The BCI Paper Solution 2022 by Suraku Academy provides detailed and verified answers for all questions of the Basic Computer Instructor exam. While preparing the solution, Suraku Academy put hard work into delivering clear and thorough explanations for students. This resource helps candidates understand concepts deeply and prepares them confidently for the exam. Check out the verified solutions first, then begin your focused learning journey.
| S.N. | Name of Subjects | No. of Questions Asked |
|---|---|---|
| 01. | Pedagogy | 04 |
| 02. | Mental Ability | 08 |
| 03. | Computer Fundamentals | 10 |
| 04. | Data Processing (Word, PowerPoint, Excel) | 10 |
| 05. | Computer Networks (CN) | 04 |
| 06. | Programming Languages (C, C++, Java, Python) | 10 |
| 07. | Data Structure and Algorithms (DSA) | 08 |
| 08. | Database Management System (DBMS) & Structured Query Language (SQL) | 15 |
| 09. | IOT (Internet of Things) & Its Applications (Internet, Search Engine, HTML, XML, Multimedia & Graphics) | 08 |
| 10. | Operating System (OS) and Computer Organization (CO) | 06 |
| 11. | Network Security | 08 |
| 12. | System Analysis and Design (SAD) | 08 |
| 13. | Digital Electronics and Circuits (DEC) | 01 |
Q: Which is the largest unit of storage among the following?
Terabyte
Kilobyte
Megabyte
Gigabyte
[ Option A ]
Memory storage refers to devices or media used to store data and programs in a computer.
Storage units are used to measure the amount of data in a computer, starting from the smallest unit, a bit, to larger units like Byte, Kilobyte (KB), Megabyte (MB), Gigabyte (GB), and Terabyte (TB).
| Storage Unit | Abbreviation | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Bit | b | Smallest unit of data either 0 or 1 |
| Byte | B | 8 Bits |
| Kilobyte | KB | 1024 Bytes |
| Megabyte | MB | 1024 KB |
| Gigabyte | GB | 1024 MB |
| Terabyte | TB | 1024 GB |
| Petabyte | PB | 1024 TB |
| Exabyte | EB | 1024 PB |
| Zettabyte | ZB | 1024 EB |
| Yottabyte | YB | 1024 ZB |
Q: Assume that p and q are non-zero positive integers, the following program segment will perform—
while(p!=0)
{
if(p>q)
p=p-q;
else
q=q-p;
printf(“%d”,p);
}
Subtract small number from large number
Computer GCD of the given numbers
Computer LCM of the given numbers
The loop will run infinitely
[ Option D ]
The program is trying to reduce the numbers p and q by repeatedly subtracting the smaller one from the bigger one. This looks like the Euclidean method for finding the GCD, but there is a mistake in the loop condition. The loop only checks while(p != 0), so it keeps running as long as p is not zero.
When q becomes zero (which will always happen before p does), the subtraction stops changing the value of p because p = p - 0 will always give the same p. This means the program gets stuck, and the loop keeps running forever without ending.
So, instead of calculating the GCD, this program will go into an infinite loop. The correct way would be to stop when either p or q becomes zero, i.e., use while(p != 0 && q != 0).
Q: If three threads are trying to share a single object at the same time which condition will arise in the scenario?
Time-Lapse
Critical Situation
Race Condition
Recursion
[ Option C ]
A Race Condition occurs when two or more threads or processes try to access and modify the same shared resource (like an object) at the same time without proper synchronization. This leads to unpredictable and incorrect behavior.
For instance, if three threads attempt to share and modify a single object concurrently, and there is no mechanism to control access (like locks or mutex), a race condition occurs causing data corruption or inconsistent results.
Q: Identify the oldest phone hacking technique used by hackers to make free calls?
Spamming
Phreaking
Cracking
Phishing
[ Option B ]
Phreaking is an early phone hacking method from the 1960s and 70s where hackers used special sounds to trick telephone systems. They played a 2600 Hz tone to control the phone switches and make free long-distance calls. Tools called "blue boxes" were made to create these tones, and famous phreakers like John Draper (“Captain Crunch”) used a cereal box whistle that made the same tone.
Q: In decision table left-lower quadrant is called-
Condition Entry
Condition Stub
Action Entry
Action Stub
[ Option D ]
A Decision Table is a tabular method for representing logical relationships between conditions and actions in a system. It is widely used in software testing, system design, and decision-making.
| Quadrant | Position | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Condition Stub | Top-Left (Upper-Left) | Lists the conditions to be tested. |
| Condition Entry | Top-Right (Upper-Right) | Shows possible values for each condition. |
| Action Stub | Bottom-Left (Lower-Left) | Lists all possible actions. |
| Action Entry | Bottom-Right (Lower-Right) | Specifies the actions to take for each condition combination. |
Q: Which of the following is not a valid file extension of an audio file?
.wav
.mp3
.mid
.rar
[ Option D ]
Audio file formats are specialized file types designed to store or manage sound data.
Q: The correct statement regarding WiFi and Wi-Max technology is/are-
(I) WiFi uses radio waves to create wireless connection, WiMax uses spectrum to deliver connection.
(II) WiFi is defined under IEEE 802.11x standards, while WiMax is defined under IEEE 803.16y standards.
(III) WiMax covers comparatively larger area than WiFi.
Only (II)
Only (I) and (II)
Only (I) and (III)
(I), (II) and (III)
[ Option C ]
WiFi and WiMAX are two popular wireless communication technologies, but they differ in coverage and standards. WiFi, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, is mainly used for creating local area wireless networks with coverage typically up to 100 meters.
On the other hand, WiMAX is defined under the IEEE 802.16 standard and is designed for broadband wireless access over much larger distances, covering up to several kilometers.
The IEEE stands for Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. IEEE develops global standards and supports a large community of engineers and scientists worldwide.
Q: Command to open Snipping Tool menu to take a screenshot of only a section of your screen—
Window Key + Ctrl + S
Window Key + Shift + S
Window Key + Alt + X
Ctrl + Shift + K
[ Option B ]
Snipping Tool / Snip & Sketch in Windows allows you to capture screenshots of a specific area, window, or full screen. Pressing Windows Key + Shift + S opens the screen snipping menu, letting you select a rectangular area, freeform area, window, or full screen. After selection, the screenshot is copied to the clipboard, and you can paste it into apps like Paint, Word, or email.
Q: In C, what are the various types of real data type (floating point data type)?
float, long, double
long, double, short int
float, double, long double
short int, double long int, float
[ Option C ]
In C programming, floating point data types are used to represent real numbers, numbers that have fractional parts or decimals points.
| Data Type | Size (Typical) | Precision | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | 4 Bytes | 6-7 Decimal Digits | Single Precision |
| double | 8 Bytes | 15 Decimal Digits | Double Precision |
| long double | 10, 12 or 16 Bytes (Depends on Compiler) | 18 Decimal Digits | Extended Precision |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <float.h>
void main()
{
printf("Suraku Academy\n");
printf("Size of float : %zu Bytes\n", sizeof(float));
printf("Size of double : %zu Bytes\n", sizeof(double));
printf("Size of long double : %zu Bytes\n", sizeof(long double));
printf("Range and Precision:\n");
printf("Float: Min : %e, Max : %e, Precision : %d Digits\n",FLT_MIN, FLT_MAX, FLT_DIG);
printf("Double: Min : %e, Max : %e, Precision : %d Digits\n",DBL_MIN, DBL_MAX, DBL_DIG);
printf("Long Double: Min : %Le, Max : %Le, Precision : %d digits\n",LDBL_MIN, LDBL_MAX, LDBL_DIG);
}
Suraku Academy
Size of float : 4 Bytes
Size of double : 8 Bytes
Size of long double : 16 Bytes
Range and Precision:
Float: Min : 1.175494e-38, Max : 3.402823e+38, Precision : 6 Digits
Double: Min : 2.225074e-308, Max : 1.797693e+308, Precision : 15 Digits
Long Double: Min : 3.362103e-4932, Max : 1.189731e+4932, Precision : 18 digits
Q: Which of the following is not a system software?
Programming Language Translators
Utility Programs
Database Software
Operating System
[ Option C ]
System Software is the type of software that manages computer hardware and provides a platform for running application software. Common examples of system software include the Operating System (OS), utility programs, and language translators such as compilers, interpreters, and assemblers.
Application Software is designed to help users perform specific tasks or solve particular problems. It runs on top of system software and allows users to do activities like creating documents, managing databases, browsing the internet, or editing images. Examples include word processors, spreadsheet software, Database Management Systems (DBMS) software, and web browsers.
Utility Programs are System Software tools that help maintain, manage, and protect a computer. Examples include Antivirus Software for security, Disk Cleanup tools for removing unnecessary files, file compression software like WinRAR (Windows Roshal ARchive) or 7-Zip for reducing file size, backup software for data safety, and disk defragmenters for improving storage performance.
Q: Which of the following statement is/are incorrect with respect to abstract classes?
(i) Subclasses of an abstract class that do not provide an implementation of an abstract method, are also abstract.
(ii) Constructor and static methods cannot be declared in abstract class.
(iii) Sometimes we can create objects directly.
(iv) A method must always be redefined in a subclass of abstract class.
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
[ DELETE ]
The statement (i) is correct because if a subclass does not implement all abstract methods, it must also be declared abstract. Otherwise, there will be compile time error.
abstract class Person {
abstract void setName(); // abstract method
}
// Subclass does not implement setName(), so it must also be abstract
abstract class Student extends Person {
// no setName() defined here
}
// If we try to make Student concrete without implementing setName(), error occurs, Student is not abstract and does not override abstract method setName() in Person
class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Suraku Academy Program");
}
}The statement (ii) is incorrect because abstract classes can have constructors and static methods. The constructors are called when concrete subclasses are instantiated, and static methods do not require object instantiation.
abstract class Person {
Person(){ //Constructor
System.out.println("Person Constructor.");
}
static void staticMethod() { // Static method
System.out.println("Static method in abstract class Person");
}
}
// Subclass does not implement setName(), so it must also be abstract
class Student extends Person {
Student() {
super();
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Suraku Academy Program.");
Person.staticMethod();
Student s1 = new Student();
}
}
Output
Suraku Academy Program.
Static method in abstract class Person
Person Constructor.The statement (iii) is incorrect because we cannot create object of an abstract class directly.
abstract class Person {
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Suraku Academy Program.");
Person p1 = new Person(); //Error: Person is abstract; cannot be instantiated.
}
}The statement (iv) is incorrect because only abstract methods need to be redefined. But an abstract class can also have concrete methods (method with body), and those need not be redefined.
In another aspect, only concrete subclasses (non-abstract class) must implement all abstract methods. An abstract subclass does not have to reimplement inherited abstract methods. Redefinition is only mandatory in a concrete class.
abstract class Person {
abstract void setName();
}
abstract class Student extends Person {
// Does not implement 'setName()', so must remain abstract.
}
class Employee extends Person {
void setName() {
System.out.println("Setting Name.");
}
}We carefully discussed this question and observed that statement (i) is correct, while statements (ii), (iii), and (iv) are incorrect. The question required us to identify the incorrect statements, but none of the provided options matched the correct combination.
Additionally, there were duplicate/confusing options such as (b) (ii) and (iii), and (c) (ii) and (iv). Due to this ambiguity in the answer choices, this question was removed from the final answer key.
Q: Which of the following statement contains an error?
Select * from emp where empid = 10003;
Select empid from emp where empid = 1006;
Select empid from emp;
Select empid where empid = 10009 and last name = ‘GELIER’;
[ Option D ]
The error in this SQL statement occurs because the FROM clause is missing, which is required to specify the table from which data should be retrieved. A correct SELECT query must always include the FROM keyword followed by the table name. Additionally, if a column name contains spaces (for example, last name), it should be enclosed in quotes or brackets to avoid syntax errors.
| Syntax Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table; | Select specific columns from a table. |
| SELECT * FROM table; | Select all columns from a table. |
| SELECT DISTINCT column FROM table; | Select unique or distinct values from a column. |
| SELECT column1, column2 FROM table WHERE condition; | Select with filtering rows based on condition. |
| SELECT column1, COUNT(*) FROM table GROUP BY column1; | Select grouped data with aggregation function. |
| SELECT column1, COUNT(*) FROM table GROUP BY column1 HAVING condition; | Grouped data with filtering on groups. |
| SELECT column1, column2 FROM table ORDER BY column1 ASC | Select specific columns from a table and arrange them either in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order. |
| SELECT column1 INTO new_table FROM old_table; | Create new table by copying selected data from another table. |
| SELECT column1 FROM table1 JOIN table2 ON table1.col = table2.col; | Select data combining rows from two tables with join condition. |
Q: Which of the following is not a first-generation computer?
ENIAC
PDP-11
UNIVAC-I
IBM-701
[ Option B ]
Computer generations are classified based on the technology used in their hardware. Each generation shows significant improvements in speed, size, reliability, and efficiency over the previous one. They also differ in the type of memory, input/output devices, and programming languages used, reflecting the evolution of computing technology over time.
| GENERATION | TECHNOLOGY USED | EXAMPLES | PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES USED |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Generation | Vacuum Tubes | ENIAC, UNIVAC-I, IBM 701, EDVAC, EDSAC, Mark-1 | Machine Language |
| Second Generation | Transistors | IBM 1401, IBM 7090, UNIVAC 1108, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, IBM 1620 | Assembly Language, FORTRAN, COBOL |
| Third Generation | Integrated Circuits (ICs) | PDP-8, PDP-11, IBM 360, Honeywell 6000, IBM 370 | COBOL, FORTRAN, ALGOL |
| Fourth Generation | Microprocessors | Intel 4004, Intel 8086, Intel 80486, IBM PC, Apple II, CRAY-1 | C, C++, BASIC, Pascal |
| Fifth Generation | AI, ULSI Tech, Parallel Processing | IBM Deep Blue, Modern AI Computers, Supercomputers, Quantum Computers | Prolog, Lisp, Python, Java, R, MATLAB, Mercury, Ruby |
Q: Which one of the following is usually used in the process of Wi-Fi hacking?
Aircrack—ng
Wireshark
Norton
All of the above
[ Option A ]
Aircrack-ng is a widely used toolset for Wi-Fi hacking and security testing. It includes tools for capturing network traffic, testing wireless card capabilities, and cracking WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), and WPA2 encryption keys.
It supports various attacks such as deauthentication and replay attacks to capture handshake data needed for cracking passwords. This tool is popular among security professionals and hackers for analyzing and testing Wi-Fi network security.
Wireshark is a powerful packet analyzer useful for inspecting network traffic and can assist in wireless troubleshooting or analysis, but it is not primarily a Wi-Fi cracking tool.
Q: Which of the following memory is used to minimize memory-processor speed mismatch?
UVEPROM
Flash Memory
DVD
Cache Memory
[ Option D ]
Cache memory is a small, high-speed storage area located between the CPU and the main memory (RAM). Its primary function is to store copies of frequently accessed data and instructions, enabling the CPU to retrieve them more quickly than if it had to access the slower main memory every time.
1. L1 Cache (Level 1)
2. L2 Cache (Level 2)
3. L3 Cache (Level 3)
UVEPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), used for storing firmware. It can be erased with UV light and reprogrammed multiple times.
Flash Memory, it is non-volatile storage used in USB drives, SSDs, and memory cards. It retains data without power and allows fast read and write operations.
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc), optical storage media for large data, very slow compared to CPU. It is commonly used for movies, software distribution, and backup purposes.
Q: You have realised that two students of your class always create a problem in classroom management. What efforts would be made by you?
Ask them to stand at the back in the class and punish them.
Observe them continuously by assigning them small projects.
Give no attention on them.
Ask them to go out of the class.
[ Option B ]
Q: A tiny bootstrap loader program is situated in —
Hard Disk
ROM
BIOS
None of these
[ Option B ]
A bootstrap loader is a small program that starts the process of loading the operating system (OS) when a computer is powered on. It is stored in ROM (Read-Only Memory) because ROM is non-volatile, meaning its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off.
Q: Which of the following is valid pair of schema change statements in SQL?
DELETE, ALTER
DROP, UPDATE
DROP, ALTER
DELETE, UPDATE
[ Option C ]
Schema change statements in SQL are used to modify the structure of existing database objects like tables, columns, or constraints. These changes can include adding or removing tables, columns, or other schema elements. The most common schema change statements are DROP and ALTER.
Q: Which of the following database object does not physically exist?
Base Table
Index
View
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A view in a database is a virtual table that represents the data retrieved by a stored SQL query from one or more base tables.
Unlike base tables and indexes, which physically exist and store data on disk, a view does not store data itself. Instead, it holds only the SQL query defining it.
When a user queries the view, the database engine executes the stored query dynamically on the underlying base tables to fetch the current data. This allows views to provide a customized and simplified representation of data, enforce security by controlling data access, and reduce complexity without duplicating storage.
Views serve as logical abstractions that help organize and present data efficiently without physically occupying storage space.
Q: What will be the output of the following in MS-Excel?
=LCM(5,7,35)
70
1225
12
35
[ Option D ]
In MS Excel, the LCM function is used to calculate the Least Common Multiple of one or more numbers. The LCM is the smallest number that is divisible by all the given numbers with remainder 0. For example, the formula =LCM(5, 7, 35) calculates the LCM of 5, 7, and 35.
Q: In Excel 2016, if you want to insert 3 columns between Column G and H you would-
Select column G and right click and select insert for 3 times
Select column H and right click and select insert for three times
Select column E, F and G and right click and select insert for three times
Select column D, E and F and right click and select insert for three times
[ Option B ]
In Excel 2016, when you want to insert multiple columns, it is important to understand that Excel always inserts new columns to the left of the selected column(s).
To insert 3 columns between Column G and H, we need to select Column H first. By right-clicking and choosing Insert, a new column will appear to the left of H. Repeating this process three times will insert three new columns exactly between G and H.
Q: What is the outcome of the prefix expression
+, - , *, 3, 2, /, 8, 4, 1 ?
12
11
5
4
[ Option C ]
To evaluate a prefix expression, also known as Polish notation, the operator precedes its operands. The evaluation process involves scanning the expression from right to left. When an operand is encountered, it is pushed onto a stack. When an operator is found, the two most recent operands are popped from the stack, the operator is applied to these operands, and the result is pushed back onto the stack.
This continues until the entire expression has been scanned. The final result of the expression is the sole remaining value on the stack.
Q: Which of the following is a Sans Serif font?
Arial
Times New Roman
Courier
Gothic
[ DELETE ]
Most likely, the question was deleted due to ambiguity in font classification and potential for confusion.
Q: Choose the incorrect statement—
If a method is declared as final, that method cannot be overridden in sub class.
The finalize() is a method of Java, which is called by garbage collector thread before removing an object from the memory.
If a class is declared final, it cannot be inherited. If you do so it will give you compile-time error.
If we declare any variable as final, the value of the variable can be modified in final method.
[ Option D ]
In Java, the final keyword is used to restrict modification and ensure immutability where needed. A method declared as final cannot be overridden in subclasses, which helps in maintaining consistent behavior.
class Parent {
final void show() {
System.out.println("This is a final method");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
void show() {} // Compile-Time Error.
}A class declared as final cannot be inherited, which is useful for creating immutable classes or preventing extension.
final class MyClass {
int value = 100;
}
class NewClass extends MyClass { } //Compile-Time Error.If a variable is declared final, its value cannot be changed, regardless of whether it is inside a final method.
final int p = 33;
final void modifyValue() {
p = 20; //Compile-Time Error.
}The finalize() method in Java is a special method of the Object class that is called by the garbage collector before an object is removed from memory. It can be used to perform cleanup tasks, such as closing file streams, releasing network connections, or freeing other system resources held by the object.
class MyClass {
protected void finalize()throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Object is being Garbage Collected");
}
}
Q: Which phase is not included in virus life cycle?
Dormant
Execution
Start
Triggering
[ Option C ]
A Computer Virus is a type of malicious software that attaches itself to files or programs and can spread from one system to another. Just like a biological virus, it has a life cycle made up of different stages.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Dormant Phase | The virus stays inactive, waiting for specific conditions to occur like date, event, or user action. |
| Propagation Phase | The virus spreads by making copies of itself and attaching to files, programs, or boot sectors. |
| Triggering Phase | The virus is activated when certain conditions are met, e.g., opening a file, reaching a set date. |
| Execution Phase | The malicious payload runs, performing harmful actions such as deleting data, corrupting files, or displaying messages. |
Q: Which of the following is not a valid Master View option in Microsoft PowerPoint 2016?
Notes Master
Outline Master
Slide Master
Handout Master
[ Option B ]
In Microsoft PowerPoint 2016, the Master Views allow users to control the overall look, layout, and formatting of slides, handouts, and notes in a presentation. The main Master View options are:
Slide Master: This is the primary master that controls the design, layout, fonts, colors, and placeholders for all slides in the presentation. Any changes made here automatically apply to all associated slides.
Handout Master: This master controls the appearance and layout of printed handouts, including the number of slides per page, headers, footers, and page orientation.
Notes Master: This master is used to format the notes pages, which include slide thumbnails and speaker notes. It allows customization of fonts, colors, and layout for printing or viewing.
Q: A special software to create a job queue is called—
Linkage Editor
Interpreter
Drive
Spooler
[ Option D ]
A SPOOLER is special system software used to manage and create a job queue. It stands for Simultaneous Peripheral Operations On-Line. The spooler collects jobs and stores them in a queue (FIFO), then executes them one by one in order, ensuring efficient use of resources. The spooler ensures jobs are executed in the correct order without conflicts or loss.
Q: Which of the following E-Mail protocol is used to move messages through the internet from source to destination?
SMTP
IMAP
POP
UDP
[ Option A ]
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the protocol used to transfer email messages from the sender's mail server to the recipient's mail server across the internet. It is an application layer protocol that uses TCP to reliably send and relay email messages between servers until reaching the destination server.
The IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP (Post Office Protocol) are involved in email retrieval from mail servers to client devices, not in sending emails through the internet. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a transport protocol used for fast, connectionless communication.
Q: Identify the most accurate statement about the application of XML-
XML must be used to produce XML and HTML output.
XML cannot specify or contain presentation information.
XML is used to describe hierarchically organized information.
XML performs the conversion of information between different e-business applications.
[ Option C ]
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is designed to organize and store data in a clear, hierarchical structure. It allows creating custom tags to describe the data, making it easy for both humans and machines to understand. XML is especially useful for managing complex information where the relationships between data need to be clearly shown.
Unlike HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which is mainly used to display content on web pages, XML focuses on transporting and storing data rather than how it looks. XML is often used in documents, configuration files, and web services where data needs to be shared or transferred between different systems in an organized way. This separation of data and presentation helps keep information consistent and easy to update.
Q: Which of the following statements is/are true regarding Java?
(A) Constants that cannot be changed are declared using the ‘static’ keyword.
(B) A class can only inherit one class that can implement multiple interfaces.
(A) is true
(B) is true
Both (A) and (B) are true
Neither (A) nor (B) is true
[ Option B ]
In Java, constants that cannot be changed are declared using final, often combined with static for class-level constants, example, static final int P = 33;. Simply using static does not make a variable constant.
Java supports single inheritance for classes, meaning a class can extend only one superclass. However, a class can implement multiple interfaces, allowing it to inherit behavior from multiple sources like multiple inheritance.
class Super {}
interface A {}
interface B {}
class Sub extends Super implements A, B
{
}
Q: In context of memory card, SD and MMC stands for-
Secure Digital, Multimedia Card
Secure Data, Memory Management Card
Safe Data, Mega Memory Card
Safe Digits, Multimedia Card
[ Option A ]
SD (Secure Digital, launch in the year 1999 by Panasonic, Toshiba, SanDisk), a type of non-volatile memory card used in cameras, mobiles, laptops, etc. The term "Secure Digital" refers to the original purpose, providing secure, portable storage for digital devices.
MMC (Multimedia Card, launch in the year 1997 by Siemens & SanDisk), an older memory card standard developed before SD cards. These are similar in size, but slower and less secure compared to SD.
Q: Find x = ? If (356)8 = (x)16
EE
EA
7E
A8
[ Option A ]
To quickly convert a number from octal to hexadecimal, first convert the octal number into binary by replacing each octal digit with its 3-bit binary equivalent. Then, group the binary digits into 4-bit groups starting from the right. Finally, convert each 4-bit group into its hexadecimal equivalent.
For example, to convert 3568to hexadecimal:
So, 3568 = EE16.
Q: In SQL ________ is an aggregate function.
SELECT
CREATE
AVG
MODIFY
[ Option C ]
An aggregate function in SQL performs a calculation on a set of values and returns a single summarized result. These functions are commonly used to analyze and summarize data, especially when combined with the GROUP BY clause. The aggregate functions include:
Aggregate functions help in generating reports, insights, and statistical summaries from large datasets efficiently.
Q: A relation in which every non-key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the primary key and which as no transitive dependencies is in—
5NF
3NF
4NF
BCNF
[ Option B ]
A relation is in Third Normal Form (3NF) if:
This means each non-key attribute depends only on the primary key and not on other non-key attributes, which helps eliminate redundancy and update anomalies.
| Normal Form | Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1NF (First NF) | Atomicity | Each column contains atomic, indivisible values; no repeating groups. |
| 2NF (Second NF) | Full Functional Dependency | Every non-key attribute is fully dependent on the entire primary key. |
| 3NF (Third NF) | No Transitive Dependency | No non-key attribute depends on another non-key attribute. |
| BCNF (Boyce-Codd NF) | Stricter form of 3NF | Every determinant is a candidate key. It resolves some anomalies left by 3NF. |
| 4NF (Fourth NF) | No Multi-valued Dependency | No table contains two or more independent multi-valued dependencies. |
| 5NF (Fifth NF) | Join Dependency | Every join dependency in the table is a consequence of candidate keys. |
Q: Which statement is/are true about exception handling?
(i) There can be try block without catch block but vice versa is not possible.
(ii) There is no limit on the number of catch block corresponding to a try block.
(iii) The object must be created of a specific class of which the error has occurred otherwise runtime error will occur.
(iv) To execute a code with each and every run of program, the code is written in finally block.
Only (i), (ii) and (iv)
Only (ii)
Only (iii)
Only (ii) and (iv)
[ Option A ]
(i) There can be try block without catch block but vice versa is not possible.
(ii) There is no limit on the number of catch blocks corresponding to a try block.
(iii) The object must be created of a specific class of which the error has occurred otherwise runtime error will occur.
(iv) To execute a code with each and every run of program, the code is written in finally block.
public class ExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
int c = a / b;
System.out.println("Result: " + c);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Error: Cannot divide by zero!");
}
catch (NullPointerException e)
{
System.out.println("Error: Null value encountered!");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("Finally block: This will always execute.");
}
System.out.println("Program continues after exception handling.");
}
}
Q: In MS-Word ‘Gutter’ is related to-
Orientation
Page Size
Margins
Equation
[ Option C ]
In MS Word, a gutter is extra space added to the margin of a document to allow for binding, such as in books, reports, or manuals. It ensures that text does not get hidden in the spine or fold of the bound document.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Margins | Space between the text and the edge of the page. |
| Orientation | Direction of the page, Portrait (Vertical) or Landscape (Horizontal). |
| Page Size | Size of the paper, like A4, Letter, Legal. |
| Gutter | Extra space added to a margin to allow for binding, prevents text from being hidden in spine. |
| Header/Footer | Area at the TOP (Header) or BOTTOM (Footer) of the page for text, page numbers, or images. |
| Columns | Divides the page into Vertical Sections, often used in newsletters or brochures. |
Q: A RAM chip has a capacity of 1024 words of 8 bits each (1K X 8). The number of 2 X 4 decoders with enable line needed to construct a 16K X 16 RAM from 1K X 8 RAM is—
4
5
6
7
[ Option B ]
Q: What will be the output list after completing first pass of bubble sort on input array 32, 51,27,85,66,23,13,57?
32,27,51,66,23,13,57,85
32,51,27,66,23,13,57,85
27,33,51,23,13,57,66,85
23,13,27,33,51,57,66,85
[ Option A ]
The input array is 32, 51, 27, 85, 66, 23, 13, 57. In bubble sort, we compare adjacent elements and swap them if the left element is greater than the right. During the first pass, the largest element moves to the last position.
During first pass, compare 32 and 51 → no swap, 51 and 27 → swap, 51 and 85 → no swap, 85 and 66 → swap, 85 and 23 → swap, 85 and 13 → swap, and 85 and 57 → swap. After completing these comparisons and swaps, the array becomes 32, 27, 51, 66, 23, 13, 57, 85.
Q: The ‘ptrdata’ is a pointer to a data type. The expression *ptrdata++ is evaluated as (C++)—
*(ptrdata++)
(*ptrdata)++
*(ptrdata)++
Depends on compiler
[ DELETE ]
Before understanding why this question was deleted in the BCI Exam 2022, we need to study the concept behind it. The question involved the use of increment (++) / decrement (--) operators with the dereference (*) operator in C/C++. Since operator precedence and associativity decide whether the pointer moves or the value changes, such expressions become tricky and ambiguous, which often leads to confusion in exams.
To fully grasp the essence of this question and to understand the concept clearly, please read this blog attentively. This will provide you with a comprehensive explanation and deeper insight into the topic.
Q: What are the applications of “Essay Questions”?
Check person’s ability to make comparison
Apply principles of new situations
Communication of ideas
All of the above
[ Option D ]
Q: Which is not a type of NoSQL?
CouchDB
MongoDB
HBase
QBase
[ Option D ]
NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases are non-relational databases designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. They are categorized into different types based on their data models: document-based, key-value, column-family, and graph databases.
| NoSQL Database | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | Document-Oriented | Stores data in BSON (Binary JSON), flexible schema, widely used in web apps and analytics for its scalability and flexibility. |
| CouchDB | Document-Oriented | JSON-based documents, supports replication and offline storage. It is good for distributed applications. |
| HBase | Column-Family | Handles very large datasets across clusters, modeled after Bigtable, It is used in big data. |
| Redis | Key-Value | In-memory database, extremely fast and used for caching, session management, real-time analytics. |
| Cassandra | Column-Family | Highly scalable and fault-tolerant, ideal for big data and real-time applications. |
| Neo4j | Graph | Stores data as nodes and relationships, excellent for social networks, recommendations, and network analysis. |
| DynamoDB | Key-Value / Document | Fully managed by AWS (Amazon Web Services) scalable, low-latency access. It is supports both key-value and document models. |
Q: Which of the following methods will create string in Java?
(i) String S = “Hello Java”;
(ii) String S2 = New string(“Hello Java”);
Only (i)
Only (ii)
Both (i) and (ii)
Neither (i) nor (ii)
[ Option A ]
In Java, strings can be created in two ways. The first method is by using string literals, for example: String s = "Hello Java";. In this case, the string is stored in the String Constant Pool (SCP), which allows Java to reuse memory efficiently.
The second method is by using the new keyword, for example: String s2 = new String("Hello Java");. This approach creates a new String object in heap memory, separate from the SCP, even if an identical string already exists in the pool.
However, in the given question, option (ii) is written as String S2 = New string("Hello Java");. This is incorrect due to Java’s case sensitivity:
Because of these errors, option (ii) will cause a Compile-Time Error (CTE), and only option (i) is valid as written.
Q: Consider the following statements regarding key-
(I) A super key is an attribute or combination of attributes that uniquely identifies records in a RDBMS table.
(II) A candidate key is a subset of a super key.
(III) All super keys are candidate keys but vice versa is not true.
Only (I) is true
Only (II) is true
(I) and (III) are true
(I) and (II) are true
[ Option D ]
In a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), keys are used to uniquely identify records in a table or relation. A super key is an attribute or a combination of attributes that ensures the uniqueness of each record. Among these super keys, a candidate key is a minimal set of attributes that can still uniquely identify a record, meaning it does not contain any unnecessary attributes.
In other words, every candidate key is a subset of a super key, but not all super keys are candidate keys because some may include extra attributes that are not needed for uniqueness.
Q: Which one of the following is not a software process model?
Linear Sequential Model
Prototype Model
The Spiral Model
COCOMO Model
[ Option D ]
A software process model is a structured approach that defines the sequence of steps or phases to be followed for systematic software development.
| Software Process Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Linear Sequential Model | A structured, step-by-step approach where each phase is completed before the next begins, best for well-defined projects but inflexible to changes. |
| Prototype Model | Builds a working prototype early to clarify requirements and gather user feedback, useful when requirements are unclear but may extend development time due to multiple iterations. |
| Spiral Model | Risk-driven iterative model combining repeated development cycles with risk analysis at each stage. It suitable for large and complex projects requiring risk management and frequent refinement. |
| Agile Model | Emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and iterative incremental delivery through frequent releases and feedback, ideal for projects with evolving requirements. |
| Incremental Model | Develops the system in small, manageable parts called increments; each increment goes through requirement, design, testing, and implementation, enabling early partial delivery and adaptation. |
| V Model | A variation of the waterfall model emphasizing Verification and Validation. In this, every development phase has a corresponding testing phase, ensuring systematic testing but less flexible for changes. |
The COCOMO (Constructive Cost Model) is a well-known software cost estimation model developed by Barry W. Boehm in the late 1970s. It helps predict the amount of effort, time, and resources required to complete a software development project based on software size, usually measured in lines of code (LOC).
| COCOMO Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic COCOMO | Provides a quick, rough estimate of effort based mainly on project size (KLOC). It uses a simple formula and does not consider factors like reliability or personnel experience. |
| Intermediate COCOMO | Extends Basic COCOMO by including 15 cost factors such as product complexity, hardware constraints, and personnel capability to improve estimation accuracy. |
| Detailed COCOMO | Further extends Intermediate COCOMO by assessing the impact of cost drivers on each phase of the software development process. It divides the software into modules, estimating effort for each, enabling precise and phase-wise estimation. |
Q: The information that gets transformed in encryption is-
Plain Text
Parallel Text
Encrypted Text
Decrypted Text
[ Option A ]
Cryptography, the science of securing communication by using encryption and decryption techniques.
The information that gets transformed during encryption is called Plain Text. Plain text refers to the original, human-readable data such as messages, files, or any sensitive information.
Encryption is the process of converting readable information, called plain text, into an unreadable or scrambled format known as Cipher Text, using algorithms and cryptographic keys. The Cipher Text, ensures that unauthorized users cannot understand it without the proper key.
Decryption is the reverse of encryption. It transforms encrypted data (cipher text) back into its original readable form (plain text) using a decryption key.
Q: What would be the prefix notation for the given equation?
(a+(b/c)*(d^e)-f)
+-a*/^bcdef
-+a*b/c^def
-+a*/bc^def
-+fa*/bc^de
[ Option C ]
The given infix expression is a + (b/c) * (d^e) - f. To convert it into prefix form, we first look at the inner brackets. The term (b/c) in prefix becomes / b c, and the term (d^e) becomes ^ d e.
Next, these two are multiplied, so (b/c) * (d^e) becomes * / b c ^ d e. Now, this result is added to a, so the expression a + ((b/c) * (d^e)) becomes + a * / b c ^ d e. Finally, we subtract f from this whole result, so the complete prefix form becomes - + a * / b c ^ d e f.
Q: In relational database minimal super keys is known as-
Primary Keys
Foreign Keys
Candidate Keys
Reference Keys
[ Option C ]
A super key is a set of one or more attributes that uniquely identify each record in a table. However, a super key may include extra attributes that are not necessary for uniqueness.
When we remove all unnecessary attributes from a super key, leaving the minimal set of attributes that still uniquely identify each record, it becomes a candidate key.
Every candidate key is a minimal super key, meaning it cannot be reduced any further without losing the ability to uniquely identify records. From among the candidate keys, one is selected as the primary key to uniquely identify rows in the table.
Q:
Match the following—
| List – I | List – II |
|---|---|
| (A) DDL | (i) LOCK TABLE |
| (B) DML | (ii) COMMIT |
| (C) TCL | (iii) Natural Difference |
| (D) Binary Operation | (iv) REVOKE |
A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii)
A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i), D-(iv)
A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
[ Option D ]
Q: To increase the “Critical Thinking” ability among students, which of the following teaching method is most effective?
Project Based Teaching Learning
Lecture Method
Lecture cum Demonstration Method
Inductive-Deductive Method
[ Option A ]
Q: Consider the following stack implemented using stack-
#define SIZE 11
struct STACK
{
int arr[SIZE];
int top=-1;
}
What would be the maximum value of top that does not cause the overflow of the stack?
8
9
11
10
[ Option D ]
In the given stack implementation, the size of the array is defined as 11, which means the stack can hold elements from index 0 to 10. Initially, the value of top is -1, and each time an element is pushed, the value of top increases by one.
When the stack is completely filled, the top will point to the last valid index, which is 10. At this stage, the stack contains 11 elements in total, and if we try to push one more element, it will cause an overflow. Therefore, the maximum value of top that does not cause overflow is 10.
Q: Which testing focuses on heavily testing of one particular module?
Gorilla Testing
Fuzz Testing
Inter System Testing
Breadth Testing
[ Option A ]
Gorilla Testing is a software testing technique that focuses heavily on testing a specific module or feature of an application. It involves intense, repetitive, and rigorous testing of one particular part to find as many defects as possible in that area. This method ensures the robustness and reliability of critical modules, uncovering hidden bugs that might be missed in broader testing.
Fuzz Testing involves providing random or invalid inputs to the software to check how it handles unexpected data.
Inter-System Testing, tests the interaction between two or more different systems to ensure they work together correctly.
Breadth Testing, focuses on testing all modules at a shallow level without going deep into any single one.
Q: Which of the following is not a super key in a relational schema with attributes V, W, X, Y, Z and primary key VY?
VXYZ
VWXZ
VWXY
VWXYZ
[ Option B ]
A super key is any set of attributes that contains the primary key or a superset of it. Since the primary key is VY, any super key must at least include both attributes V and Y.
(a) VXYZ: Has V,X,Y,Z. It contains both V and Y. So, this is a super key.
(b) VWXZ: Has V,W,X,Z. It contains V but does not have Y. So, this is not a super key.
(c) VWXY: Has V,W,X,Y. It contains both V and Y. So, this is a super key.
(d) VWXYZ: Has V,W,X,Y,Z. It contains both V and Y. So, this is a super key.
Q: Which of the following is not related to format of animation?
File Format (FLI/FLC)
MPEG (.mpg)
Quick Time (QT/Moov)
Amiga (SGI)
[ Option D ]
Animation formats are special file types or containers made to store moving images or animated sequences. FLI and FLC are examples of animation file formats created by Autodesk for frame-based animations. MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group) (MPEG files usually have extensions like .mpg, .mpeg, .mp4) is a widely used video format that supports motion content, while QuickTime (QT/Moov), developed by Apple, works as a multimedia container for both animations and videos.
On the other hand, SGI (Silicon Graphics Image) is not an animation format. It is an image file format designed for Silicon Graphics workstations and is mainly used for storing static raster images. Since it does not support animated or moving content, it cannot be considered an animation format like the others.
Q: Which of the following declarations is incorrect in python language?
xyzp = 5,000,000
xyzp = 5000 6000 7000 8000
x, y, z, p = 5000, 6000, 7000, 8000
x_y_z_p = 5,000,000
[ Option B ]
In Python, writing xyzp = 5,000,000 is syntactically correct, but it does not store the integer 5000000. Instead, Python treats the commas as separators and creates a tuple (5, 0, 0). If we want to store 5000000 in python variable then correct way is either xyzp = 5000000 or xyzp = 5_000_000 for readability.
The statement, x, y, z, p = 5000, 6000, 7000, 8000 uses tuple unpacking, assigning each number to a separate variable: x = 5000, y = 6000, z = 7000, and p = 8000. This is a valid and commonly used Python syntax.
The statement, x_y_z_p = 5,000,000, is similar to statement xyzp = 5,000,000. It is syntactically correct, and the variable name is valid, but the value becomes a tuple (5, 0, 0).
The statement, xyzp = 5000 6000 7000 8000, is completely invalid in Python. The numbers cannot be written separated by spaces, and this will throw a syntax error.
Q: Which of the following are correct statements with respect to XML?
(i) It is used to display data only.
(ii) XML can be used as a database.
(iii) XPATH is used to store the IP address of the server.
(iv) XLL definition is used along with XML to specify the links with other documents.
Only (i) and (ii)
Only (i), (ii) and (iii)
Only (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Only (ii) and (iv)
[ Option D ]
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a flexible, text-based markup language designed to store, organize, and transport structured data. It uses custom tags to represent information in a hierarchical format, making it both human-readable and machine-readable. XML is widely used in web applications, data exchange, configuration files, and document storage because it is platform-independent and supports integration across different systems.
| Technology | Usef For |
|---|---|
| XSL | Extensible Stylesheet Language. It is used for styling and transforming XML documents. |
| XPath | Language for navigating and selecting nodes in XML documents. |
| XLink | Defines links (hyperlinks) between XML documents or resources. |
| XPointer | Extends XPath to point to specific parts of XML documents. |
| XQuery | Query language to extract and manipulate data from XML documents. |
| XML Schema (XSD) | Defines the structure and data types of XML documents for validation. |
| DTD | Document Type Definition. It defines the legal building blocks of an XML document. |
| DOM | Document Object Model. API for accessing and modifying XML documents as tree structures. |
| SAX | Simple API for XML. An event-driven API for reading XML documents sequentially. |
Q: Hacktivism is –
A process of break into systems and dig out its information and make it public.
Gaining access to systems with an intention to fix the identified weaknesses.
A test technique for an existing internet infrastructure and to find its loopholes.
The act of hacking a computer system, for politically or socially motivated purpose.
[ Option D ]
Hacktivism is the combination of "hacking" and "activism." It refers to the act of breaking into computer systems or networks with the intention of promoting political or social causes (not for financial gain).
Hacktivists use hacking techniques to raise awareness, protest against injustices, or support specific movements by targeting organizations, governments, or corporations they oppose.
Common hacktivist activities include:
Q: In FTP, there are three types of ……………., stream, block and compressed.
File Types
Data Types
Transmission Modes
None of these
[ Option C ]
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used to transfer files between a client and a server on a network. In FTP, data can be transferred using different transmission modes that determine how the file data is sent over the connection.
Q: The test levels are performed in which of the following order?
Unit, Integration, System, Acceptance
It is based on nature of the project
Unit, Integration, Acceptance, System
Unit, System, Integration, Acceptance
[ Option A ]
Software Testing is the process of evaluating a software application to check whether it meets the specified requirements and works as expected. It helps to identify defects, errors, or gaps so that they can be fixed before the product is delivered. The main goals of testing are:
After this, testing is usually carried out in different levels (Unit, Integration, System, Acceptance) to make sure the software is correct at every stage.
| Test Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Tests individual components or functions of the software to ensure they work correctly in isolation. Usually performed by developers during coding. It helps catch bugs early and ensures each part functions as intended. |
| Integration Testing | Tests the interaction and data flow between multiple units or modules to verify they work together properly. Helps identify interface defects between integrated components. Typically performed after unit testing. |
| System Testing | Validates the complete, integrated system to ensure it meets specified requirements. Tests the software as a whole in an environment close to production, including functional and non-functional testing. Usually done by QA teams. |
| Acceptance Testing | The final level of testing to verify the system meets user needs and requirements. Often performed by end-users or clients to decide if the software is acceptable for release. Includes User Acceptance Testing (UAT). |
Q: In context of information gathering, ranking scale questions ask the respondents to-
Choose one among given answer choices
Rank list of items in order of importance
Mark a level of satisfaction on a given scale
Say Yes or No
[ Option B ]
Information Gathering is the process of collecting facts, opinions, and requirements from stakeholders, users, or sources to understand a problem or design a system. It is a crucial step in software engineering, system analysis, and research because decisions made later depend on accurate and complete information. The main objectives are to:
In the context of information gathering, different types of questions are designed to capture different kinds of responses from participants:
| Question Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple-choice | Ask respondents to choose one option from a list. | Which device do you use most? (Laptop / Mobile / Tablet) |
| Ranking scale | Ask respondents to arrange items in order of importance or preference. | Rank the following features: Security, Cost, Speed, Ease of Use. |
| Rating scale | Ask respondents to mark a level of satisfaction on a scale. | Rate your satisfaction? (1 = Very Dissatisfied, 5 = Very Satisfied) |
| Dichotomous (Yes/No) | Ask respondents to give a two option answer. | Do you use online banking? (Yes / No) |
Q: Checksum is used for—
Error Correction
Error Detection
Both (a) and (b)
None of these
[ Option B ]
A checksum is used in networking to verify data integrity. It works by adding binary values of data segments and sending the result with the packet. At the receiver’s end, the same calculation is done and compared. If they do not match, an error is detected. However, checksum only supports error detection, not correction.
| Checksum | CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) |
|---|---|
| Uses simple addition of data words. | Uses polynomial division (modulo-2 arithmetic). |
| Simple, fast, low overhead. | More complex, requires extra computation. |
| Detects single-bit errors and some small errors. | Detects burst errors, multiple bit errors, and more complex patterns. |
| Less reliable. | Highly reliable and accurate. |
| IP, TCP, UDP headers in networking. | Ethernet frames, storage devices, advanced communication protocols. |
Q: In context of MS-Word, fill in the blank-
“Create a ……………… to assign a name to a specific point in a document”.
ClipArt
Cross-Reference
Hyperlink
Bookmark
[ Option D ]
In MS Word, a Bookmark is used to give a name to a specific place in a document. This makes it easy to jump to that spot quickly or link to it from another part of the document using a Hyperlink or Cross-Reference.
Q: Which of the operations constitute a basic set of operations for manipulating relational data?
Predicate Calculus
Relational Calculus
Relational Algebra
None of these
[ Option C ]
Relational algebra is a set of basic operations used to manipulate data in relational databases. These includes:
These operations take relations as input and produce new relations as output, forming the foundation for querying data efficiently and systematically.
Q: In tuple relational calculus P1 → P2 is equivalent to—
¬P1˅P2
P1˅P2
P1˄P2
P1˄¬P2
[ Option A ]
Q: Consider the given binary search tree, if the root node will be deleted, the new root can be-
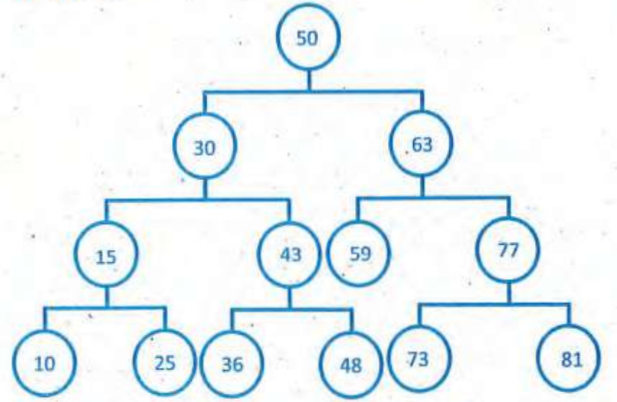
43 or 48
63 or 81
48 or 59
30 or 63
[ Option C ]
Q: How many states can be processed in operating system?
2
3
4
5
[ Option D ]
In an Operating System (OS), a process is a program in execution. Each process moves through various states during its life cycle, from creation to termination. Typically, a process can exist in five main states.
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| New | The process is being created. |
| Ready | The process is loaded into memory and waiting for CPU allocation. |
| Running | The process is currently executing on the CPU. |
| Waiting (Blocked) | The process is waiting for some event, input-output, or resource before it can proceed. |
| Terminated (Exit) | The process has finished execution and is removed. |
Q: A counting semaphore was initialized to 8. Then 12 P (wait) operations and 7 V (signal) operations were completed on this semaphore. The resulting value of semaphore is—
4
3
5
1
[ Option C ]
Q: In context with Relational Algebra, which of the following are Unary Operators?
1. Select
2. Project
3. Union
4. Product
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1 and 2 only
All are binary
[ Option C ]
Unary operators operate on a single relation (table) and produce a relation as output.
Binary operators work on two relations (tables) and produce a new relation as output.
Q: What will be post order traversal of a binary Tree T, if preorder and inorder traversals of T are given by ABCDEF and BADCFE respectively?
BDFECA
BCFDEA
BFDECA
BEFDCA
[ Option A ]
In a tree data structure, there are three primary types of traversal sequences used to visit all the nodes systematically: Preorder, Inorder, and Postorder traversal.
So,
(1) Preorder Traversal: Root → Left → Right
(2) Inorder Traversal: Left → Root → Right
(3) Postorder Traversal: Left → Right → Root
The preorder traversal of the tree is ABCDEF, which means the root of the tree is A. Looking at the inorder traversal BADCFE, we see that A splits the tree into a left subtree (B) and a right subtree (DCFE). Thus, B is the left child of A, and the rest of the nodes (DCFE) belong to the right subtree.
In the right subtree, the preorder sequence is CDEF, so the root here is C. From the inorder sequence DCFE, the node C splits the subtree into D on the left and FE on the right. For the FE part, preorder tells us the root is E, and inorder (FE) shows that F is on the left of E. This gives the right subtree structure: C has left child D and right child E, with E having left child F.
Now, constructing the postorder traversal: start with the left subtree of A which is B, then the right subtree rooted at C. For C, its left subtree gives D, and its right subtree rooted at E gives F followed by E. After these, we add the root C. Finally, we append the overall root A. Putting this together, the Postorder is B D F E C A.
Q: A black hole in a DFD is-
A data store with no in bound flows
A data store with only in bound flows
A data store with more than one in bound flow
None of these
[ Option B ]
In a Data Flow Diagram (DFD), a Black Hole is a process or data store that receives data but does not produce any output. In other words, information flows into it, but nothing comes out. This situation usually indicates an error or a missing component in the diagram, as every process should normally transform or pass on data through both input and output flows.
Apart from a Black Hole, there are several other common errors in Data Flow Diagrams (DFD):
| DFD Error Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Black Hole | A process has inputs but no outputs. Data enters but nothing comes out. | A process “Calculate Salary” takes employee details but produces no salary slip. |
| Miracle | A process has outputs but no inputs. Data appears without any source. | A process “Generate Report” creates reports without receiving any input data. |
| Gray Hole | A process has inputs and outputs, but the outputs are not logically possible from the given inputs. | A process “Calculate GPA” generates a GPA without having any marks or grade data as input. |
| Data Store with No Flows | A data store has neither input nor output flows. | A database symbol in the DFD is drawn but never connected to any process. |
| Unconnected Process | A process has no data flows connected or it is isolated. | A process “Update Inventory” is shown but has no input or output arrows. |
| Data Flow Errors | Data flows directly between external entities or between data stores without a process. | An arrow directly linking two databases or two users without a process in between. |
Q: Which type of research can be done for the solution of problem related to understanding of difficult concepts in the class?
Case Study
Action Research
Interaction Analysis
Fundamental Research
[ Option B ]
Q: Which of the following are line printer and page printer respectively?
Laser Printer, Dot-Matrix Printer
Drum Printer, Band Printer
Drum Printer, Laser Printer
Laser Printer, Chain Printer
[ Option C ]
A printer is an output device that produces a hard copy of text, images, or graphics from a computer or other digital devices. Printers are classified based on the mechanism used to print, speed, and quality of output.
1. Impact Printers, print by physically striking an ink ribbon against the paper.
2. Non-Impact Printers, print without physically striking the paper, using heat, laser, or ink.
3. 3D Printers, create three-dimensional objects by layering material according to a digital model.
4. Multifunction Printers (MFPs), combine printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing into a single device.
| Category | Definition | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Printers | Print by physically striking an ink ribbon against the paper. | Dot Matrix Printer | Uses pins to strike ribbon; prints text / graphics; good for multi-part forms. |
| Daisy Wheel Printer | Characters embossed on a wheel; prints letter-quality text. | ||
| Line Printers | Prints one entire line at a time; high-speed printing. | ||
| Non-Impact Printers | Print without physically striking the paper; uses ink, laser, or heat. | Laser Printer | Uses laser beams and toner; prints a full page; high-quality output. |
| Inkjet Printer | Sprays tiny ink droplets; high-resolution; suitable for images. | ||
| Thermal Printer | Uses heat to transfer ink or burn images; used for receipts/labels. | ||
| 3D Printers | Create 3D objects layer by layer from digital models. | 3D Printers | Builds objects layer by layer using plastic, resin, or metal. |
| Multifunction Printers (MFPs) | Combine printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing in one device. | MFPs | All-in-one devices for office / home use; save space and cost. |
Q: In context of MS-Excel, find the odd one out—
Portrait
Scenario Manager
Goal Seek
Data Table
[ Option A ]
In MS Excel, several tools are used for What-If Analysis, which helps in forecasting and decision-making. Tools like Scenario Manager, Goal Seek, and Data Table allow users to analyze different input values and see their impact on results. On the other hand, Portrait refers to the page orientation in the Page Layout settings and has nothing to do with data analysis or forecasting.
Q: Decorative text in MS-Word document is called-
Bookmark
WordArt
SmartArt
ClipArt
[ Option B ]
In MS Word, decorative or stylized text that is used to make headings or titles visually attractive is called WordArt. WordArt allows you to apply special effects, colors, and shapes to text to make it stand out in a document.
Q: The first step to the system study project is to-
Define system performance criteria
Describe information needs
Staff for the study project
Announce the study project
[ Option B ]
In a system study project, the very first step is to describe the information needs of users and the organization. This step is crucial because it helps in identifying what data is required, how it should be processed, and what outputs are necessary for decision-making.
Once the information needs are clearly understood, other steps such as defining system performance criteria, staffing for the study project, and officially announcing the project can be carried out effectively. Without properly identifying user requirements at the start, the system cannot be designed to meet organizational goals.
Q: Choose true statement:
(I) Binary search is faster than linear search.
(II) Binary search may not be applied on all the input lists on which linear search can be applied.
Only (I)
Only (II)
Both (I) and (II)
Neither (I) nor (II)
[ Option C ]
Statement I says that binary search is faster than linear search. This is true because binary search works by repeatedly dividing the sorted list in half, giving it a time complexity of O(log n), whereas linear search checks each element one by one and takes O(n) time.
Statement II says that binary search may not be applied on all the input lists on which linear search can be applied. This is also true because binary search requires the list to be sorted, while linear search works on both sorted and unsorted lists.
Q: Which of the following is a combinational logic circuit that has 2n input lines and a single output line?
Multiplexer
Demultiplexer
Encoder
Decoder
[ Option A ]
A Multiplexer (MUX) is a combinational logic circuit that selects one input from 2n input lines and forwards it to a single output line based on n select lines. It effectively channels multiple inputs into a single output line by selecting one input at a time.
| Circuit | No of Inputs | No of Outputs | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiplexer (MUX) | 2n data inputs and n select lines. | 1 output | Selects one input from 2n inputs based on select lines. |
| Demultiplexer (DEMUX) | 1 data input and n select lines. | 2n outputs | Routes one input line to one of 2n outputs depending on select line values. |
| Encoder | 2n inputs. | n outputs | Converts 2n active input lines into an n-bit binary code on the output lines. |
| Decoder | n inputs. | 2n outputs. | Converts n input bits into 2n outputs where only one output is active based on input code. |
| Half Adder | 2 inputs | 2 outputs (Sum, Carry) | Adds two binary digits producing sum and carry outputs. |
| Full Adder | 3 inputs (including carry in) | 2 outputs (Sum, Carry) | Adds three binary bits including carry-in and produces sum and carry outputs. |
Q: What is the result after executing of the following code if ‘a’ is 10, ‘b’ is 5 and ‘c’ is 10?
if((a>b) && (a<=c))
a = a+1;
else
c = c+1;
a = 10, c = 10
a = 11, c = 10
a = 10, c = 11
a = 11, c = 11
[ Option B ]
Initially, the variables are a = 10, b = 5, and c = 10. The if statement checks the condition (a > b) && (a <= c). Evaluating step by step: a > b is 10 > 5, which is true, and a <= c is 10 <= 10, which is also true. Since both parts of the condition are true, the && operator makes the whole condition true. Therefore, the code inside the if block executes, which is a = a + 1, so a becomes 11. The else block does not execute, so c remains 10.
Q: What are the forms of password cracking techniques?
Attacksyllable
AttackBrut Forcing
AttackHybrid
All the above
[ Option D ]
Password Cracking is the process of attempting to discover or recover a password to gain unauthorized or authorized access to a system, account, or network. It is performed either to recover forgotten passwords or, more maliciously, to break into systems by guessing the correct password.
Attackers use various automated tools and techniques to systematically guess or decrypt passwords by exploiting weak or commonly used ones.
Q: In the …..… encoding scheme, each 24 bits become four 6-bit chunks, and eventually are sent as 32 bits.
8 bits
Binary
Base 64
Quoted-Printable
[ Option C ]
In computer networks, binary data cannot always be transmitted directly over text-based protocols like email (SMTP) or web (HTTP). To solve this problem, Base64 encoding is used. Base64 takes every 24 bits of input data (3 bytes) and divides it into four groups of 6 bits each. Each 6-bit value is then mapped to a printable ASCII character.
Since each Base64 output is an ASCII character, it requires 8 bits of storage. Therefore, four characters × 8 bits = 32 bits of output are generated from the original 24 bits. This explains why Base64 increases the size of the encoded data by about 33%.
When encoding the string "SRK" into Base64, the process begins by converting each character into its ASCII binary form. The character S has an ASCII value of 83, which is 01010011 in binary. The character R has an ASCII value of 82, represented as 01010010. Finally, the character K has an ASCII value of 75, represented as 01001011. Together, the string "SRK" produces a 24-bit binary stream:
01010011 01010010 01001011
Next, these 24 bits are divided into groups of 6 bits each:
010100 110101 001001 001011
Each 6-bit group is then converted into its decimal equivalent:
Using the Base64 index table, these decimal values are mapped to their respective characters:
Thus, the final Base64 encoded output of the string "SRK" is: U1JL
Q: To maintain materialized views in RDBMS, we use-
Trigger
Pointer
Clone Object
None
[ Option A ]
In a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), a materialized view is a database object that stores the results of a query physically. Unlike a regular view, which calculates data only when it is accessed, a materialized view keeps the data ready in advance, which helps speed up complex queries.
Since the original tables can change with INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations, the data in a materialized view can become outdated. To keep it current automatically, RDBMS uses triggers, which are special procedures that run whenever the underlying table data changes, ensuring the materialized view stays up-to-date.
Q: Which one is measure of software complexity?
Number of lines of code (LOC)
Number of man years
Number of Function Points (FP)
All of the above
[ Option D ]
Software Complexity refers to the degree of difficulty in understanding, developing, testing, and maintaining a software system. A highly complex system usually has more lines of code, intricate logic, higher development effort, and is harder to manage. Measuring complexity helps in estimating cost, time, and resources needed for software projects.
Lines of Code (LOC): Counts the total number of lines in the source code. More lines usually mean more complexity, but it does not reflect code quality or logic.
Man-Years: Shows the total human effort (time and people) needed to build the software. Bigger and more complex projects require more man-years.
Function Points (FP): Measures the software based on the functionality it provides to users (inputs, outputs, files). Independent of programming language, it gives a better view of user-side complexity.
Cyclomatic Complexity: Measures how many independent paths exist in the program’s flow (like branches, loops, conditions). Higher values mean the program is harder to test and maintain.
Q: In Artificial Intelligence (AI) which agent deals with happy and unhappy state?
Simple Reflex Agent
Model Based Agent
Learning Agent
Utility Based Agent
[ Option D ]
An Artificial Intelligence (AI) agent is a computer program that can sense what is happening around it, make decisions, and take actions to reach goals. It works on its own without needing someone to tell it every step. AI agents learn from experience and can adapt to changes in their environment. They are used in many areas to help automate tasks and solve problems.
| AGENT TYPE | USED FOR |
|---|---|
| Simple Reflex Agent | Acts only on the current percept, using condition-action rules. It selects actions based solely on the immediate input without memory of past states. |
| Model Based Agent | Maintains an internal state that depends on the history of percepts and uses this state to make decisions. It can handle partially observable environments by keeping track of past information. |
| Learning Agent | Improves its performance over time by learning from experience. It can adapt to new situations by updating its knowledge and refining its actions. |
| Utility Based Agent | Uses a utility function to evaluate the desirability of different states, considering not just goals but preferences and happiness. It chooses actions to maximize overall utility or satisfaction. |
Q: If SQL command DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE; is executed on relation EMPLOYEE having ‘n’ tuple in it, ………….. will be deleted from relation EMPLOYEE.
Zero Tuples
Only First Tuple
All ‘n’ Tuples
Only Last Tuple
[ Option C ]
The SQL command DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE; without a WHERE clause will delete all tuples (rows) from the EMPLOYEE relation or table. It removes every record, but the table structure, columns, and schema remain intact.
Q: Which of the following is used by banking industry to handle large volume of cheques?
Digitizer
MICR
Barcode Reader
Captcha
[ Option B ]
MICR : Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
Digitizer : Converts drawings or images into digital form. It is commonly used in graphic design and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) applications.
Barcode Reader (BCR) : Reads barcodes on products. It helps in fast product identification and inventory management in stores and warehouses.
Captcha : Used to verify human users online, not for banking. It prevents automated bots from accessing websites and submitting forms.
Q: _________ is malicious software that alters the regular functionality of an OS, takes full control on the targeted system and acts as the system administrator on the victim’s system.
Spyware
Virus
Rootkit
Trojan Horse
[ Option C ]
A Rootkit is a type of Malicious Software (Malware) designed to gain unauthorized administrator-level control over an operating system. Once installed, it alters the normal functioning of the OS, allowing the attacker to take full control of the system and act as its administrator.
Rootkits are especially dangerous because they actively hide themselves, making detection and removal very difficult.
| Malware Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Virus | Infects files and programs, spreads when infected files are shared or executed. |
| Worm | Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks without user action. |
| Trojan Horse | Appears as legitimate (genuine) software but secretly creates backdoors or installs malware. |
| Rootkit | Hides deep in the OS, modifies system functions, and gives attackers administrator control. |
| Spyware | Monitors user activities, stealing data such as browsing history, keystrokes, and credentials. |
| Ransomware | Encrypts files and demands payment for the decryption key. |
| Adware | Displays intrusive advertisements, often bundled with free software. |
| Keylogger | Records user keystrokes to steal sensitive information like passwords and credit card details. |
Q: An INI file in Windows 95 is –
A Program File
A Message File
A Text File
Link File
[ Option C ]
An INI file (initialization file (.ini)) in Windows 95 is a plain text configuration file used to store settings and configuration data for the operating system and applications. These files are organized into sections containing key-value pairs and are readable and editable using any text editor like Notepad.
Q: Network layer firewall works as a—
Frame Filter
Packet Filter
Both (a) and (b)
None of these
[ Option B ]
A Network Layer firewall functions as a Packet Filter. It examines and manages the flow of data packets according to rules defined by IP addresses, Port Numbers, and communication protocols. Operating at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, this type of firewall makes decisions on whether to permit or deny packets without analyzing the actual data content inside them.
Q: LB are UB are lower bound and upper bound of a linear array LA. Consider following algorithm-
1. Repeat for K=LB to UB apply PROCESS to LA[K]
2. Exit.
The algorithm ………….. the array LA.
Sorts
Searches
Traverses
Merges
[ Option C ]
Q: In MS-PowerPoint we can run slide show from beginning using …….. key and from current slide using …… key.
F5, F7
F6, F8
F7, Shift + F7
F5, Shift + F5
[ Option D ]
To run the slide show from the beginning, press the F5 key, which starts the presentation from the very first slide. If we want to run the slide show from the currently selected slide, press Shift + F5, which begins the presentation from that particular slide without going back to the first one.
Q: An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 01000010. Which of the following is correct?
The number of hops this packet can travel is 2.
The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
The upper layer protocol is ICMP.
The receiver rejects the packet.
[ Option D ]
When an IP packet arrives, the first 8 bits of its header play a crucial role in determining how it is processed. These 8 bits are divided into two fields: the first 4 bits represent the IP version, and the next 4 bits indicate the Internet Header Length (IHL).
In this case, the first 8 bits are 01000010. The first 4 bits, 0100, correspond to version 4, which confirms that this is an IPv4 packet. The next 4 bits, 0010, represent the IHL value of 2.
The IHL specifies the number of 32-bit words in the header. Since each word equals 4 bytes, the total header length here is 2 × 4 = 8 bytes. However, the minimum valid IPv4 header length is 20 bytes (IHL = 5).
Therefore, an IHL value of 2 is invalid and indicates a malformed packet. As a result, the receiver will reject this packet because it does not meet the minimum requirements for processing.
Q: The commonly used protocol for webpage transfer is-
HTML
HTTP
WML
WTTP
[ Option B ]
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), is the standard protocol used to transfer web pages over the internet. It works at the Application Layer, allowing communication between web browsers and web servers. When a browser requests a webpage, HTTP facilitates sending that request to the server and receiving the webpage content, such as HTML, images, and videos, in response.
This protocol follows a client-server model, where the browser acts as the client initiating the request, and the server processes the request and sends back the required webpage data. Through this request-response communication, HTTP enables users to access and view websites on the internet efficiently.
Q: Which of the following view is most suitable to rearrange slide in MS-PowerPoint?
Slide Sorter
Notes Page
Normal
Slide Show
[ Option A ]
In Microsoft PowerPoint 2016, the Presentation Views help users create, organize, and customize slides effectively. The main options are:
Normal View: This is the default editing view where you can work on individual slides. It shows the slide pane, outline pane, and notes pane, allowing users to design slides and add content.
Outline View: Displays the text content of all slides in a structured outline format. This view is useful for organizing ideas and editing slide text efficiently.
Slide Sorter View: Shows all slides as thumbnails on a single screen. This view helps in rearranging, deleting, or duplicating slides quickly.
Notes Page View: Displays each slide along with its speaker notes. This view is useful for reviewing and editing notes before presentations or printing.
Reading View: Presents the slides in full-screen mode but within the PowerPoint window. It is useful for reviewing the presentation without switching to Slide Show mode.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.