5 4 3 2 1
Runtime error
1 2 3 4 5
[ Option D ]
In this Java code, an integer array a is created with the elements {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}. The method printn(a) is called, which receives this array and uses a for-each loop to iterate through each element. The for-each loop processes elements in the same order in which they appear in the array. Therefore, the values are printed sequentially: 1 2 3 4 5.
Q: What will be the output of the code after the given code executes?
int a = 5;
int b = a++;
System.out.println(“a = ”+a+”b = ”+b);
a = 6 b = 5
a = 5 b = 6
a = 6 b = 6
a = 5 b = 5
[ Option A ]
In this code, the variable a is first assigned the value 5. When the statement int b = a++; executes, the operator used is the post-increment operator (a++).
In post-increment, the current value of the variable is used first, and then the increment happens afterward. This means that the value of a is first assigned to b, and only after this assignment does a increase by 1. As a result, after the statement executes, a becomes 6 while b remains 5.
Q: Which of the following is not an access modifier in Java language?
public
private
protected
external
[ Option D ]
In Java, access modifiers are keywords used to define the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and variables. They control which parts of a program can access a particular class member. Java provides four main access levels, public, private, protected, and the default (no modifier).
The public modifier allows access from anywhere, private restricts access to within the same class, and protected allows access within the same package and subclasses.
Q: A _____________ describes how a user interacts with the system by defining the steps required to accomplish a specific goal.
DFD
Program Flow Chart
Use Case Diagram
System Chart
[ Option C ]
A Use Case Diagram describes how a user interacts with a system by defining the steps or scenarios required to accomplish a specific goal. It visually represents the actors and the use cases they perform with the system. This helps stakeholders understand system behavior from the user's perspective, facilitating requirement gathering and system design.
Q: Which keyword is used in Java to inherit a class?
inherits
extends
implements
super
[ Option B ]
To inherit a class, Java provides the extends keyword, which indicates that the subclass will acquire all non-private (private members are never inherited) fields and methods of the superclass.
Q: What is the correct sequence of steps for handling a client in a Java servlet lifecycle of a servlet?
init method, service method, doPost/doGet method
init method, doPost/doGet method, service method
service method, doPost/doGet method, destroy method
init method, service method, destroy method
[ Option D ]
The lifecycle of a Java servlet involves these key steps in sequence:
Q: What will be the output of the following code?
class Vehicle {
public void move() {
System.out.println("Vehicle is moving");
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
public void move() {
System.out.println("Car is moving");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle v = new Car();
v.move();
}
}
Runtime error
Vehicle is moving
Compilation error
Car is moving
[ Option D ]
When a class inherits another class using the extends keyword, it can reuse or modify the methods of the parent class. This concept is called inheritance.
Java also supports Method Overriding, which allows a subclass to provide its own implementation of a method defined in the parent class.
When a method is overridden, the version of the method that belongs to the actual object (not the reference type) is called at runtime, this is known as Runtime Polymorphism.
In the given code, the Vehicle class has a method move() that prints "Vehicle is moving". The Car class extends Vehicle and overrides the move() method to print "Car is moving".
In the main method, a reference of type Vehicle is used to create an object of type Car: Vehicle v = new Car();. When v.move() is called, Java checks the actual object type at runtime, sees that it is a Car, and executes the overridden move() method in the Car class. Therefore, the program prints "Car is moving".
Q: Which of the following is not a valid variable name in Java language?
x15
rate
rate_of_taxi
rate-of-taxi
[ Option D ]
Java naming convention is a mechanism to follow as you decide what to name your identifiers such as class, package, variable, constant, method, etc.
Rules For Writing Variable Name:
The variable name rate-of-taxi contains hyphens (-), which Java treats as subtraction operators and it is invalid variable name.
Q: What is the correct way to close a file in Java after writing to it?
fileInput.close();
file.close();
fileWriter.close();
fileStream.close();
[ Option C ]
The correct way to close a file in Java after writing to it is to use the close() method of the FileWriter class. This method is called on the FileWriter object after all writing operations are complete.
Closing the file writer releases any system resources associated with it, flushes buffers, and ensures that data is properly saved to the file. For example, fileWriter.close(); is the standard way to close the file after writing.
Q: Which of these classes are the direct subclasses of the Throwable Class?
Exception and VirtualMachineError Class
Error and Exception Class
IOException and VirtualMachineError Class
RuntimeException and Error Class
[ Option B ]
In Java, Throwable is the root class for all exceptions and errors that can occur during program execution. It defines the common behavior for objects that can be thrown using the throw keyword. It has two direct subclasses, Error and Exception.
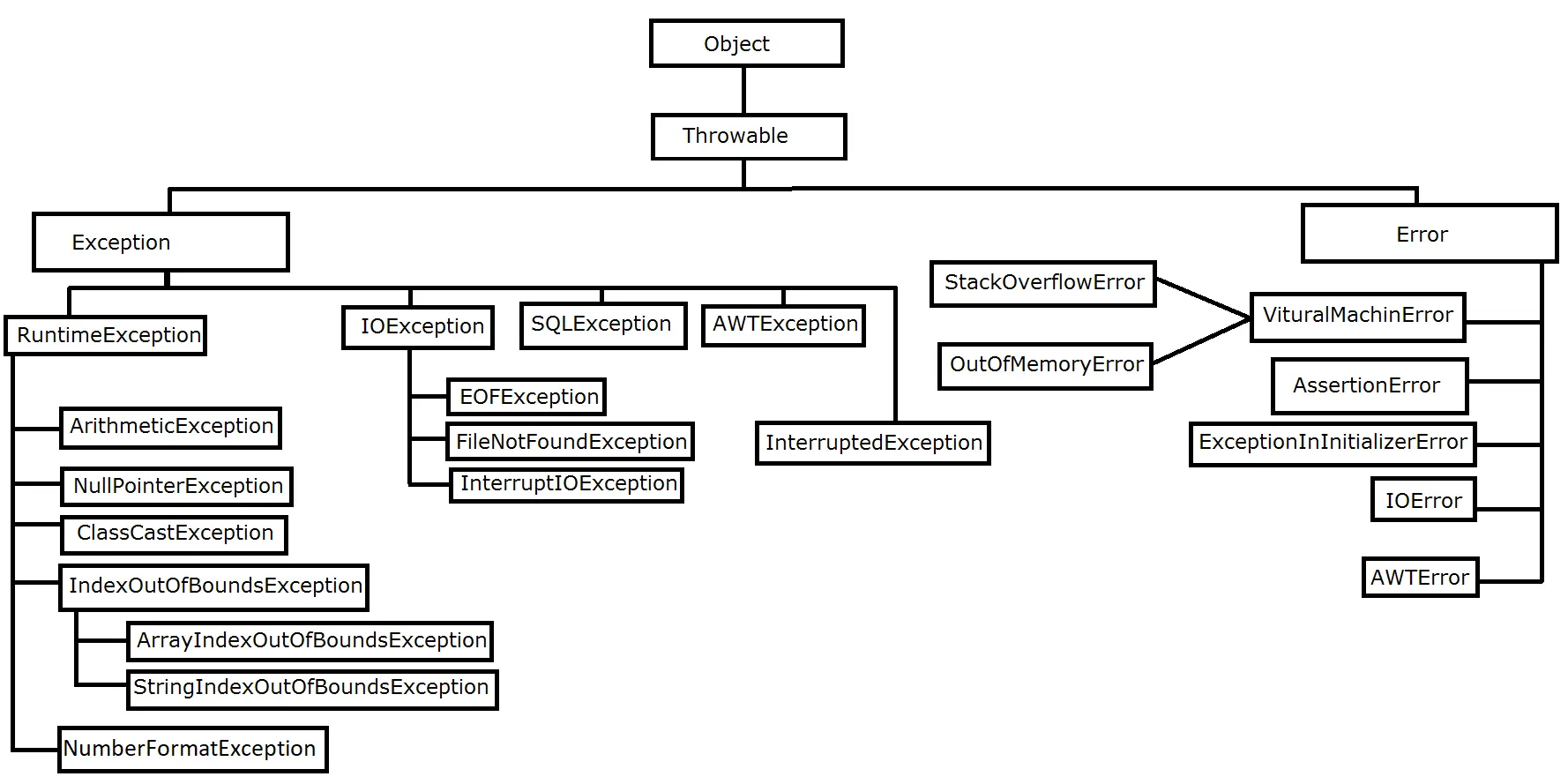
Note:
Q: Code _________ is the quality of a good coded program that makes it easy to understand, modify and maintain by other developers.
Resistance
Adaptability
Effectiveness
Readability
[ Option D ]
Code Readability is the quality of a well-written program that makes it easy for other developers to understand, modify, and maintain. Readable code is clear, logically structured, and communicates its intent, making it easier for others to work on it without confusion or errors.
THE READABLE CODE HAS:
Q: Consider the following class definition:
public class Test {
int var;
String myString;
public Test() {
this(0, “Default”); }
public Test(int var, String myString) {
this.var = var;
this.myString = myString;
}
}
What will the following code do?
Test test = new Test();
Create an object test with var = 0 and myString =”Default”
Throw a runtime exception
Create an object test with var = 0 and myString = null
Throw a compilation error
[ Option A ]
The class Test contains two constructors, a zero argument constructor and a parameterized constructor. When the zero argument constructor is called, it does not directly initialize the variables. Instead, it uses the keyword this(0, "Default") to explicitly call the parameterized constructor. This means the execution is transferred to the constructor Test(int var, String myString), which assigns the values var = 0 and myString = "Default" to the object.
As a result, the object is successfully created, and both instance variables receive valid initial values. Therefore, the object test is created with the expected initialized properties.
Q: Size of “int” data type in Java language is—
64-bits
16-bits
8-bits
32-bits
[ Option D ]
In Java, the size of each primitive data type is fixed, regardless of the operating system or machine architecture. The int data type always occupies 32 bits (4 bytes) of memory. This consistency is a key feature of Java Portability across different platforms.
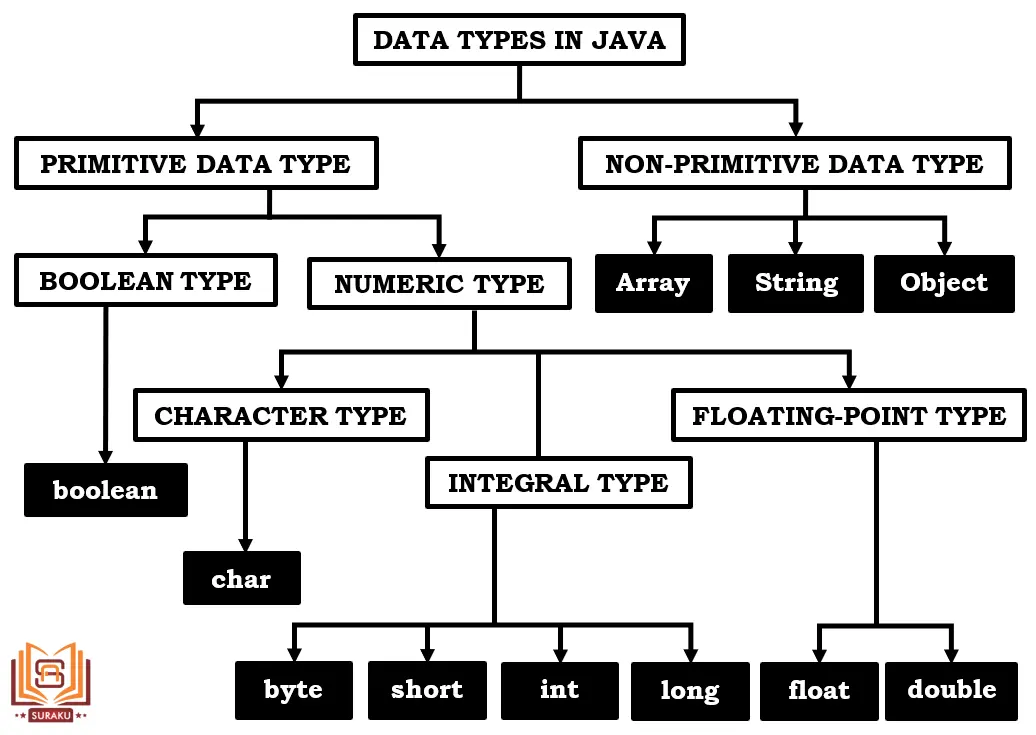
| DATA TYPE | SIZE | DEFAULT VALUE | WRAPPER CLASS |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 Bit | false | Boolean |
| char | 2 Byte | ‘\u0000’ | Character |
| byte | 1 Byte | 0 | Byte |
| short | 2 Byte | 0 | Short |
| int | 4 Byte | 0 | Integer |
| long | 8 Byte | 0 | Long |
| float | 4 Byte | 0.0 | Float |
| double | 8 Byte | 0.0 | Double |
Q: Which of the following class in Java is responsible for handling files in Java?
FileStream
FileHandler
File
FileManager
[ Option C ]
In Java, the File class (java.io package) is responsible for handling operations related to files and directories. It allows you to create files, check whether a file exists, delete files, get file information (size, name, path), and work with folders as well.
Although File does not directly read or write data, it plays the key role in managing and accessing files. For reading or writing content, Java uses other classes like FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader, and FileWriter.
Q: Which user acceptance testing is generally performed by the external users and normally involves sending the product outside for real world exposure?
Beta Testing
Gamma Testing
Alpha Testing
Regression Testing
[ Option A ]
Beta Testing is a type of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) performed by external users outside the development organization. It involves releasing the nearly completed product to a select group of external users or a broader audience to gain real-world exposure and feedback.
This helps identify issues that may not have been caught during internal testing and validates the product's usability and stability in a real environment.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.