Get complete RPSC Programmer Exam Paper-1 solved questions with detailed explanations. Practice previous year papers, boost your subject knowledge, and prepare effectively for the RPSC Programmer exam with authentic and accurate solutions.
In addition, this solution guide is not just about answers, it is designed as a learning companion. By studying these explanations, students can strengthen their problem-solving skills and approach future exams with greater clarity and confidence.
| Unit | Unit Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Unit 1 | Reasoning Test & Numerical Analysis & General Knowledge | Problem solving, Data Interpretation, Data Sufficiency, Logical Reasoning and Analytical Reasoning. General Knowledge and Current Affairs relating to India and Rajasthan. |
| Unit 2 | Data Base Management Systems | ER Diagram, Data Models - Relational and Object Oriented Databases. Data Base Design: Conceptual data base design, Normalization Primitive and Composite data types, concept of physical and logical databases, data abstraction and data independence, data aggregation and Relational Algebra.Application Development using SQL: Host Language interface, embedded SQL programming, Stored procedures and triggers and views, Constraints assertions.Internal of RDBMS: Physical data organisation in sequential, indexed random and hashed files. Inverted and multilist structures, B trees, B+ trees, Query Optimisation, Join algorithm.Transaction Processing, concurrency control and recovery management. Transaction model properties and state serialisability. Lock base protocols, Two Phase Locking. |
| Unit 3 | Data Communication and Computer Networks | Computer Network Architecture, Circuit Switching, Packet And Massage Switching, Network Structure. Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Framing. Retransmission Algorithms.Multiple Access and Aloha. CSMA/CD and Ethernet. High Speed LANs and Topologies. Broadcast Routing and Spanning Trees.TCP/IP Stack. IP Networks and Internet. DNS and Firewalls. Intrusion Detection and Prevention.Transport Layer and TCP/IP. Network Management and Interoperability. |
| Exam Name | RPSC Programmer Exam Paper-1 : 2024 | |
|---|---|---|
| Exam Date | 27th October 2024 | |
| S.N. | Name of Subjects | No. of Questions Asked |
| 01. | Reasoning Test & Numerical Analysis & General Knowledge | 40 |
| 02. | Database Management Systems (DBMS) | 32 |
| 03. | Data Communication and Computer Networks (DCN) | 28 |
Q: Two phase locking protocol has which of the following problem(s)?
Chances of Deadlock
Cascading Rollback
Neither (a) nor (b)
Both (a) and (b)
[ Option D ]
Two-Phase Locking (2PL) protocol, which is used for concurrency control in database systems, has the problems of deadlock and cascading rollback.
Q: Consider following two instances of relations, X and Y:
| X | |
|---|---|
| Code | Item |
| 100 | A |
| 200 | B |
| 300 | B |
| 400 | C |
| Y | |
|---|---|
| Item | Quantity |
| A | 5 |
| B | 6 |
| C | 3 |
How many total tuples a Cartesian Product between the two relations X and Y will produce?
12
7
4
3
[ Option A ]
A Cartesian Product between two relations (tables) pairs every row of the first table with every row of the second table. So the total number of tuples is:
Total Tuples = (Number of tuples in X) × (Number of tuples in Y)
Here, Number of tuples in X = 4 and Number of tuples in Y = 3. This means every row of X will pair with every row of Y, producing 4×3 = 12 total tuples.
Q: Consider a relation with attributes {A, B, C, D} and the following functional dependencies:
A → B, B → C, and C → D. If A is the primary key, which of the following is true regarding BCNF?
The relation is in BCNF because all determinants are super keys.
The relation is in 3NF but not in BCNF.
The relation is not in BCNF.
The relation is in BCNF because it is in 3NF.
[ Option C ]
Given the relation R(A, B, C, D) with functional dependencies:
A → B
B → C
C → D
Primary Key: A
Check for BCNF:
A relation is in Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF) if for every functional dependency X→Y, X is a candidate key or super key.
So, BCNF ensures that each non—key (non—prime) attributes is dependent only on the candidate key.
A→B: A is the primary key (Super Key): Satisfy BCNF condition.
B→C: B is not a Super Key : Violates BCNF condition.
C→D: C is not a Super Key : Violates BCNF condition.
Check for 3NF:
The relation is in 3NF if there is no transitive dependency i.e., no non—prime attribute can determine another non—prime attribute.
A→B: A is the prime attribute : Satisfy 3NF condition.
B→C: Both B and C are non—prime attributes : Violates 3NF condition.
C→D: Both C and D are non—prime attributes : Violates 3NF condition.
Check for 2NF:
The relation is in 2NF if there is no partial dependency i.e., no proper subset of candidate key can determine the non—prime attribute.
The relation is at least in 2NF, if key contains only one attribute (here A is primary key, only one attribute no subset possible), then there is no partial dependency because one attribute has no subset. So, the relation is in 2NF. Among the given options the correct answer is The relation is not in BCNF.
Q: Which of the following concurrency control protocols ensure both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock?
(I) 2PL (Two Phase Lock)
(II) Time-Stamp ordering
(III) Multiple granularity protocol
I only
II only
III only
Both I and II
[ Option B ]
Concurrency Control in a database ensures that when multiple transactions run at the same time, they do not interfere with each other. Its main goal is to maintain correctness, consistency, and isolation so that the final result remains the same as if transactions were executed one by one.
When we check concurrency control protocols, we look for two important properties:
Two Phase Locking (2PL) ensures conflict serializability by enforcing that transactions lock data in two phases (growing and shrinking), but it does not guarantee freedom from deadlock. The deadlocks can still occur in 2PL.
Timestamp Ordering Protocol guarantees both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock because it assigns timestamps to transactions and schedules operations based on these timestamps, avoiding cyclic waits and deadlocks.
Multiple Granularity Protocol primarily helps reduce lock overhead and increase concurrency by using locks at different levels of granularity, but it does not guarantee deadlock freedom by itself. The deadlock can still occur.
Q: Which operation allows us to find tuples that are in one relation but are not in another relation?
Cartesian Product Operation
The Union Operation
The Set-Difference Operation
The Set Intersection Operation
[ Option C ]
In relational algebra, the set-difference operation (−) allows us to retrieve tuples that are present in one relation but not in another. It is written as R−S, returns all tuples that are in R but not in S.
This operation requires both relations to be Union-Compatible, meaning they must have the same set of attributes with compatible domains.
Q: Indices whose search key specifies an order different from the sequential order of the file are called—
Primary Indices
Random Indices
Sequential Indices
Secondary Indices
[ Option D ]
An Index in a database is a special data structure that helps the system locate records quickly without scanning the entire table.
Primary Indices correspond to the sequence of the data file itself, meaning the index key and the file are ordered the same way.
Secondary Indices have a search key order that is different from the sequential order of the data file. This allows access to data organized by non-primary keys, where the actual data storage is unrelated to the index ordering.
Q: What is the advantage of setting up a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) using firewall?
Improve network performance
To create multiple zones of trust
Load balancing on the server
Brings internet service into home from internet service provider
[ Option B ]
The primary advantage of setting up a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) using a firewall is to create multiple zones of trust within a network, which enhances security. A DMZ acts as a buffer zone between the public Internet and the internal private network, isolating public-facing servers (such as web, email, and DNS servers) from sensitive internal resources. This setup allows external users to access services in the DMZ while preventing direct access to the internal network.
Q: Consider the following instance of a relation District –
| District | |
|---|---|
| Name | Population |
| JA | 10 |
| AJ | 50 |
| MM | 5 |
Which of the District names will be returned by the following relational algebra expression?
(πName(σName=“AJ”(District)))–[(πName(σPopulation>5(District))∩(πName(σName=“AJ”(District)))]
MM
JA
JA, AJ
AJ
[ DELETE ]
Q: The primary use of scramblers in Line Coding Schemes is to—
Make the data look random
Compress transmission data
Decrease signal bandwidth
Increase signal bandwidth
[ Option A ]
A scrambler is used in line coding schemes to modify the original data before transmission.
Q: Which of the following is true for Circuit Switching handling multiple simultaneous connections?
A single path is used and shared for all data
It encodes all data into a single channel
Separate physical paths are allocated for each channel
All connections are multiplexed into a single channel
[ Option C ]
In Circuit Switching, a dedicated physical path (circuit) is created between the sender and receiver before communication starts. This path remains reserved for the entire duration of the call.
So, when multiple users communicate at the same time, each user gets a separate circuit.
Q: A Reverse Lookup in DNS means a lookup to _________ using _________ records.
map domain names to IP address, A
map IP address to domain name, PTR
determine the authoritative name servers, CNAME
identify mail servers, SOA
[ Option B ]
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phonebook of the internet. It helps us convert easy-to-remember domain names into numerical IP addresses that computers use to communicate. DNS makes browsing the internet simple and user-friendly.
There are two types of DNS lookups:
Forward Lookup: This converts a domain name to an IP address using A or AAAA records.
Reverse Lookup: This converts an IP address back to a domain name using a PTR (Pointer) record. It helps in verification, logging, and network troubleshooting.
Q: How many bits for ‘Fragment Offset’ field are there in IPv4 header?
10 bits
32 bits
13 bits
16 bits
[ Option C ]
The Fragment Offset field in the IPv4 header is 13 bits long. In the IPv4 header, the Fragment Offset field is used to indicate the position of a fragment in the original packet when fragmentation occurs.
Q: Which SQL statement is used in embedded SQL to fetch data into host variables?
INSERT INTO
UPDATE
DELETE
SELECT INTO
[ Option D ]
In embedded SQL, we write SQL statements inside a host programming language like C, Java, or COBOL. When we want to fetch data from a table and store it directly into host variables, we use the SELECT INTO statement.
The SELECT is used to read data from a table.
The INTO is used to store the fetched values into host language variables.
EXEC SQL SELECT column_name INTO :host_name FROM table_name WHERE condition;
E.g.:
Host variables in C:
char student_name[50];
int student_marks;
Embedded SQL SELECT INTO:
EXEC SQL SELECT name, marks
INTO :student_name, :student_marks
FROM Student
WHERE roll_no=101;
Q: The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used for –
Finding the IP address from the DNS.
Finding the IP address that corresponds to a MAC address.
Finding the IP address of the default gateway.
Finding the MAC address that corresponds to an IP address.
[ Option D ]
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used for finding the MAC address that corresponds to a given IP address within a Local Network.
When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it needs the MAC address (Physical Address) of the destination device to actually send the data.
ARP helps in this process by broadcasting a request with the target IP address to all devices on the network. Only the device with the matching IP responds with its MAC address, enabling the sender to Map the IP Address to the correct MAC Address.
Q: Let us assume that there are four (4) network segments in Bus topologies A1—A2, B1—B2—B3, C1—C2 and D1—D2—D3. If A1, B1, C1 and D1 are interconnected in mesh, then how many mesh connections are required?
45
6
10
12
[ Option B ]
Given 4 network segments represented by points A1, B1, C1, and D1 interconnected in a mesh, we need to find the total number of mesh connections.
With 4 nodes the number of connections is [4(4-1)/2] = [4*3/2] = 12/2 = 6.
Q: In ER Model, which of the following relationship is correct for a condition that a person in INDIA has an Aadhaar Card?
One to one relationship
One to many relationship
Many to many relationship
Many to one relationship
[ Option A ]
In India, each person has only one Aadhaar Card, and each Aadhaar number belongs to only one person.
This is a One-to-One (1:1) relationship in the ER Model.
Q: Which of the following Multiple Access Protocols is not suitable for wired networks?
CSMA/CA
CSMA/CD
TGMA
TDMA
[ Option A ]
In networking, multiple access protocols are used to manage how devices share the same communication medium.
In wired networks (Ethernet), devices can easily detect collisions, so CSMA/CD is used. But in wireless networks, devices cannot detect collisions properly because they cannot listen while transmitting. Therefore, CSMA/CA is used in Wi-Fi, and it is not suitable for wired networks.
Q: The size of the total length field of IPv4 datagram is–
16 bits
4 bits
8 bits
32 bits
[ Option A ]
The Total Length field in an IPv4 datagram header is 16 bits long. This field specifies the complete size of the IP packet, which includes both the header and the data portion.
Because it is a 16-bit field, it can represent values ranging from a minimum of 20 bytes (when no payload) up to a maximum of 65535 bytes.
| FIELD NAME | SIZE |
|---|---|
| Version | 4 bits |
| IHL (Internet Header Length) | 4 bits |
| DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) | 6 bits |
| ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) | 2 bits |
| Total Length | 16 bits |
| Identification | 16 bits |
| Flags | 3 bits |
| Fragment Offset | 13 bits |
| Time To Live (TTL) | 8 bits |
| Protocol | 8 bits |
| Header Checksum | 16 bits |
| Source IP Address | 32 bits |
| Destination IP Address | 32 bits |
| Options (if present) | Variable |
| Padding (if options present) | Variable |
Q: Correct order of applying 3 passes in ARIES recovery algorithm is—
Undo, Analysis, Redo
Analysis, Redo, Undo
Undo, Redo, Analysis
Analysis, Undo, Redo
[ Option B ]
ARIES stands for Algorithms for Recovery and Isolation Exploiting Semantics. It is a robust and widely-used database recovery algorithm designed to ensure data integrity and consistency in the event of system failures or crashes.
ARIES is based on the Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) protocol, which guarantees that any changes to the database are first recorded in a log before being applied to the database itself.
The correct order of applying the three passes in the ARIES recovery algorithm is Analysis, Redo, Undo.
| PHASE | PURPOSE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Determines the state of the system at crash time. | Starts from the latest checkpoint and scans forward to reconstruct active transactions and dirty pages. Identifies the starting point for redo. |
| Redo | Reapplies all modifications to ensure durability. | Repeats history by redoing all updates from the log starting at the earliest dirty page until the crash, bringing the database to the exact pre-crash state. |
| Undo | Rolls back incomplete transactions. | Scans the log backward to undo the effects of uncommitted or aborted transactions to maintain atomicity and consistency. |
Q: In a slotted ALOHA with G-stations attempting to transmit in one slot, the throughput is equal to –
e-G
G × e-2G
G × e-G
2G × e-G
[ Option C ]
ALOHA is a Random-Access Protocol used in computer networks for sharing a common communication channel.
It allows multiple users or stations to send data whenever they want, but collisions can occur if two or more stations send data at the same time.
Throughput means the rate of successful data transmission over a communication channel.
| TYPE OF ALOHA | DESCRIPTION | THROUGHPUT (EFFICIENCY) |
|---|---|---|
| Pure ALOHA | Stations transmit data anytime without synchronization. Collisions can occur if frames overlap. | S=G×e−2G Max = 18.4% |
| Slotted ALOHA | Time is divided into equal slots. The stations can transmit only at the start of a slot, reducing collisions. | S=G×e−G Max = 36.8% |
| PROTOCOL | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| ALOHA | Simple method but has high collisions. |
| Slotted ALOHA | Improved version using time slots to reduce collisions. |
| CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) | Stations listen to the channel before transmitting. |
| CSMA/CD (CSMA with Collision Detection) | Detects collisions and stops transmission. Used in Ethernet (IEEE 802.3). |
| CSMA/CA (CSMA with Collision Avoidance) | Avoids collisions using backoff and acknowledgment. Used in Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11). |
Q: What network property is achieved through the use of the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) mechanism?
Reliability
Availability
Confidentiality
Scalability
[ Option A ]
Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) is a network protocol used to achieve Reliability in data transmission. Its primary function is to ensure that data packets sent from a sender are correctly received by the receiver. If an error is detected in a transmitted packet or if an acknowledgement is not received within a specified timeout period, ARQ triggers the retransmission of that packet until it is correctly received and acknowledged.
This mechanism helps to maintain data integrity and overcome issues such as lost or corrupted packets in unreliable communication channels.
Q: Consider below statements –
(I) Each non-leaf node in B+ tree has between [n/2] and n children, where n is fixed for a particular tree.
(II) The search key of a clustering index is always primary key.
(III) Secondary indices must be dense.
(IV) In a dense index, an index entry appears for only some of the search-key values.
Which of the above statements are true?
I and IV
II and III
I and III
I and II
[ Option C ]
The statement (I) is true because, in B+ trees, to maintain balance and efficient use of space, the number of children for each internal (non-leaf) node must be at least half of the maximum allowed children, up to the maximum n.
The statement (II) is false because, a clustering index is based on the order in which data records are stored physically. The search key for the clustering index is the attribute(s) on which the file is ordered, which may or may not be the primary key.
The statement (III) is true because, secondary indices typically maintain an index record for every tuple in the data file to provide quick access regardless of the clustering. Hence, secondary indices are dense meaning an index entry exists for every search-key value.
The statement (IV) is false because, by definition, a Dense Index has an index record for every search-key value in the data file. A Sparse Index has entries for only some search-key values.
Q: The three-way handshake mechanism in TCP aims to—
Secure the communication.
Send bits from one device to another over an optical fibre connection.
Perform error detection and correction.
Establish connection and synchronize sequence numbers.
[ Option D ]
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol, which means it establishes a reliable connection before sending data. The three-way handshake involves three steps, SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK.
After these three steps, the connection is established and both sides have agreed on initial sequence numbers.
Q: What does /24 denote in CIDR?
24 bits are used for network portion.
24 addresses are available in the subnet.
24 subnets are created.
24 bits are used for host portion.
[ Option A ]
In CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation, the suffix “/24” denotes that 24 bits are used for the network part of the IP address. This means that the first 24 bits out of the total 32 bits in an IPv4 address identify the network, while the remaining 8 bits are used for host addresses within that network.
The "/24" notation corresponds to a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 in traditional dotted decimal format. It essentially tells how many bits are fixed for the network prefix, allowing flexible subnetting and efficient allocation of IP address space.
Q: For Stop-and-Wait ARQ, for 10 data packets sent, ________ acknowledgements are needed?
11
9
10
20
[ Option C ]
Stop-and-Wait ARQ is a protocol in which the sender transmits one data packet and waits for an acknowledgement before sending the next packet. Each data packet requires exactly one acknowledgement to confirm its successful receipt. Hence, if 10 data packets are sent, the receiver must send 10 acknowledgements.
Q: Consider following two instances of relation Student and Faculty with operation on these instances –
| Student | |
|---|---|
| D-Name | Strength |
| CS | 900 |
| IT | 500 |
| Cyber | 300 |
| ME | 1000 |
| CIVIL | 2000 |
| Faculty | |
|---|---|
| D-Name | Strength |
| EE | 2000 |
| ECE | 5000 |
| Cyber | 300 |
| DS | 100 |
| CIVIL | 2000 |
(A) Student – Faculty
(B) (Student ∩ Faculty) ∪ (Faculty ∩ Student)
(C) (Student ∪ Faculty) – (Student ∩ Faculty)
(D) Student ∩ Faculty
Identify the correct option that produces equivalent output –
B,C,D
B,D
A,B
B,C
[ Option B ]
To find which operations give the same output, we first identify the common tuples in both relations. The only matching rows between Student and Faculty are Cyber (300) and CIVIL (2000). This means the intersection Student ∩ Faculty contains exactly these two tuples.
Now, expression (B) calculates (Student ∩ Faculty) ∪ (Faculty ∩ Student). Since both intersections are the same, their union also gives the same two tuples: Cyber (300) and CIVIL (2000). Expression (D) directly performs Student ∩ Faculty, which naturally results in the same pair of tuples. Hence, B and D produce identical outputs.
Q: Which of the following protocol may be used as zeroconf and plug-and-play?
DHCP
ICMP
NAT
TCP
[ Option A ]
Zeroconf (Zero Configuration) and Plug-and-Play mean that a device should automatically get network settings without manual configuration. The protocol that helps devices automatically get an IP address, subnet mask, and other settings is DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Q: The physical layer is responsible for –
Process to process delivery.
Bit-by-bit delivery.
Application to application delivery.
Port to port delivery.
[ Option B ]
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model has seven layers, with the Physical Layer at the bottom (Layer 1).
The physical layer main job is to send raw bits (0s and 1s) from one device to another through a physical medium like cables, radio waves, or fiber optics. It does not understand data, packets, or addresses, it only deals with electrical signals, light signals, or radio signals.
| LAYER NAME | MAIN ROLE |
|---|---|
| Physical Layer | Bit-by-bit delivery over physical transmission medium. |
| Data Link Layer | Node-to-node delivery, framing, and error detection. |
| Network Layer | Logical addressing, routing, and packet forwarding. |
| Transport Layer | Process-to-process delivery, flow and error control. |
| Session Layer | Establishing, maintaining, and terminating sessions. |
| Presentation Layer | Data formatting, encryption, and translation. |
| Application Layer | Provides network services to end-user applications. |
Q: An organization has a Class B network and wishes to form subnets for 64 departments. The subnet mask would be –
255.255.0.0
255.255.252.0
255.255.64.0
255.255.128.0
[ Option B ]
To create subnets in a Class B network, we start with the default subnet mask 255.255.0.0. The organization wants 64 departments, which means they need 64 subnets. To find how many bits are needed for subnetting, we check powers of two, i.e., 2n ≥ 64.
When we try 26, we get 64, which matches the requirement. This means the network must borrow 6 bits from the host portion to create the subnets.
In a Class B address, the subnetting begins in the third octet. When we borrow 6 bits, the first 6 bits of the third octet become 1s. In binary, these 6 ones followed by two zeros give the value 252.
255.255.11111100.00000000
So, the subnet mask becomes, 255.255.252.0
Q: Consider a schema R(A, B, C, D) and functional dependencies A → B, C → D. Then, the decomposition of R into R1 and R2 where R1(AB) and R2(CD), is –
Dependency preserving but not lossless join
Not dependency preserving and not lossless join
Lossless join but not dependency preserving
Dependency preserving and lossless join
[ Option A ]
The decomposition of schema R(A,B,C,D) with functional dependencies A→B and C→D into R1(AB) and R2(CD), is dependency preserving but not lossless join.
Lossless Join: A decomposition is lossless if you can always recover the original relation by joining the decomposed relations, without losing any data. For a lossless join, the intersection of the schemas must be a key in at least one of the decomposed relations.
Dependency Preserving: A decomposition is dependency preserving if every functional dependency in the original relation is still enforceable in at least one of the decomposed relations without needing to join.
Q: An organized collection of logically related data is called—
Transaction
Metadata
Database
Data type
[ Option C ]
An organized collection of logically related data is called a Database. A database is designed to efficiently store, manage, and retrieve large amounts of data.
A Student database stores data like name, roll number, class, fees, marks, percentage, all related to Students.
Q: Consider Relation R1 and R2 as given below –
| R1(P,Q,R) | ||
|---|---|---|
| P | Q | R |
| p | q | r |
| k | i | j |
| m | q | r |
| d | e | f |
| R2(Q,R,S) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Q | R | S |
| q | r | n |
| l | c | o |
| q | r | a |
| q | r | b |
| e | f | g |
The number of tuples in output of R1 ⋈ R2 will be –
20
5
6
7
[ Option D ]
A Join is a relational database operation that combines rows from two tables based on a related attribute. It helps in retrieving connected information stored across multiple tables.
Among different types of joins, the Natural Join is a special type that automatically matches rows based on all columns with the same name and then merges them, removing duplicate columns in the output.
In this question, the natural join between R1 and R2 is performed on the common attributes Q and R. First, we identify matching pairs. In R1, the pairs (q, r) appear twice, and in R2, the same pair appears in three different rows. Each matching pair from R1 combines with all matching rows in R2, giving 2×3=6 tuples.
Additionally, the pair (e, f) in R1 matches one row in R2, giving 1 more tuple. The other pair (i, j) has no match, so it contributes zero. Adding them together, the Natural Join produces 6+1+0 = 7 tuples.
Q: Which operation requires two relations as input to form a new relation and these two relations must have a common attribute?
Division operation
Cartesian product operation
Natural join operation
Projection operation
[ Option C ]
The operation that requires two relations as input and needs these two relations to have a common attribute to form a new relation is the Natural Join operation.
Natural join automatically joins two relations based on all attributes with the same name and compatible data types in both relations. It matches and combines rows where the common attribute values are equal.
Relation Student:
| RollNo | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Suresh |
| 2 | Salman |
| 3 | Ramesh |
Relation Marks:
| RollNo | Marks |
|---|---|
| 1 | 85 |
| 2 | 90 |
| 4 | 75 |
Natural Join (Student ⋈ Marks) : The join matches rows where RollNo is common.
| RollNo | Name | Marks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suresh | 85 |
| 2 | Salman | 90 |
Q: Consider following relation S(S1, S2, S3, E1, E2) and functional dependencies hold on the schema are as—
FD1: S1 → {S2, S3}
FD2: {E1, S3, S2} → S1
FD3: E2 → {S3, S2, E1}
What is the highest normal form of the relation S?
1NF
2NF
BCNF
3NF
[ Option B ]
To determine the highest normal form of the relation S(S1,S2,S3,E1,E2) with the given functional dependencies:
FD1: S1→{S2,S3}
FD2: {E1,S3,S2}→S1
FD3: E2→{S3,S2,E1}
First of all, find the key. Using the above functional dependencies the E2 determine all the attributes, so, E2 is candidate key. That makes E2 the only prime attribute.
Prime Attribute : E2.
Non-Prime Attribute : S1, S2, S3, E1.
Check 2NF:
The relation is at least in 2NF, if key contains only one attribute, then there is no partial dependency because one attribute has no subset. So, the relation is in 2NF.
Check 3NF:
The relation is called in 3NF it is already exists in 2NF and there is no transitive dependency exists.
In the given relation FD set, the S1 can determine S2 and S3. The S1, S2 and S3 are non-prime attributes so these violets the rule of transitive dependency.
So, the highest normal form the relation satisfies is Second Normal Form (2NF).
Q: ICMP protocol is a ________ layer protocol.
Data link
Application
Transport
Network
[ Option D ]
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol in the OSI model. It is used for sending error messages and network status information. For example, commands like ping and traceroute use ICMP to check if a device is reachable.
Q: Which of the following is not related to data link layer?
Congestion Control
Error Control
Framing
MAC Addressing
[ Option A ]
The Data Link Layer is responsible for Node-To-Node Delivery and ensures reliable communication over a physical link. It performs key functions such as Framing, Error Control, and MAC Addressing, all of which are essential for organizing data into frames, detecting, or correcting errors, and identifying devices on the network.
However, Congestion Control is typically not a function of the data link layer; it is primarily handled by higher layers such as the network or transport layer to manage traffic load and avoid network congestion.
Q: Total time to access a disk block is given by the—
Seek time + rotational delay
Seek time + rotational delay + transfer time
Seek time + transfer time
Seek time
[ Option B ]
Accessing a disk block involves three main components:
Seek Time: The time taken for the disk arm to move the read/write head to the track where the desired block is located.
Rotational Delay (Latency): The time it takes for the disk platter to rotate so that the desired sector is under the read/write head.
Transfer Time: The time required to actually read or write the data once the head is in position.
All three components combined give the total time required to access a disk block.
Total Access Time = Seek Time + Rotational Delay + Transfer Time
Q: In Relational Model, which type of constraint does not allow composite and multivalued attributes?
Entity integrity constraints
Domain constraints
Referential integrity constraints
Uniqueness constraints
[ Option B ]
In the Relational Model, every attribute in a table must store a single, indivisible value. This means the model does not allow composite attributes, which can be divided into sub-parts, or multivalued attributes, which can hold more than one value at the same time. The type of rule that enforces this requirement is known as a Domain Constraint.
Domain constraints define what type of values an attribute (column) can store. They ensure that:
Thus, domain constraints automatically prevent composite and multivalued attributes.
Q: In ER Model constructs, which type of attribute is most suitable to represent the skill(s) of an employee for an organization?
Derived Attribute
Composite Attribute
Atomic Attribute
Multivalued Attribute
[ Option D ]
In an ER (Entity–Relationship) Model, an attribute is a property or characteristic of an entity. It tells us something about the entity. Attributes describe the entity with the help of values.
For example, for entity Employee the Name, Age, Salary, Skills and for entity Student the Roll No, Course, Address are attributes.
| Attribute Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple or Atomic Attribute | This type of attribute cannot be divided into smaller meaningful parts. It contains a single, indivisible value that represents one property of the entity. | Age of an employee or salary of an employee. |
| Composite Attribute | This type of attribute can be broken down into smaller sub-parts, and each sub-part represents a more detailed level of information. It is useful when an attribute naturally consists of multiple components. | An address can be divided into street, city, and state. Similarly, the name can be divided into first_name, middle_name, and last_name. |
| Derived Attribute | This type of attribute does not store its value permanently. Instead, its value can be calculated from other attributes whenever needed. It is not physically saved in the database but can be obtained through computation. | Age can be calculated from date of birth. |
| Multivalued Attribute | This type of attribute can hold more than one value for the same entity. It is used when the number of possible values is not fixed, meaning an entity may have zero, one, or many such values. | An employee can have multiple skills or multiple phone numbers. |
| Key Attribute | This attribute uniquely identifies each record in an entity set. No two entities share the same value for a key attribute. | Roll number for a student or employee ID for an employee. |
| Single-Valued Attribute | This attribute holds only one value at a time for an entity. It cannot contain multiple values simultaneously. | A person's gender or a student's blood group. |
Because an employee can have multiple skills, and ER models represent such attributes as Multivalued Attributes.
Q: The cardinality of a relational table with 5000 rows and 10 columns is—
5000
10
500
50000
[ Option A ]
In a relational database table, Cardinality refers to the total number of rows or records present in the table. It represents how many individual data entries the table holds.
The Degree refers to the total number of columns or attributes in the table, which describe the structure of each record.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Rows (Cardinality) | 5000 |
| Number of Columns (Degree/Arity) | 10 |
Q: Consider a relation R with attributes (A, B, C), where B is the only candidate key. Identify the total number of possible super keys of the relation R.
1
3
4
2
[ Option C ]
A superkey is any set of attributes that can uniquely identify a tuple in a relation. If you have a relation with n attributes and one candidate key consisting of k attributes, the total number of super keys is 2n−k.
Remember, this formula can only work with a relation has only one candidate key consisting of k attributes.
Given,
Relation: R(A, B, C)
Total Attributes (A,B,C) n = 3.
Candidate key B : k = 1
Total super keys: 23−1 = 22 = 4.
Q: Consider following schedule with a sequence of operations on a data object Q having the initial value of 500:
| T1 | T2 |
|---|---|
| Read (Q) | |
| Read (Q) | |
| Q = Q + 100 | |
| Q = Q + 100 | |
| Write (Q) | |
| Write (Q) |
What will be the final value of Q after the last operation is completed?
600
700
550
500
[ Option A ]
The data item Q initially = 500.
Schedule Step by Step:
Because both transactions read the original value 500 and each computed 600, the second write simply overwrites the first with the same value. The final value of Q after the last operation is 600.
Q: Which of the following protocol is used for transferring email messages from one machine to another?
SNMP
TELNET
SMTP
FTP
[ Option C ]
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to send email from one computer (Mail Server) to another over the internet. Whenever you send an email, SMTP is responsible for transferring your message from the sender’s server to the receiver’s server.
The SMTP operates over TCP, commonly on port 25, ensuring reliable delivery of messages across networks.
Q: The operation which can be used to specify automatic actions that the database system will perform when certain events and conditions occur is known as—
CREATE TRIGGER
CREATE VIEW
CREATE ASSERTION
CREATE TABLE
[ Option A ]
In SQL, the operation used to define automatic actions that the database system should perform when specific events occur (such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE) is called Trigger. A trigger is a stored program that executes automatically whenever a specified event happens on a table.
Triggers help in maintaining data integrity, enforcing business rules, automating tasks like auditing changes, and validating data before or after modification. They run without explicit invocation by users, ensuring consistent and automatic enforcement of rules defined at the database level.
Q: IP address 172.16.123.213 is found to be residing on a sub-network with the following subnet mask 255.255.255.240. What is the network address of this subnet?
172.16.123.213
172.16.123.240
172.16.123.245
172.16.123.208
[ Option D ]
To find the network address of the subnet where:
IP address 172.16.123.213
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.240
First, convert the subnet mask to binary 255.255.255.240 corresponds to: 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000
The last octet’s binary mask is 11110000, meaning the subnet block size is 256−240=16.
Find the subnet block where 213 belongs:
| Subnet | Range |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0–15 |
| 1 | 16–31 |
| 2 | 32–47 |
| 3 | 48–63 |
| 4 | 64–79 |
| 5 | 80–95 |
| 6 | 96–111 |
| 7 | 112–127 |
| 8 | 128–143 |
| 9 | 144–159 |
| 10 | 160–175 |
| 11 | 176–191 |
| 12 | 192–207 |
| 13 | 208–223 |
| 14 | 224–239 |
| 15 | 240–255 |
213 falls in 208–223, so, network address is 172.16.123.208
Another alternative solution to find the network address for IP 172.16.123.213 with subnet mask 255.255.255.240 is to perform a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask.
IP: 172.16.123.213, last octet binary : 213=11010101
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240 last octet binary 240=11110000
Perform bitwise AND between IP and subnet mask
IP : 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
Mask: 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
Bitwise AND: 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
Decimal of binary 11010000 is 208. So, combine with first three octets 172.16.123. Finally the network address is 172.16.123.208
Q: Any relation that is not a part of the Logical Model, but is made visible to a user as a virtual relation is called a –
Tuple
View
Instance
Schema
[ Option B ]
In a database, a View is a relation that does not actually exist as a stored table in the logical model. Instead, it is created using a query and shown to the user as a Virtual Table. The data in a view comes from one or more real tables, but the view itself does not store data permanently.
To create a view, we use the CREATE VIEW command followed by the view name and a SELECT query that determines the view's contents.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Q: An ER Model describes which type of schema?
Internal Schema
External Schema
Conceptual Schema
Physical Schema
[ Option C ]
An ER (Entity-Relationship) Model is used to visually represent the structure of a database.
This type of representation corresponds to the Conceptual Schema of a database.
Q: The size of MAC address (in bits) is—
24
48
36
42
[ Option B ]
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a hardware identifier assigned to each Network Interface Card (NIC). It works at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model and ensures that each device on a local network can be uniquely identified.
Q: If a Class B network on the internet has a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0, what is the maximum number of hosts per subnet?
1023
1022
1024
2046
[ Option D ]
A Class B network has a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0, meaning the first two octets (16 bits) represent the network portion. The given subnet mask is 255.255.248.0. To interpret this:
The number of usable host addresses per subnet is calculated as 211−2, which equals 2046.
We subtract 2 because one address is the Network Address and one is the Broadcast Address, which cannot be assigned to hosts.
Q: The number of attributes in a relation is known as—
Features of the relation
Address of the relation
State of the relation
Degree of the relation
[ Option D ]
The number of attributes or columns in a relation is known as the Degree of the relation. Sometimes it is also called Arity.
Q: What is the role of DNS? It is best described as –
Translate a host's IPv6 address to an IPv4 address
Maps a MAC address to an IP address
Translate a host's private IP address to a public IP address
Maps a domain name to an IP address
[ Option D ]
DNS (Domain Name System) works like the “PHONEBOOK OF THE INTERNET”. It takes a human-readable domain name like www.surakuacademy.com and finds the corresponding numerical IP address (like 46.28.45.103) so that computers can locate and connect to the correct server. Without DNS, users would have to remember and type IP addresses instead of easy names.
What DNS Does:
Q: Which one of the following statement is not correct?
Data models provide necessary means to achieve data abstraction.
Self-describing nature of database system is one of the characteristics of the database approach.
Database approach doesn't support data independence between data and programs.
Database approach supports multiple views of the data.
[ Option C ]
A database system is designed to separate data from programs, so that if the data structure changes, programs do not need major rewriting. This feature is called Data Independence, and it is supported by the database approach.
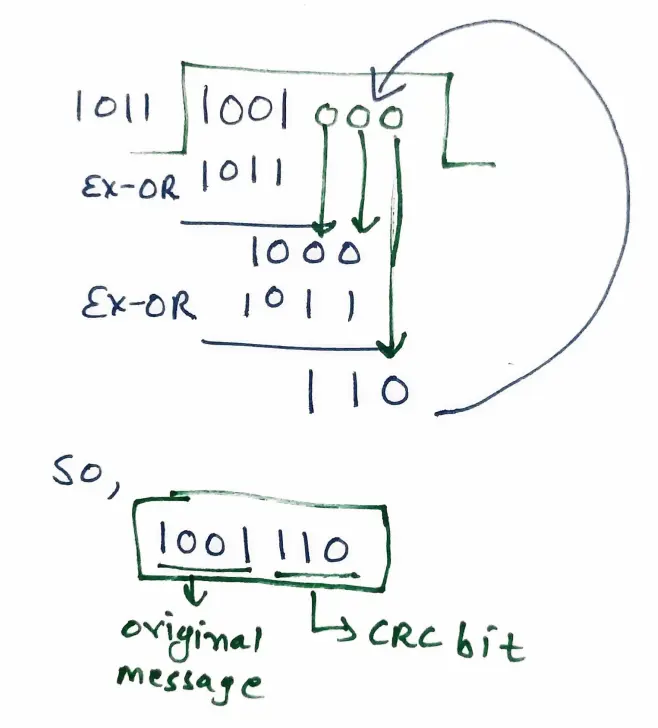
Q: The message 1001 is to be transmitted using the CRC polynomial x3+x+1 to protect it from errors. The message that should be transmitted is—
1001000
1001100
1001110
1001011
[ Option C ]
Given,
Message : 1001
CRC Polynomial (CRC Generator) : x3+x+1, binary 1011 (Degree 3)
Append 3 zero to the message because degree of polynomial is 3 or n-1 times (if n is CRC Generator).
Now perform Binary Division (Modulo 2):
Divide 1001000 by 1011 (Binary Division, XOR for Subtraction)
1001000 ÷ 1011, Remainder is 110.
This remainder is CRC bit.
Transmitted Message : Original Message + CRC Bits = 1001 + 110 = 1001110
Q: Network Allocation Vector (NAV) is associated with which of the following MAC technologies?
CSMA/CD
Bluetooth
Wi-Fi
Ethernet
[ Option C ]
NAV (Network Allocation Vector) is a virtual carrier sensing mechanism used in Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) networks as part of the CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) protocol.
It acts as a timer that indicates how long the wireless medium will be busy based on the duration information contained in MAC frame headers.
Q: The reliable data transfer is implemented by ______________.
Network Layer
Presentation Layer
Physical Layer
Transport Layer
[ Option D ]
Reliable data transfer means ensuring that data reaches the receiver without errors, without loss, and in the correct order.
Reliable data transfer is implemented by the Transport Layer in the OSI model. The transport layer is responsible for providing end-to-end communication services for applications.
It ensures reliable delivery of data through mechanisms such as error detection and correction, flow control, segmentation, acknowledgment of received data, and retransmission of lost or corrupted segments.
Protocols like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) at this layer offer connection-oriented and reliable communication by managing data packets and maintaining the order and integrity of the data transmitted between sender and receiver.
Q: In IPv4, packet fragmentation and reassembly is handled by _______________.
using the More Fragments and Fragment Offset Fields
using the Header Checksum
encapsulating packets in larger data frames
using the MAC Header
[ Option A ]
In IPv4, a packet may need to be fragmented if it is larger than the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of the network.
Fragmentation: The large packet is broken into smaller fragments.
Reassembly: The receiver combines the fragments back into the original packet.
IPv4 uses two fields in the IP header to manage this process:
These fields allow the receiver to correctly reassemble all fragments in order.
Q: What are the maximum number of spanning trees (Tn) possible for a complete graph K5 on 5 vertices?
100
20
200
125
[ Option D ]
A spanning tree of a graph is a tree that connects all the vertices without forming any cycle.
For a complete graph Kn ,where every vertex is connected to every other vertex, the number of possible spanning trees is given by Cayley’s formula, Tn=nn−2.
Here, n = 5 so, T5=55−2 = 53 = 125.
Q: There are n stations in a slotted LAN. Each station attempts to transmit with a probability p in each time slot. What is the probability that only one station transmits in a given time slot?
1 – (1 – p)n-1
(1 – p) n-1
n × p × (1 – p)n-1
p × (1 – p)n-1
[ Option C ]
In a slotted LAN, all n stations get a chance to send data in every time slot. Each station tries to send with a probability p. To find the probability that only one station sends data, we think about two things:
Because any one of the n stations could be the one that transmits successfully, we multiply by n. So, the probability that only one station transmits is n×p×(1−p)n−1.
Q: View in a database is –
A method to improve database performance
A physical table that stores data
A virtual table created by querying one or more tables
A backup copy of a database
[ Option C ]
In SQL (Structured Query Language), a view is a virtual table that is created based on the result of a query. It does not store data physically.
To create a view, we use the CREATE VIEW command followed by the view name and a SELECT query that determines the view's contents.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Q: Which set of SQL language commands is used to query and update a database?
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Both Data Control Language (DCL) and Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
[ Option D ]
The Data Manipulation Language (DML) is the part of SQL used to query and update data in a database.
| Category | Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDL (Data Definition Language) | CREATE | Creates a new database, table, or other database object. | CREATE TABLE Students (Rollno INT, Name VARCHAR(50)); |
| ALTER | Modifies the structure of an existing database object (add/drop column, change datatype). | ALTER TABLE Students ADD Age INT; | |
| DROP | Deletes a database, table, or object permanently. | DROP TABLE Students; | |
| TRUNCATE | Deletes all rows from a table but keeps the table structure. | TRUNCATE TABLE Students; | |
| RENAME | Renames a table or database object. | ALTER TABLE Students RENAME TO PGStudent; | |
| DML (Data Manipulation Language) | INSERT | Adds new rows (tuples) to a table. | INSERT INTO Students VALUES (1001, 'Suresh'); |
| UPDATE | Modifies existing rows in a table. | UPDATE Students SET Age = 31 WHERE Rollno = 1001; | |
| DELETE | Removes specific rows from a table. | DELETE FROM Students WHERE Rollno= 1001; | |
| DCL (Data Control Language) | GRANT | Gives privileges/permissions to users. | GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON Students TO User1; |
| REVOKE | Removes privileges/permissions from users. | REVOKE INSERT ON Students FROM User1; | |
| DQL (Data Query Language) | SELECT | Retrieves data from one or more tables. | SELECT Name, Age FROM Students; |
| TCL (Transaction Control Language) | COMMIT | Saves all changes made in the current transaction permanently. | COMMIT; |
| ROLLBACK | Undoes all changes made in the current transaction. | ROLLBACK; | |
| SAVEPOINT | Sets a point within a transaction to which you can roll back. | SAVEPOINT sp1; |
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.