The BPSC Teacher Recruitment Exam (TRE) Paper Solution by Suraku Academy offers detailed, accurate, and fully verified answers for every question of the BPSC TRE exam. Each solution is prepared with great care to provide clear explanations and deeper concept understanding. This resource helps candidates strengthen their preparation with trusted solutions before starting their focused study journey. Improve your exam readiness with concept-wise clarity and solved answers. A must-have guide for every BPSC TRE aspirant."
Q: What is the value of ‘p’ in the following C++ code snippet?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int p;
bool a=true;
bool b=false;
int x=10;
int y=5;
p=((x|y)+(a+b));
cout<<p;
return 0;
}
12
16
2
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In this code, the expression (x | y) performs a bitwise OR on 10 and 5.
10 in binary : 1010
5 in binary : 0101
Bitwise OR : 1111 which is 15.
Next, (a + b) adds the Boolean values:
true : 1
false : 0
So, a + b = 1.
Finally, p = 15 + 1 = 16.
Q: The Boolean expression x(x+y) is equal to
x
y
xy
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Given Boolean Expression:
=x(x+y)
=xx+xy
=x+xy
=x(1+y)
=x.1
=x
Q: After performing following set of operations, what does the final list look contain?
InsertFront(10);
InsertFront(20);
InsertRear(30);
DeleteFront();
InsertRear(40);
InsertRear(10);
DeleteRear();
InsertRear(15);
Display();
10 30 10 15
20 30 40 15
10 30 40 15
None of the above
[ Option C ]
These operations are performed on a double-ended queue (deque) or a list that allows insertion and deletion at both front and rear.
Now apply the operations one by one and show the list after each step:
So, the final list is 10 30 40 15.
Q: A computer program that converts an assembly language program into equivalent machine language program is called
Compiler
Assembler
Linker
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
A computer program that converts an assembly language program into its equivalent machine language is called an assembler.
Assembly language uses symbolic instructions like MOV, ADD, SUB etc. called mnemonics, which are easier for humans to understand but must be translated into binary machine code for the computer to execute.
Q: How many edges does a spanning tree of a graph with N vertices have?
N
N-1
N(N-1)/2
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A spanning tree is a subgraph of a connected graph that includes all the vertices but only enough edges to keep the graph connected without forming any cycles.
Q: If circular queue is implemented using array having size MAX_SIZE in which array index start with 0, front points to the first element in the queue, and rear points to the last element in the queue. Which one of the following conditions is used to specify that the circular queue is empty?
front = rear = -1
front = rear =0
front = rear +1
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In a circular queue implemented using an array, the queue is considered empty when there are no elements stored in it. The most common and standard way to represent an empty circular queue is if front=rear=-1.
When the circular queue is first created, it contains no elements. To show this, both front and rear are initialized to -1. As soon as we insert the first element both front and rear becomes 0. When all elements are deleted again, we reset them to -1 to show the queue is empty.
Q: The logic gate that provides high output for same input is
NOT
X-NOR
XOR
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The X-NOR gate, produces a high (1) output when both inputs are the same, either both 0 or both 1.
Truth—Table:
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | Y=A⊙B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q: Which of the following is NOT a step in the Divide and Conquer algorithm?
Combine
Conquer
Divide
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A Divide and Conquer algorithm are a problem-solving technique where a big problem is broken into smaller ones, solved individually, and then combined to produce the final answer. This method is used in algorithms like Merge Sort, Quick Sort, and Binary Search. The Divide and Conquer approach follow three main steps:
Q: Which of the following statements is not true about the doubly linked list?
We can traverse in both the directions.
It requires extra space.
Implementation of doubly linked list is easier than the singly linked list.
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A doubly linked list is a linked list where each node contains three parts:
We can traverse in both the directions. This is true. Because each node has a prev pointer, we can move forward and backward.
It requires extra space. This is true. Every node stores an additional pointer (prev), so space required is more than a singly linked list.
Implementation of doubly linked list is easier than the singly linked list. This statement is not true. A doubly linked list is more difficult to implement because you must maintain both next and prev pointers during insertion and deletion. Singly linked list is simpler.
Q: Which of the following is an example of a digital electronic?
Computers
Mobile phones
Digital cameras
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
Digital electronics are devices that operate using binary signals. They process information in discrete steps rather than continuous signals.
Examples of digital electronic devices include computers, which use digital circuits for all processing tasks, mobile phones, which contain digital processors and memory and digital cameras, which convert images into digital data.
Q: The correct statement for a function that takes pointer to a float, a pointer to a pointer to a char and returns a pointer to a pointer to an integer is
int** fun(float**, char **)
int* fun(float*, char*)
int** fun(float*, char**)
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, function declarations specify the return type, function name, and parameter types. Pointers use * (float* for pointer to float, char** for pointer to pointer to char, int** for pointer to pointer to int).
Combining these, the correct function declaration is int** fun(float*, char**);.
Q: What will be the output of the following C++ code?
#include<iostream.h>
using namespace std;
void square(int *x, int *y)
{
*x=(*x)*--(*y);
}
int main()
{
int number=30;
square(&number,&number);
cout<<number;
return 0;
}
30
870
Segmentation fault
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In this program, the variable number is passed to both parameters x and y, meaning both pointers refer to the same memory location. Inside the function, the statement *x = (*x) * --(*y); first decreases the value of number using the pre-decrement operator --(*y), so number becomes 29.
Then, the expression multiplies the original value by 29. Since the original value was 30, the calculation becomes 30 * 29, resulting in 870.
Q: What is virtual inheritance in C++?
C++ technique to enhance multiple inheritance.
C++ technique to ensure that a private member of the base class can be accessed somehow.
C++ technique to avoid multiple copies of the base class into children/derived class.
None of the above.
[ Option C ]
Virtual inheritance in C++ is used to solve the Diamond Problem that occurs in multiple inheritance. Without virtual inheritance, a derived class may receive multiple copies of the same base class due to different inheritance paths. To prevent this duplication, C++ allows a class to be inherited virtually.
This ensures that only one shared copy of the base class is passed to all derived classes, avoiding ambiguity and memory waste.
Diamond Problem:
When classes B and C both inherit from A, and D inherits from both B and C, D gets two copies of A's members.
A
/ \
B C
\ /
D
Q: A constructor is called whenever
An object is created
A class is created
A class is declared
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
A constructor is a special function inside a class that runs automatically when an object of that class is created. Its main purpose is to initialize the object data members.
A class is just a blueprint or logical design, and it does not do anything on its own. Only when an object is created from that class does memory get allocated, and at that moment, the constructor is automatically called to set initial values.
Q: In a binary search tree, which subtree of a node contains elements that are greater than the node’s value?
Left Subtree
Right Subtree
Both Subtrees
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special type of binary tree where the arrangement of elements follows a strict rule:
This property allows fast searching, because at each step, the tree decides whether to go left (for smaller values) or right (for larger values).
Q: The cout in C++ stands for
class output
character output
common output
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The cout is a predefined object in C++ from the iostream library used for console output. Generally the name cout is breaks down as, "c" for character (handles character streams) and "out" for output. It works with the insertion or put to operator << to print data.
Q: What is the scope of the variable declared in the user-defined function?
Whole program
Only inside the { } block
Inside the main function
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, a variable declared inside a user-defined function has local scope, meaning it is accessible only within the curly braces { } block of that function. It cannot be accessed from other functions or outside the function in which it is declared. Once the function execution ends, the variable is destroyed and its memory is released.
Q: Which language is better for writing structured code?
PASCAL
FORTRAN
BASIC
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
Structured code means writing programs in an organized way using sequence, selection, loops, and functions or procedures. This style makes a program easier to read, understand, and maintain.
PASCAL is considered the best for writing structured code because it was specially designed for teaching good programming practices. It strongly supports structured programming and encourages programmers to divide the program into clear, logical parts.
Q: What is abstract class in C++?
Any class in C++ is an abstract class/Class from which any class is derived
Class specifically used as a base class with at least one virtual function
Class specifically used as a base with at least one pure virtual function
None of the above
[ Option C ]
An abstract class in C++ is a class that is designed only to be a base class and cannot be instantiated on its own mean we cannot create object of abstract class.
The key feature of an abstract class is that it contains at least one pure virtual function. A do-nothing function is called pure virtual function which is declared using the syntax virtual returnType functionName() = 0;.
Derived classes must override these pure virtual functions to provide a concrete implementation.
Q: All members of a structure in C++ are ___________ by default.
public
private
protected
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In C++, a structure (struct) is similar to a class, but one key difference lies in the default access specifier. When you create a structure and define variables or functions inside it, those members are public by default.
While a class keeps its members private by default, meaning they cannot be accessed directly from outside unless specified.
Q: Which of the following is an advantage of using arrays?
Constant time insertion and deletion
Ability to store elements of different data types
Random access to elements using an index
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
An array is a linear data structure in which elements are stored in contiguous memory locations. This layout allows for random access, meaning any element can be directly accessed using its index in constant time O(1).
Q: The data structure in which data are added at the rear and deleted from front is called
Stack
Queue
Linked list
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A data structure in which elements are inserted at the rear and deleted from the front follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. This is exactly how a queue works. In a queue, new data always enters from the rear (back or end), and the oldest data is removed from the front.
Q: Which of the following is NOT and NP-Complete problem?
Traveling Salesman Problem
Boolean Satisfiability Problem
Shortes Path Problem
None of the above
[ Option C ]
NP-Complete problems are a class of computational problems that are considered difficult because, while a proposed solution can be verified quickly (in polynomial time), there is no known algorithm that can solve all instances of the problem efficiently. Examples include the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), which involves finding the shortest possible route visiting all cities, and the Boolean Satisfiability Problem (SAT), which asks whether a boolean formula can be satisfied.
The Shortest Path Problem, which finds the minimum path between nodes in a graph, is not NP-Complete, because it can be solved efficiently in polynomial time using algorithms like Dijkstra’s or Bellman-Ford.
Q: Which feature of OOP is indicated by the following code?
class student {int marks;);
class topper: public student{int age; topper (int age) {this.age=age;}};
Encapsulation and inheritance
Inheritance and polymorphism
Polymorphism
None of the above
[ Option A ]
The given code demonstrates two core features of Object-Oriented Programming: encapsulation and inheritance.
Encapsulation means binding data and functions together inside a class. In the given code, class student { int marks; };, the variable marks is inside the class student. This shows encapsulation, because the data is protected inside the class structure.
Inheritance means creating a new class from an existing class.
class topper : public student {
int age;
topper(int age) { this.age = age; }
};
The toppers is inheriting from the student class using public inheritance. So, the class topper automatically gets the properties of the student class.
Since the code does not use virtual functions or method overriding, it does not show polymorphism.
Q: What does the control unit generate to control other units?
Transfer signals
Command signals
Control signals
None of the above
[ Option C ]
The control unit in a computer is responsible for directing the operations of the processor. It does this by generating Control Signals, which coordinate and manage the activities of other components, such as the ALU, memory, and input-output devices. These control signals tell each component what action to perform, when to perform it, and how to respond to various instructions.
Q: In C++, what does a class hold?
Array
Data
Data and functions
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
A class in C++ is a blueprint that can hold different types of members. Its main purpose is to group data and related functions together, but it can store many kinds of data, including arrays, simple variables, and functions.
Q: Which of the following is NOT a basic operation performed on a data structure?
Encryption
Deletion
Insertion
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
Data structure is way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. For example, dictionary is good example of organized data in which the words are arranged in a particular order.
| OPERATION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Insertion | Adding a new element to the data structure. |
| Deletion | Removing an existing element from the data structure. |
| Traversal | Accessing or visiting each element of the data structure. |
| Searching | Finding whether a particular element exists or not. |
| Sorting | Arranging elements in a particular order either in ascending or descending. |
| Update | Changing the value of an existing element. |
Q: Simplified Boolean function of Boolean function F=A’C+A’B+AB’C+BC is
F=C+A’B
F=A’B+B’C
F=BC+A’B
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Given Expression:
F=A’C+A’B+AB’C+BC
F=A’C+A’B+C(B+AB’)
F=A’C+A’B+C((A+B)(B+B’))
F=A’C+A’B+C(A+B)
F=A’C+A’B+AC+BC
F=A’C+AC+A’B+BC
F=C(A’+A)+A’B+BC
F=C+BC+A’B
F=C(1+B)+A’B
F=C+A’B
Q: The preorder traversal of a binary search tree is 15, 10, 12, 11, 20, 18, 16, 19. Which one of the following is the postorder traversal of the tree?
20, 19, 18, 16, 15, 12, 11, 10
11, 12, 10, 16, 19, 18, 20, 15
19, 16, 18, 20, 11, 12, 10, 15
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special type of binary tree that is designed to allow fast searching, insertion, and deletion of data. In BST:
The preorder traversal sequence is given and in case of BST, the inorder traversal always sorts the tree nodes into ascending order.
Preorder : 15, 10, 12, 11, 20, 18, 16, 19
Inorder : 10, 11, 12, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20
WHEN PREORDER AND INORDER TRAVERSAL GIVEN:
So, the resultant BST is:
15
/ \
10 20
\ /
12 18
/ / \
11 16 19
Final Postorder traversal sequence is 11, 12, 10, 16, 19, 18, 20, 15
Q: Which of the following can be considered as the members that can be inherited but not accessible in any class?
pubic
protected
private
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, private members of a class cannot be accessed directly by derived classes, even though they are technically inherited. They exist in memory but remain inaccessible to ensure encapsulation.
Q: In a balanced binary tree, the height of two sub-trees of every node can not differ by more than
2
1
0
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure in which each node can have at most two children, called the left child and the right child.
Now, some binary trees can grow in an uneven manner. For example, all nodes may keep inserting to the left side only. This makes the tree skewed, and searching becomes slow. To avoid this, we use a balanced binary tree.
A Balanced Binary Tree is a special type of binary tree in which the height (depth) of the left and right subtrees of every node is kept nearly equal.
Height of left subtree and right subtree differ by 0 or 1 only.
This condition must hold at every node in the tree, not just the root.
So, in a balanced binary tree (AVL Tree), the difference between the heights of the left and right subtree of any node is allowed to be at most 1.
Q: If a semicolon is not used at the end of the statement, what message will be displayed by C++?
Semicolon Missing
Statement Missing
Error in Statements
None of the above
[ Option D ]
In C++, every statement must end with a semicolon. If a programmer forgets to write a semicolon, the compiler shows an error, but it does not display the messages given in the options.
Different C++ compilers show different error messages, such as “expected ‘;’ before …” or “missing ‘;’,” but none of these matches exactly with “Semicolon Missing,” “Statement Missing,” or “Error in Statements.”
Q: Which of the following is not a valid variable name in most programming languages?
myVariable
123Variable
_myVariable
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
A variable is a named location in memory that is used to hold or store the value. The value of variable can be modified in the program by the instruction. The variable names must follow the rules of identifiers.
RULES FOR WRITING IDENTIFIERS:
| Variable Name | Result | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| myVariable | Valid. | Starts with a letter, follows identifier rules. |
| 123Variable | Invalid. | Variable names cannot start with digits. |
| _myVariable | Valid. | First character is underscore. Alphabets and underscore is allowed as the first character. |
Q: Which of the following is user-defined header file extension used in C++?
hg
cpp
h
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, a header file contains declarations such as functions, classes, constants, and macros. These files are included in a program using the #include directive. There are two types of header files, predefine header files iostream.h, conio.h and user-defined header files created by the programmer.
User-defined header files in C++ typically use the extension “.h”. For example, #include "myheaderfile.h"
Q: Which data structure is required to covert the infix to prefix notation?
Queue
Stack
Linked List
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
To convert an infix expression to a prefix expression, we need a data structure that can temporarily hold operators while respecting their precedence and associativity. A stack is ideal for this purpose because it follows the LIFO (Last In First Out) principle.
Q: How can we describe an array in the best possible way?
Arrays are immutable
Container that stores the elements of similar types
The array is not a data structure
None of the above
[ Option B ]
An Array is a linear data structure that holds multiple elements of the same data type (homogeneous) in contiguous memory locations. This allows easy and efficient access to elements using their index. The index of an array usually starts from 0.
Q: What is the purpose of the “don’t care” condition in digital logic?
To indicate that the value of a variable does not affect the output
To prioritize certain inputs over others
To ensure that all possible input combinations are covered in truth tables
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In digital logic, a “don’t care” condition indicates that the value of a particular input does not affect the final output of the circuit. These conditions are used during simplification of Boolean expressions or Karnaugh maps (K-maps).
Because the output does not depend on certain inputs, we are free to treat those inputs as either 0 or 1, whichever helps produce the simplest possible expression.
“Don’t care” conditions do not prioritize inputs nor ensure completeness of truth tables, instead, they are a tool for simplification.
Q: Which concept of C++ is used to reuse the written code?
Polymorphism
Inheritance
Encapsulation
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
One of the main goals of C++ is to make programming easier by allowing developers to reuse code instead of writing everything from scratch. The concept in C++ that supports this is inheritance.
Inheritance allows a new class (derived class or child class or sub class) to acquire the properties and functions of an existing class (base class or parent class or super class).
Q: Which is correct syntax of inheritance?
class base_classname : access derived_classname { /* define class body */ };
class derived_classname : access base_classname { /* define class body */ };
class derived_classname : base_classname { /* define class body */ };
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
In C++, inheritance means creating a new class (derived class) from an existing class (base class). The correct syntax places the derived class first, followed by a colon, then the access specifier (public, private, protected), and then the base class name. Option (b) correctly follows this format.
However, if you do not specify any access specifier, the compiler does not produce an error, instead it uses a default access mode based on the type of class. In C++, the default inheritance for a class is private. This means class Derived : Base { }; is valid and treated as private inheritance. Therefore, option (c) is also a correct syntax.
Q: What will be the output of the following C++ code?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long factorial(long a)
{
if(a>1)
return(a*factorial(a+1));
else
return(1);
}
int main()
{
long num=3;
cout<<num<<”!=”<<factorial(num);
return 0;
}
6
24
Segmentation fault
None of the above
[ Option C ]
Normally, factorial of n is calculated as n*factorial(n-1). Here, factorial(a+1) increases a instead of decreasing it, so the function never reaches the base case (a<=1). This causes infinite recursion, which eventually overflows the stack.
When the program runs, it will produce a runtime error called a segmentation fault, because the system runs out of memory due to too many recursive calls.
Q: Machine language is
Machine Dependent
Difficult to program
Error prone
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
Machine language is the lowest-level language consisting of binary instructions. It is machine dependent, meaning programs written for one type of machine cannot run on another without modification.
It is also difficult to program because it uses only 0s and 1s, making it hard for humans to read or write. Additionally, due to its complexity, it is highly error-prone.
Q: The range of the numbers that can be represented in 8-bit using 2’s complement representation is
-128 to +128
-127 to +127
-128 to +127
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In 8-bit 2’s complement representation, the Most Significant Bit (MSB) acts as the sign bit, where 0 represents positive numbers and 1 represents negative numbers.
The range of numbers in 2’s complement is calculated as -2n-1 to 2n-1-1, where n is the number of bits.
For 8 bits (n=8):
Q: A compiler is a translating program which
Translates instruction of a high-level language into machine language
Translates entire source program into machine language program
It is not involved in program execution
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
A compiler translates high-level language source code into machine language, processing the entire source program at once to produce an executable machine language program.
Unlike interpreters, compilers are not involved in the execution phase, the compiled program runs independently.
Q: The C++ code which causes abnormal termination/behaviour of a program should be written under _______ block.
catch
throw
try
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
Any unwanted or unexpected event that disturbs the normal flow of the program is called exception.
Any code that might cause an error or abnormal program termination should be placed inside a try block. The try block allows the program to monitor risky statements.
If an exception occurs, control is immediately transferred to the matching catch block. The throw keyword is only used to signal an exception.
Q: Which one of the following techniques is not used in the binary tree?
Randomized traversal
Preorder traversal
Postorder traversal
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
A binary tree is commonly traversed using three standard tree traversal techniques:
These methods are systematic and widely used in all tree-related algorithms.
Q: Which of the following is the prefix form of A+B*C?
+A*BC
ABC+*
+AB*C
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Prefix notation (Polish notation) places the operator before its operands. Operator precedence is handled by position, no parentheses needed.
To convert an infix expression to its prefix form, we first need to understand operator precedence. The given expression is A+B*C. Since multiplication (*) has higher precedence than addition (+), B*C is evaluated first. Converting B*C to prefix gives *BC. Then combining it with A+ gives the full prefix expression +A*BC.
Q: Which of the following is the original creator of the C++ language?
Dennis Ritchie/ Brain Kernighan
Ken Thompson
Bjarne Stroustrup
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
C++ is an object-oriented programming language. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup at AT&T bell laboratories in the Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA in the year 1979. It is an extension to C with number of new features added.
The starting name of C++ was “C with Classes” and in 1983 the name is changed to C++.
The first use of class construct in a programming language occurred in 1962 in the language Simula67.
Q: Which data structure is used to convert infix notation to postfix notation?
Stack
Queue
Tree
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
To convert an infix expression into postfix form, we need a data structure that can temporarily hold operators and help manage precedence and parentheses. A Stack is used for this purpose because it allows operators to be pushed and popped in a LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) manner, which perfectly matches the needs of the conversion process.
Q: In C++, all members of a class are _________ by default.
public
private
protected
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, the member of class whether variables or functions are private by default. This is an important basic concept in Object-Oriented Programming because it helps in data hiding.
struct Student
{
int marks;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.marks=101; // Works fine (public access).
return 0;
}
class Student
{
int marks;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.marks=101; // Compile time error (private access).
return 0;
}
Q: Which data structure is used for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion of elements?
Stack
Queue
Hash Table
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A Hash Table provides very fast searching, insertion, and deletion, generally in O(1) time on average, because it uses a hash function to compute the index of the element.
Hash Table stores data in an associative manner using a hash function to compute an index where the value is stored.
Q: What will be the output of the following?
int a=5;
cout<<”FIRST”<<(a<<2)<<”SECOND”;
FIRST52SECOND
FIRST20SECOND
SECOND25FIRST
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In this code, the left shift operator << is applied to the integer a, which has the value 5. The expression a << 2 shifts the bits of 5 two positions to the left. In binary, 5 is 00000101, and shifting it left by 2 positions gives 00010100, which is 20 in decimal.
Then, the cout statement prints "FIRST", followed by the result of a<<2, and then "SECOND". As a result, the output of the program is FIRST20SECOND.
Q: The postfix expression equivalent of the prefix expression * + ab – cd is
ab + cd - *
abcd + - *
ab + cd * -
None of the above
[ Option A ]
To convert prefix notation expression into postfix form then the following mechanism is used:
Given infix notation expression : * + a b - c d
| SYMBOL | ACTION | STACK STATUS |
|---|---|---|
| d | Operand, push it onto stack. | d |
| c | Operand, push it onto stack. | d, c |
| - | Operator, pop c, d and form cd-. Push result back onto stack. | cd- |
| b | Operand, push it onto stack. | cd-, b |
| a | Operand, push it onto stack. | cd-, b, a |
| + | Operator, pop a, b and form ab+. Push result back onto stack. | cd-, ab+ |
| * | Operator, pop ab+, cd- and form ab+ cd- *. Push result back onto stack. | ab+ cd- * |
The postfix notation expression : ab+ cd- *
Q: A computer program that converts a high-level language program into an equivalent machine language program is called
Assembler
Compiler
Loader
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
A high-level language like C, C++, Java is human-readable. A compiler is a special program that translates this high-level source code into an equivalent machine language program that the CPU can execute.
| Translator | Description | Translation Method | Example Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compiler | Converts entire program from high-level languages to machine code at once. | Whole program translated before execution. | C, C++, Java |
| Interpreter | Converts and executes program one line at a time from high-level language. | Line-by-line translation and execution. | Python, JavaScript, Perl |
| Assembler | Converts assembly language (low-level) to machine code. | One-to-one mnemonic to machine code translation. | x86 Assembly, ARM Assembly |
Q: Which of the following is a pillar of OOP?
Inheritance
Encapsulation
Abstraction
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is based on several core principles, often called the pillars of OOP.
Encapsulation: Combining data and functions into a single unit (class) and restricting direct access to some of the object’s components.
Inheritance: Creating a new class from an existing class to reuse code and extend functionality.
Abstraction: Hiding the complex implementation details and showing only the essential features to the user.
Polymorphism: Allowing objects to behave differently based on their data type or class.
Q: Which one of the following is the correct definition of “is_array();” function in C++?
It checks that the specified variable is of the array or not
It checks that the specified array is of single dimension or not
It checks that the specified array is of multi-dimension or not
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
In C++, is_array<T>::value is a type trait provided in the <type_traits> header. Its purpose is only to determine whether the given type T is an array type or not.
It does NOT check whether an array is 1D or multi-dimensional. It only checks “Is this type an array?”
Q: Which of the following correctly declares an array in C++?
array{10};
int array;
int array[10];
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
An array in C++ is a collection of similar type (homogeneous) items a single variable, stored in unique and successive (contiguous) memory location. An array items are accessed by index (starting from 0). To declare an array, specify the data type, array name, and size inside square brackets [].
Q: A computer program consists of
System flowchart
Program flowchart
Algorithms written in computer language
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A computer program is a set of instructions written in a computer language. These instructions are usually based on an algorithm, which is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem.
Q: What is the difference between delete and delete[] in C++?
delete is syntactically correct but delete[] is wrong and hence will give an error if used in any case
delete is used to delete normal object whereas delete[] is used to delete pointer objects
delete is used to delete single object whereas delete[] is used to delete multiple (array/pointer of) objects
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, delete and delete[] are used to free dynamically allocated memory, but they serve different purposes.
The delete keyword is used when a single object has been allocated using new. On the other hand, delete[] is used when an array of objects has been allocated using new[].
Q: How many select lines are required for an 8 to 1 multiplexer?
2
3
4
None of the above
[ Option B ]
An 8-to-1 multiplexer selects one input out of 8 possible inputs. To uniquely select any one of these 8 inputs, we need enough select lines to represent all combinations. The number of select lines (n) required is determined using the formula 2n=8. Solving this gives n=3.
Q: Digital circuit can be made by the repeated use of the _________.
NAND gate
NOR gate
AND gate
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
In digital electronics, a Universal Gate is a gate that can be used to build any digital circuit. Both NAND and NOR gates are considered universal gates. This means that by repeatedly using only NAND gates, we can construct AND, OR, NOT, XOR, XNOR and any other logic circuit. Similarly, by repeatedly using only NOR gates, we can implement all other logic functions as well.
Q: Which of the following statements is completely true?
I. In an object-oriented programming language, all the function calls are resolved at compile-time.
II. In a procedure programming language, all the function class are resolved at compile-time.
Only II
Only I
Both I and II
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
In procedural programming languages, all function calls are typically resolved at compile-time, because the functions are fixed and there is no concept of dynamic binding or late binding.
In object-oriented programming languages, not all function calls are resolved at compile-time. Functions that are declared as virtual are resolved at run-time using dynamic binding to support polymorphism. Only non-virtual functions are resolved at compile-time.
Q: The Boolean expression A+BC equals
(A’+B)(A’+C)
(A+B)(A’+C)
(A+B)(A+C)
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
Apply distributive law.
Q: In a half-adder circuit, what are the outputs?
Sum and Carry
Difference and Borrow
Sum and Difference
None of the above
[ Option A ]
A half-adder is a basic digital circuit used to add two single-bit binary numbers. It produces two outputs:
Q: Inheritance in OOP allows a class to:
Inherit properties and behavior from another class.
Create instances of another class.
Override methods of another class.
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Inheritance allows a class to inherit properties and behavior from another class, enabling code reuse through the "is-a" relationship.
Q: Which of the following highly uses the concept of an array?
Binary Search Tree
Scheduling of Processes
Spatial Locality
None of the above
[ Option C ]
Spatial Locality is a principle of memory access that states if a memory location is accessed, nearby memory locations are likely to be accessed soon. Since arrays store data in contiguous memory locations, accessing elements sequentially benefits heavily from spatial locality. Thus, arrays highly utilize this concept.
Q: The Boolean expression x+x’y equals
x+y
x+xy
y+yx
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Given Boolean Expression:
x+x’y
To simplify the expression, we apply Boolean algebra rules:
(x+x’) (x+y) Apply Distributive Law.
(1)(x + y) Because x+x’=1
x+y Because A.1=A
So, x+x’y = x+y
Q: Pick the incorrect statement about inline function in C++.
They save overhead of a return call from a function.
They are generally very large and complicated function.
These functions are inserted/substituted at the point of call.
More than one of the above.
[ Option B ]
Inline functions in C++ are meant to improve performance by avoiding the overhead of a function call. Instead of jumping to a function and returning back, the compiler substitutes the function’s code directly at the place where it is called.
This helps save time, especially for small and frequently used functions. However, inline functions are not supposed to be large or complex.
Q: What is another name for the circular queue among the following options?
Rectangle buffer
Square buffer
Ring buffer
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In a normal Queue, we can insert elements until queue becomes full. But once queue becomes full, we cannot insert the next element even if there is a space in front of queue.
A Circular Queue is a type of queue in which the last position is connected back to the first position, forming a circle. This allows efficient use of memory by reusing empty spaces when elements are deleted.
Another common name for a circular queue is a Ring Buffer, because conceptually the storage forms a ring where the front and rear wrap around.
If we want to insert new element in circular queue using REAR end, then the value of REAR can be calculated as: REAR=(REAR+1)%CAPACITY
Similarly, when we want to delete existing element from the circular queue using FRONT end, then the value of FRONT can be calculated as: FRONT=(FRONT+1)%CAPACITY
Q: A queue has configuration a, b, c, d. if you want to get the configuration d, c, b, a, you need a minimum of ___________.
2 deletions and 3 additions
3 deletions and 3 additions
4 deletions and 4 additions
None of the above
[ Option B ]
To reverse a queue from configuration [a, b, c, d] to [d, c, b, a] using only queue operations, the minimum required is 3 deletions and 3 additions.
| STEP | OPERATION | DEQUEUED ELEMENT | ENQUEUED ELEMENT | QUEUE STATUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initially | — | — | — | [a,b,c,d] |
| 1 | Dequeue | a | — | [b,c,d] |
| 2 | Dequeue | b | — | [c,d] |
| 3 | Dequeue | c | — | [d] |
| 4 | Enqueue | — | c | [d,c] |
| 5 | Enqueue | — | b | [d,c,b] |
| 6 | Enqueue | — | a | [d,c,b,a] |
Q: What will be the output of the following program fragment?
int i=10;
void main()
{
int i=20;
{
int i=30;
printf(“%d,%d”,i,::i);
}
}
30, 10
30, 20
20, 30
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In C++, variables declared in inner scopes (blocks, functions) hide outer scope variables with the same name. The scope resolution operator :: accesses the global variable from any nested scope. In statement printf(“%d,%d”,i,::i);
Q: The number of access specifiers in class of C++ is
2
3
4
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, access specifiers are keywords used inside a class to control how the members (data and functions) can be accessed from outside the class. They help in implementing the OOP concept called Data Hiding.
C++ PROVIDES THREE ACCESS SPECIFIERS:
| ACCESS SPECIFIER | ACCESSIBILITY |
|---|---|
| public | Fully accessible, from anywhere in the program. |
| private | Most restricted, only inside the same class. |
| protected | Limited access, inside the class and its derived classes. |
| Access Specifier | Same Class | Derived Class | Outside Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| public | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| private | Yes | No | No |
| protected | Yes | Yes | No |
Q: Derive the Boolean expression for the logic circuit shown below:
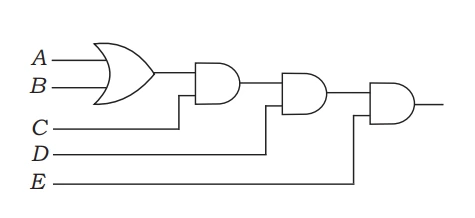
C(A+B)DE
[C(A+B)D+E’]
[[C(A+B)D]E’]
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Q: Which shortcut key is used to compile and run the program in C++?
Alt+F9
Alt+F5
Ctrl+F9
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In the traditional Turbo C++ environment, two different shortcut keys are used:
Q: Which of the following options is not true about the binary search tree?
The value of the left child should be less than the root node.
The value of the right child should be greater than the root node.
The left and right subtrees should also be a binary search tree.
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree where nodes follow a strict ordering rule for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion. Each node has at most two children.
BST Rule:
Q: Which of the following statements is true about the new and malloc?
I. The ‘new’ is a type of operator while ‘malloc’ is a kind of function.
II. The ‘new’ invokes a constructor, whereas ‘malloc’ does not invoke the constructor.
III. The ‘malloc’ returns void pointer and also needed to typecast whereas ‘new’ returns required pointer.
Only I
Only I and II
I, II and III
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, new and malloc are both used for dynamic memory allocation, but they behave differently:
The new is an operator, while malloc is a function. This means new is handled by the compiler, whereas malloc is a library function from C. The statement (I) is true.
The new invokes the constructor for object initialization, while malloc only allocates raw memory and does not call any constructor. The statement (II) is true.
The malloc returns a void pointer, so it often needs typecasting in C++, whereas new automatically returns a pointer of the required type. The statement (III) is true.
| Feature | new | malloc() |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Operator. | Function. |
| Constructor | Called. | Not called. |
| Return Type | T* | void* |
Q: What is the postfix expression for the corresponding infix expression?
a+b*c+(d*e)
abc*+de*+
abc+*de*+
a+bc*de+*
None of the above
[ Option A ]
To convert an infix expression to postfix, we must remember the basic rule of operator precedence and associativity. The operator * and / has higher precedence than + and -.
Infix to postfix conversion for a + b * c + ( d * e ) using a stack, and display the stack state after every step.
| READ SYMBOL | ACTION | STACK (BOTTOM TO TOP) | POSTFIX (P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | Operand. Append to output. | (Empty) | P : a |
| + | Push + onto Stack. | + | P : a |
| b | Operand. Append to output. | + | P : ab |
| * | * has higher precedence than top +. So, push * onto Stack. | + , * | P : ab |
| c | Operand. Append to output. | + , * | P : abc |
| + | Pop while top has ≥ precedence than read operator. Finally pushed read operator + onto stack. | + | P : abc*+ |
| ( | Push onto Stack. | + , ( | P : abc*+ |
| d | Operand. Append to output. | + , ( | P : abc*+d |
| * | Push * onto Stack because stack top is (. | + , ( , * | P : abc*+d |
| e | Operand. Append to output. | + , ( , * | P : abc*+de |
| ) | Pop until ( is not encountered then ignore both ( and ). | + | P : abc*+de* |
| End. | Pop remaining operators. | (Empty) | P : abc*+de*+ |
Q: Among the following, which statement is correct about the modularity?
Modularity means hiding the parts of the program.
Modularity refers to dividing a program into subsequent small modules or independent parts.
It refers to overloading the program’s part.
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Modularity in programming is the concept of dividing a large program into smaller, independent, and manageable modules. Each module is designed to perform a specific task and can be developed, tested, and maintained separately. This makes the program easier to understand, debug, and reuse.
Q: Which of the following logic gates is called universal gate?
AND
OR
NAND
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
The gate through this we can design or construct any type of digital circuit without using any other gate is called universal gate. Basically, these are of two types:
Q: How can one implement the compile-time polymorphism in the C++ programming language?
By using the template
By using the concepts of inheritance by using both the virtual functions and inheritance
More than one of the above
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In C++, compile-time polymorphism is achieved when the function or class behavior is determined at compile time. This can be done using:
Function Overloading: Multiple functions with the same name but different parameters.
Operator Overloading: Redefining operators for user-defined types.
Templates: Allow writing generic functions or classes that work with any data type.
Q: Which one of the following is not the application of the stack data structure?
Asynchronous data transfer
String Reversal
Backtracking
None of the above
[ Option A ]
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle, meaning the last element inserted is the first one to be removed. Some applications of stacks are:
Q: Which of the following statements is correct about the C++ programming language?
In C++, both the static and dynamic types checking are allowed.
In C++, member function are allowed to be of the type const.
In C++, dynamic checking is allowed.
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
C++ primarily uses static type checking (at compile time) for variables and functions, catching most errors early. It also supports dynamic type checking at runtime via RTTI (Run-Time Type Information) features like dynamic_cast and typeid, allowing safe polymorphic casts.
Additionally, C++ allows const member functions, which promise not to modify class data and can be called on const objects.
Q: Queue data structure uses
FIFO
LIFO
LILO
None of the above
[ Option A ]
A queue is a linear data structure that manages elements in a specific order, like people waiting in line at a ticket counter, the first to arrive is served first. A queue follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle.
Q: Which one of the following is the overflow condition if linear queue is implemented using an array with a size MAX_SIZE?
rear=MAX_SIZE-1
rear=MAX_SIZE
rear=front+1
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In a linear queue implemented using an array, overflow occurs when the rear index reaches the last valid index of the array. Since array indexing starts from 0, the last index is MAX_SIZE−1. Once rear becomes MAX_SIZE−1, no more elements can be inserted, even if elements at the front have been dequeued.
Q: Which data structure is mainly used for implementing the recursive algorithm?
Queue
Stack
Binary tree
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Recursion is a technique where a function calls itself to solve smaller versions of the same problem until reaching a simple base case that stops the calls.
When a function calls itself, the computer must remember the current state of the function before jumping to the next call. To manage these multiple pending function calls, the system uses a stack.
Each time a function is called, a stack frame is pushed onto the stack, and when the function returns, the stack frame is popped.
Q: In the deque implementation, using singly linked list, what would be the time complexity of deleting an element from the rear end?
O(1)
O(N log N)
O(N)
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In a deque implemented using a singly linked list, deletion from the rear end is inefficient. Since the list is singly linked, you do not have a direct pointer to the previous node. To delete the last node, you must traverse the entire list from the start or head to find the second-last node. This traversal takes linear time, i.e., O(N).
Q: The expression Y=AB+BC+AC show the ____________ operations.
EX-OR
SOP
POS
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
The given Boolean expression is Y=AB+BC+AC. Here, each term (AB, BC, AC) is a product term (logical AND). These product terms are then summed together (logical OR). This format of “logical sum of several product terms” is known as Sum of Products (SOP).
Q: Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is not possible to combine two or more files opening mode in open() method.
2. It is possible to combine two or more files opening mode in open() method.
3. ios::in and ios::out are input and output file opening modes respectively.
1, 3
2, 3
3 only
1 only
[ Option B ]
In C++, when working with files, the open() method of file streams allows you to specify the mode in which the file should be opened.
Q: The dual of the Boolean expression is obtained by
Interchanging all 0s and 1s
Interchanging all 0s and 1s, all + and ‘.’ Signs
Interchanging all 0s and 1s, all + and ‘.’ Signs and complementing all the variables
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Principle of Duality says, every algebraic expression remains valid if you interchange:
In simple words, for every Boolean law or expression, there exists a dual expression that is also valid. E.g.:
Q: Which of the following refers to the wrapping of data and its functionality into a single individual entity?
Modularity
Abstraction
Encapsulation
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In object-oriented programming, encapsulation refers to the wrapping of data (variables) and functions (methods) into a single unit, usually a class. This concept ensures that the internal representation of an object is hidden from the outside, and access to the data is only allowed through public methods.
Q: What is the use of ios::trunc mode?
To open a file in input mode
To open a file in output mode
To truncate an existing file to zero
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, file streams use modes to control how files are opened and accessed. The ios::trunc is a file mode used with output streams. Its purpose is to truncate an existing file, which means it deletes all the current content of the file and makes its size zero before writing new data.
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ofstream file("myfile.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
file<<"New Content Added.";
file.close();
return 0;
}
Q: Which of the following constructors is provided by the C++ compiler if not defined in a class?
Copy constructor
Default constructor
Parameterized constructor
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, if a class does not explicitly define a constructor, the compiler automatically provides a default constructor. A default constructor is a constructor that takes no arguments. It does not initialize members to specific values unless explicitly coded.
Q: Group of instructions that directs a computer is called
Memory
Storage
Program
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A computer program is a set of instructions that tells the computer exactly what tasks to perform and in what order.
Q: Which of the following statements is true about Big-O notation?
It represents the lower bound of an algorithm’s runtime.
It represents the upper bound of an algorithm’s runtime.
It represents the average runtime of an algorithm.
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Big-O notation is used to describe how fast an algorithm grows in terms of its input size (n). It helps us understand the worst-case (upper bound) performance of an algorithm.
Q: Which of the following is correct for digital circuits?
They use analog signals for communication
They process information using continuous voltage levels
They are not suitable for high speed operations
None of the above
[ Option D ]
Digital circuits work with discrete (binary) voltage levels, usually represented as 0 (Low) and 1 (High). They do not use analog or continuous signals for processing, instead, they rely on step-like voltage changes.
The digital circuits are actually highly suitable for high-speed operations, that’s is why they are used in modern computers, microprocessors, and communication systems.
Q: Which language does a browser use to display information from the World Wide Web?
Machine Code
Assembly Language
C++
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A web browser shows the information from the World Wide Web by reading and interpreting code that websites are written in, like HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript. The main part of the browser that does this is called the Rendering Engine.
Machine Code and Assembly Language are low-level languages used by hardware and system programmers, not by browsers. C++ is a high-level programming language used to build software applications.
Q: #include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=5,j=10,k=15;
printf(”%d ”,sizeof(k/=i+j));
printf(”%d”,k);
return 0;
}
Assume size of an integer as 4 bytes. What is the output of above program?
2 1
4 1
4 15
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
The first printf statement uses sizeof(k/=i+j), where k/=i+j is an expression of type int. The sizeof operator determines the size of the operands type at compile time without evaluating the expression itself, so no side effect occurs, no assignment modifies k, which remains 15.
Given that the size of an int is 4 bytes, the first printf outputs 4. The second printf then outputs the unchanged value of k, which is 15. Thus, the complete output is 4 15.
Q: Which of the following data structures stores elements in a non-linear relationship?
Stack
Queue
Array
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A Data Structure is a way of storing and organizing data in computer system so that it can be used efficiently. Different data structures are used depending on what operations we need. Choosing the right data structure makes programs faster and easier to manage.
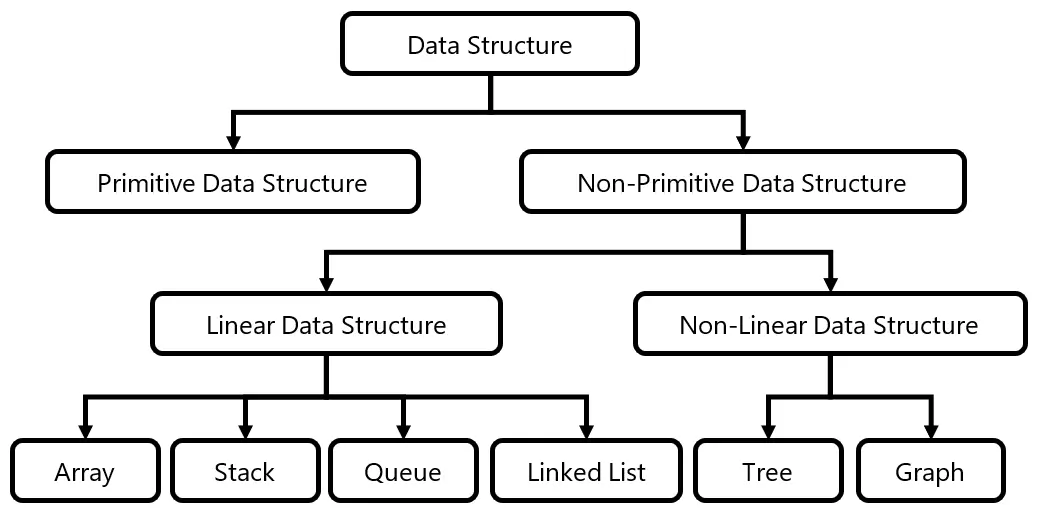
In a Linear data structure, elements are arranged one after another in a sequence. Each element has a unique predecessor and unique successor, except the first and last elements. Array, Stack, Queue, Linked List are example of linear data structure.
In a Non-Linear data structure, elements are not arranged sequentially. An element can connect to multiple elements, forming structures like hierarchical or networks. Tree and Graph are example of non-linear data structure.
Q: To display time in railway stations which digital circuit is used?
Seven-segment decoder
Eight-segment encoder
8 : 3 multiplexer
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Railway stations typically use digital clocks that display time numerically. These clocks use seven-segment displays, where each digit (0–9) is formed by lighting specific segments.
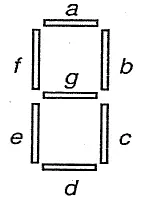
The decoder accepts four BCD inputs A, B, C and D and seven outputs a, b, c, d, e, f and g to display any decimal number from 0 to 9.
To convert BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal) input into signals that light up the correct segments, a seven-segment decoder is used. This decoder determines which segments should glow to represent each digit.
Q: Which of the following is a divide-and-conquer algorithm?
Merge sort
Heap sort
Bubble sort
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
Merge Sort is a classic example of the divide-and-conquer algorithm. It works by dividing the array into two halves, recursively sorting each half, and then combining or merging the sorted halves.
LIST OF PROBLEMS THAT SOLVED USING DIVIDE AND CONQUER APPROACH:
| PROBLEM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Merge Sort | Divides array into halves, sorts them recursively, and merges them. |
| Quick Sort | Divides array using a pivot, recursively sorts left and right subarrays. |
| Binary Search | Recursively divides sorted array to locate the target element. |
| Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication | Divides matrices into submatrices to speed up multiplication. |
| Closest Pair of Points | Divides points into halves and solves recursively for minimum distance. |
| Count Inversions in Array | Counts pair inversions using merge-sort style division. |
| Tower of Hanoi | Recursively divides problem into smaller subproblems. |
Q: An OR gate has 4 inputs. The number of words in truth table will be ________.
4
8
16
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A truth table shows all possible input combinations for a logic gate. If a gate has n inputs, the number of possible combinations is given by the formula 2ⁿ. For an OR gate with 4 inputs, the number of rows in the truth table will be 24=16. This means there are 16 different input combinations, each producing an output.
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | Y=A+B+C+D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q: Which of the following gives the nth element of the Array?
array[n];
array[n-1];
array[n+1];
None of the above
[ Option B ]
In most programming languages, arrays are zero-indexed, meaning the first element is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on. Therefore, to access the nth element of an array, you need to use array[n-1].
Q: Merge sort is an example of which algorithm design paradigm?
Greedy
Divide and Conquer
Dynamic Programming
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Merge Sort is an example of the Divide and Conquer algorithm design paradigm. It works by repeatedly dividing the array into two halves, conquering each half by sorting them, and then combining the two sorted halves into one sorted array.
Q: Which of the following statements is correct about the class?
An object is an instance of its class.
A class is an instance of its object.
An object is the instance of the data type of that class.
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
A class is a blueprint, and an object is a real-world instance created using that blueprint. When you create an object of a class, you are creating an instance of that class, which holds the actual data.
Q: Which of the following is used to define the members of a class externally in C++?
@
::
#
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, class members functions can be declared inside the class but defined outside using the scope resolution operator ::. This operator tells the compiler that the function you are defining belongs to a specific class.
Syntax:
Return_Type Class_Name :: Function_Name (Arguments);
class MyClass
{
public:
void myFunction(); //Declaration inside class.
};
void MyClass::myFunction() //Definition outside class.
{
// Function body.
}
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class first
{
int a,b;
public:
void get();
void show();
};
class second
{
int x,y;
public:
void input()
{
x=5; y=10;
}
void show();
};
void first::get()
{
cout<<"Enter The Two Number: ";
cin>>a>>b;
}
void first::show()
{
cout<<"\nEntered Number Is\n";
cout<<a<<endl<<b;
}
void second::show()
{
cout<<"\nIn Class Second\n";
cout<<x<<endl<<y;
}
void main()
{
first f;
f.get();
f.show();
second s;
s.input();
s.show();
}
Q: How many distinct binary search trees can be created out of 4 distinct keys?
8
24
14
None of the above
[ Option C ]
When number of node N is given then how many total numbers of possible binary trees can be drawn. This can be calculated using Catalan number. Cn=(2n)!/(n+1)!n!, where, n is number of nodes.
When n=4.
C4 = (2*4)!/(4+1)!*4!
C4 = 8!/5!*4!
C4 = 8*7*6*5!/5!*4*3*2*1
C4 = 336/24
C4 = 14
Q: What will happen if the following C++ statement is compiled and executed?
int *ptr=NULL;
delete ptr;
The program is not semantically correct
The program is compiled and executed successfully
The program gives a compile-time error
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
In this program, the pointer ptr is initialized to NULL, which means it points to nothing. When we use delete ptr;. In C++, deleting a NULL pointer is safe. If the pointer is NULL, delete does nothing and does not cause any error. Therefore, the program is semantically correct, compiles without any issues, and executes successfully without crashing.
Q: A computer program that translate high-level language program into machine language program statement-by-statement is called
Compiler
Loader
Interpreter
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
An interpreter translates a high-level language program into machine language statement-by-statement. This means it reads one line, converts it, and executes it immediately before moving to the next line.
Q: Boolean algebra can be used
for designing the digital computers
in building logic symbols
in circuit theory
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
Boolean algebra is the mathematical foundation of digital electronics. It deals with binary variables and logical operations, which makes it very useful in several areas.
Q: The simplified form of the Boolean expression (X+Y+XY)(X+Z) is
XY+YZ
X+YZ
XZ+Y
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Given Boolean Expression:
=(X+Y+XY)(X+Z)
=(Y+X(1+Y))(X+Z)
=(Y+X.1)(X+Z)
=(Y+X)(X+Z)
=XY+YZ+XX+XZ
=X+XY+XZ+YZ
=X(1+Y+Z)+YZ
=X.1+YZ
=X+YZ
Q: In two-valued Boolean algebra, the maximum number of Boolean functions for two variables will be
8
12
16
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In two-valued Boolean algebra, each variable can take only two values: 0 or 1. When we have two Boolean variables, there are four possible input combinations, (0,0), (0,1), (1,0) and (1,1).
For each of these combinations, a Boolean function can output either 0 or 1. Therefore, the total number of possible Boolean functions is calculated by raising 2 to the power of the number of input combinations. Since there are four combinations, the number of functions becomes 24=16.
Q: A set of libraries that provides programmatically access to some kind of graphics 2D function is
Graphics Package
Formatting Package
Animation Package
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
A graphics package is a set of libraries that provides programming access to 2D graphics functions such as drawing lines, circles, shapes, displaying images, and creating simple visual elements. These libraries allow programmers to write code that can display graphics on the screen.
Graphics Package is the right term for a set of libraries offering programmatic 2D graphics functions.
Q: Which of the following features must be supported by any programming language to become a pure object-oriented programming language?
Encapsulation
Inheritance
Polymorphism
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
A pure Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language is one that fully supports the key principles of object-oriented programming called PIE (Polymorphism Inheritance Encapsulation) principle.
Encapsulation: Wrapping data and functions together in a single unit (class) and restricting direct access to some of the components.
Inheritance: Ability of a class to acquire properties and behaviors from another class.
Polymorphism: Ability to take multiple forms, functions or objects to take multiple forms, enabling dynamic behavior.
Q: Which one of the following is not the application of the queue data structure?
Data is transferred asynchronously
Resource is shared between various system
Balancing of symbols
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, meaning the first element added is the first one to be removed. There are several applications of queue data structure.
Q: Which of the following is the advantage of the array data structure?
Elements of mixed data types can be stored
Easier to access the elements in an array
Index of the first element starts from 1
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Arrays are a data structure used to store multiple values of the homogeneous type (same data type) under single name in continuous memory locations. Because of this continuous storage, arrays provide a major advantage, the elements can be accessed very quickly using their index.
Q: Which one of the following techniques is not used in the binary tree?
Preorder traversal
Inorder traversal
Postorder traversal
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two children. To process or visit all nodes of a binary tree, several traversal techniques are used:
All three are standard and commonly used techniques for binary tree traversal.
Q: What will be the output of the following C++ code?
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char s1[6]=”Hello”;
char s2[6]=”World”;
char s3[12]=s1+” “+s2;
cout<<s3;
return 0;
}
Hello
World
Error
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, you cannot directly add C-style character arrays using the + operator. In the given code, s1 and s2 are character arrays, and the statement char s3[12] = s1 + " " + s2; is invalid. C++ does not allow concatenation of arrays or char* using +.
Q: What is the result of the operation 1010 AND 1100 in binary?
1000
1110
100
None of the above
[ Option A ]
The AND operation compares each corresponding bit of two binary numbers. The output is 1 only when both bits are 1, otherwise it is 0. 1010 AND 1100 = 1000
Q: How do structures and classes in C++ differ?
In structures, members are private by default whereas in classes, they are public by default
In structures, members are public by default whereas in classes, they are private by default
Structures cannot have private members whereas classes can have
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, a structure is similar to a class, but one key difference lies in the default access specifier. When you create a structure and define variables or functions inside it, those members are public by default.
While a class keeps its members private by default, meaning they cannot be accessed directly from outside unless specified.
struct Student
{
int marks;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.marks=101; // Works fine (public access).
return 0;
}
class Student
{
int marks;
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.marks=101; // Compile time error (private access).
return 0;
}
Q: When does a negative level triggered flip-flop in Digital Electronics changes its state?
When the clock is Negative
When the clock is Positive
When the inputs are all zero
None of the above
[ Option A ]
A negative level triggered flip-flop is a type of flip-flop that changes its state only when the clock signal is at the low level (0). In other words, when the clock remains at a negative (low) voltage level, the flip-flop becomes active and responds to inputs.
Q: What is the time complexity of an infix to postfix conversion algorithm?
O(N log N)
O(N)
O(N2)
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The time complexity of converting an infix expression to a postfix expression is O(N). This is because the algorithm scans the infix expression one character at a time from left to right.
For each character (operands, operators, parentheses), the algorithm may push it onto a stack or pop it from the stack. Each element is pushed and popped at most once, so the total number of operations grows directly with the length of the expression.
Since no nested loops or repeated scans are used, the overall work done is proportional to N, where N is the number of characters in the expression. Therefore, the time complexity is O(N).
| ALGORITHM | TIME COMPLEXITY |
|---|---|
| Infix to Postfix Conversion. | O(N) |
| Infix to Prefix Conversion. | O(N) |
| Postfix Expression Evaluation. | O(N) |
| Prefix Expression Evaluation. | O(N) |
| Balanced Parentheses Checking. | O(N) |
| String Reversal Using Stack. | O(N) |
Q: What is the access specifier used to make members of a class accessible only within the same package?
private
public
package-private
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In Java, access specifiers control the visibility of class members. To make members accessible only within the same package, we use package-private (default) access.
Q: Which of the following determines the need for the circular queue?
Access the queue using priority
Avoid wastage of memory
Follow the FIFO principle
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
A Circular Queue is mainly used to avoid wastage of memory that occurs in a simple linear queue when the front moves forward after deletions but empty spaces at the beginning cannot be reused.
Q: Which keyword is used in Java to implement inheritance?
extends
inherits
implements
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In Java, extends keyword is used for class inheritance where a subclass inherits properties and methods from a superclass. Syntax for inheritance in Java is class Child extends Parent {}.
Q: The Boolean expression AB+AB’+A’C+AC is independent of Boolean variable
A
B
C
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Given Boolean Expression:
=AB+AB’+A’C+AC
=A(B+B’)+C(A’+A)
=A.1+C.1
=A+C
The simplified expression A+C contains variables A and C, but does not contain B. Therefore, the Boolean expression is independent of variable B.
Q: A linear data structure in which insertion and deletion operations can be performed from both the ends is
Queue
Circular Queue
Deque
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A linear data structure that allows insertion and deletion from both the front and the rear is called a Deque (Double-Ended Queue).
A deque is special because it allows:
Q: Which of the following can be used to create an abstract class in the C++ programming language?
By using the pure virtual function in the class
By declaring a virtual function in the base class
By declaring the virtual keyword afterward the class declaration
None of the above
[ Option A ]
In C++, an abstract class is defined as a class that contains at least one pure virtual function. A pure virtual function is a virtual function declared by assigning it to zero (= 0) in its declaration, and it has no definition in the abstract class itself.
This forces derived classes to provide an implementation for this function, otherwise, they also become abstract. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated directly, they serve as blueprints for other subclasses.
class Person
{
public:
virtual void setName() = 0; // Pure Virtual Function.
};
Q: When a key is pressed on keyboard, which standard is used for converting the keystroke into the corresponding bits?
ANSI
ASCII
EBCDIC
None of the above
[ Option B ]
When you press a key on a standard computer keyboard, the key you press is converted into a unique binary code so that the computer can understand it. The ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) standard is the one most used for this purpose.
For example:
Q: How do structures and classes in C++ differ?
Structure by default hide every member whereas classes do not
In structure, members are public by default, whereas, in classes, they are private by default
Structures cannot have private members, whereas classes can have
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
In C++, both structures (struct) and classes (class) are used to group data and functions together. They are almost identical in functionality, but the main difference is in default access specifiers.
Structures (struct): By default, all members are public. This means they can be accessed directly from outside the structure.
Classes (class): By default, all members are private. This means they cannot be accessed directly from outside the class unless specified as public.
Q: Which of the following is NOT a graph traversal algorithm?
Greedy
Divide and Conquer
Dynamic Programming
None of the above
[ Option D ]
Graph traversal algorithms are specifically methods used to visit all nodes of a graph, such as:
Q: Stack data structure uses
FIFO
LIFO
LILO
None of the above
[ Option B ]
A stack works on the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. This means the element inserted last will be removed first, just like stacking plates, the last plate placed on top is the first one you take off.
Q: The order of the binary search algorithm is __________.
N
N log N
N2
None of the above
[ Option D ]
Binary Search is an efficient searching algorithm used only on sorted lists or arrays. The key idea behind binary search is that instead of checking every element one by one, it repeatedly divides the search range into two halves. At each step, it compares the target value with the middle element.
If the target is equal to the middle value, the search ends. If the target is smaller, the search continues in the left half, and if it is larger, the search continues in the right half.
Because the size of the search interval becomes half at every step, the time complexity is O(log N).
Q: The necessary condition to be checked before deletion from the queue is
Overflow
Underflow
Rear value
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Before deleting an element from a queue, we must ensure that the queue is not empty. If the queue is empty, deletion is not possible, and this condition is called underflow.
Q: Which data structure is the best for implementing a priority queue?
Linked list
Array
Binary heap
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A priority queue works by always removing the element with the highest priority first, not necessarily the first inserted one.
The best data structure for implementing a priority queue is the Binary Heap because this organizes data in such a way that both insertion and deletion of the highest-priority element take only O(log n) time, making it far more efficient and suitable.
Q: In C++, for what purpose the “rank()” is used?
It returns the size of each dimension
It returns the maximum number of elements that can be stored in the array
It returns the dimension of the specified array
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, the rank() function (std::rank<T>() from <type_traits>) is used with arrays to determine the number of dimensions of the array, not the size of each dimension or the total number of elements. For example, a one-dimensional array has a rank of 1, a two-dimensional array has a rank of 2, and so on.
This is useful when working with multidimensional arrays to programmatically determine their structure.
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr1[6];
int arr2[2][3];
int arr3[2][3][4];
cout << "Rank (Dimension) of arr1: " << std::rank<decltype(arr1)>::value << endl;
cout << "Rank (Dimension) of arr2: " << std::rank<decltype(arr2)>::value << endl;
cout << "Rank (Dimension) of arr3: " << std::rank<decltype(arr3)>::value << endl;
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
Rank (Dimension) of arr1: 1
Rank (Dimension) of arr2: 2
Rank (Dimension) of arr3: 3Q: The programming language that has the ability to create new data types is called
Overloaded
Encapsulated
Extensible
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
A programming language is called extensible if it allows the programmer to create new data types in addition to the predefined ones. This feature provides flexibility to model real-world entities and improve code reusability. For example, C++ allows users to define classes, structures, and typedef, which are user-defined types.
Q: The Boolean expression x+xy will be equal to
x
y
x+y
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Given Boolean Expression:
=x+xy
=x(1+y)
=x.1
=x
Q: An assembly language is a/an
Low-level programming language
Middle-level programming language
Internet-based programming language
None of the above
[ Option A ]
Assembly language is considered a Low-Level programming language because it is only one step above machine language. It uses mnemonic codes like MOV, ADD, and SUB instead of binary, making it slightly easier for humans to read but still closely tied to the hardware architecture.
Q: Which of the following approaches is used by C++?
Left-right
Top-down
Bottom-up
None of the above
[ Option C ]
C++ uses the bottom-up approach, which is a core philosophy of object-oriented programming. In this approach, programs are built by first creating small, reusable components such as classes and objects, and then combining them to form larger and more complex systems.
| TOP-DOWN APPROACH | BOTTOM-UP APPROACH |
|---|---|
| Breaks the program into major modules first, then divides them into smaller parts. | Builds small components/modules first and combines them to form a complete system. |
| Used mostly in procedural programming. | Used mostly in object-oriented programming. |
| Focus on functions or procedures. | Focus on objects and classes. |
| The main function designed first. | Small reusable modules are designed first. |
| Lower reusability. | Higher reusability. |
Q: Select the true statement for compiler.
The input of the compiler is source program.
It translates the source code into object code as a whole.
The output of the compiler is object code.
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
A compiler is a program that translates a high-level language into machine-readable code.
A source program is the code written by the programmer in a high-level language. The compiler takes this source code and converts it into object code, which is in machine language.
So, all three options (a), (b), and (c) are true for a compiler.
Q: Source code is available to view, modify and redistribute in
Open Source
Licensed
Proprietary
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
Open source software is allow user to view, modify, and redistribute the source code, along with the compiled software. This openness promotes collaboration, transparency, and customization.
In licensed or proprietary software where source code access is restricted, and licensed software which may allow use but not necessarily modification or redistribution of source.
Q: What are the canonical forms of Boolean expressions?
OR and XOR
NOR and XNOR
SOM and POM
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
The canonical forms of Boolean expressions are:
These forms represent Boolean functions in standard forms using all variables in each term.
Note:
Q: The minimum number of NAND gates required to implement Boolean function f=x’y+xy’ is
3
4
6
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The given Boolean function f=x’y+xy’ represents the XOR (Exclusive-OR) operation between variables x and y. It is well known that an XOR function can be implemented using 4 two-input NAND gates.
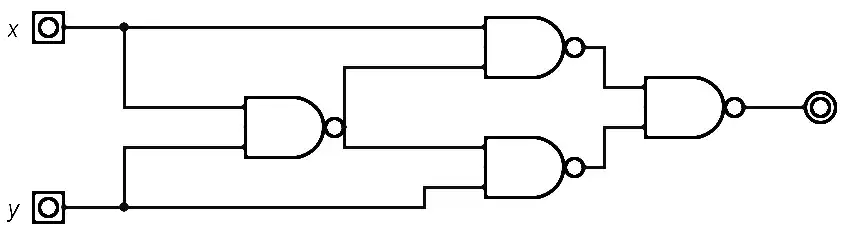
Q: Which one of the following is not the type of queue?
Linear queue
Circular queue
Double-ended queue
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. Over time, several variations of queues have been developed to solve different problems.
TYPES OF QUEUES:
Linear Queue: The simplest type of queue, where elements are inserted at the rear and deleted from the front.
Circular Queue: A variation of the linear queue, where the last position is connected back to the first to form a circle, allowing efficient use of space.
Double-ended Queue (Deque): A queue where insertion and deletion can be done from both ends (front and rear). It supports more flexible operations than simple linear or circular queues.
Q: If x is a Boolean variable, then (((x’)’)’)’ will be
x'
x
x+x’
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Evaluate the expression step by step using the double-negation (complement) rule (x’)’=x.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.