Q: 1 Which gate is equivalent to (NOR) OR (XOR)?
NAND gate
OR gate
AND gate
XOR gate
[ Option A ]
A NOR gate is the complement of the OR gate. It gives output 1 only when all inputs are 0.
Boolean Expression : = (A+B)′
An XOR gate gives output 1 when the inputs are different or if the number of 1’s are odd and 0 when the inputs are the same.
Boolean Expression : = A⊕B
Now the given expression is (NOR)OR(XOR) i.e., (A+B)’ + (A⊕B)
| A | B | (A+B)' | A⊕B | (A+B)’ + (A⊕B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Now, we construct the truth tables of NAND, OR, and AND gates and verify their behavior using the given equation.
| A | B | AND = (A.B) | NAND = (A.B)’ | OR = (A+B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
The NAND gate behavior exactly matches with given expression.
Therefore, (NOR)OR(XOR) = NAND
Q: 2 Output of 2-inputs NAND gate if one of its input is permanently connected to ‘0’ is :
0
1
High Impedance state
Not Defined
[ Option B ]
A NAND gate produces the output as the negation of the AND operation, i.e., Y=(A⋅B)’. If one of its inputs is permanently connected to 0, then the AND operation becomes 0⋅B=0. So, Y=(0⋅B)′=0′=1. This means the output of the NAND gate will always be 1 regardless of the other input. Hence, the correct answer is 1.
Q: 3 The logic gate that provides high output for same input is
NOT
X-NOR
XOR
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The X-NOR gate, produces a high (1) output when both inputs are the same, either both 0 or both 1.
Truth—Table:
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | Y=A⊙B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q: 4 The minimum number of NAND gates required for implementing the Boolean expression, AB+AB’C+AB’C’ is?
1
0
2
3
[ Option C ]
Given Boolean expression:
=AB+AB’C+AB’C’
=AB+AB’(C+C’)
=AB+AB’.1
=AB+AB’
=A(B+B’)
=A.1
=A
To get output A, there is two NAND gate required.
Q: 5 The logical output of EX-NOR gate is:
(A'.B + A. B')
(A.B + (A.B)')
(A'.B' + A.B')
(A.B + A'.B')
[ Option D ]
The EX-NOR (Exclusive-NOR) gate is the complement of the EX-OR (Exclusive-OR) gate. While an EX-OR gate gives output 1 when the inputs are different, the EX-NOR gate gives output 1 when the inputs are the same that means, both inputs are 0 or both are 1.
| Input A | Input B | Output (A ⊙ B) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The Boolean expression for an EX-NOR gate is:
Y=A⊙B = (A⊕B)’ = A.B+A’B’
Q: 6 Which of the following is an example of a digital electronic?
Computers
Mobile phones
Digital cameras
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
Digital electronics are devices that operate using binary signals. They process information in discrete steps rather than continuous signals.
Examples of digital electronic devices include computers, which use digital circuits for all processing tasks, mobile phones, which contain digital processors and memory and digital cameras, which convert images into digital data.
Q: 7 Which one of the following expressions does not represent Exclusive NOR of x and y?
xy+x’y’
x⊕y’
x’⊕y
x’⊕y’
[ Option D ]
The Exclusive-NOR (XNOR) function gives output 1 when both inputs are equal. The standard Boolean expression of XNOR is:
x⊙y = xy+x′y′
The option (A) is xy+x′y′. This is the standard form of XNOR.
The option (B) is x⊕y’. Complementing one input of an XOR gate inverts the output, so it becomes XNOR.
In other word, as we know x⊕y is equivalent to x’y+xy’. Similarly, x⊕y’ is equivalent to x’y’+xy’’, which further evaluated to x’y’+xy. This is the standard form of XNOR.
In other words, as we know that x⊕y is equivalent to x′y+xy′. Similarly, x⊕y′ is equivalent to x′y′+xy′′ (replacing y by y’). Since y′′=y, this expression further simplifies to x′y′+xy, which is the standard form of the XNOR function.
The option (C) is x’⊕y. Same logic as option (B).
The option (D) is x’⊕y’. Complementing both inputs of XOR does not change the operation.
The expression x′⊕y′ = x⊕y. This is XOR, not XNOR.
Q: 8 The minimum number of NAND gates required to realize AB+AB'C+AB'C' is?
3
2
4
0
[ Option D ]
First simplify the given boolean expression.
=AB+AB’C+AB’C’
=AB+AB’(C+C’)
=AB+AB’.1
=AB+AB’
=A(B+B’)
=A.1
=A
The given expression simplifies to A, so the output can be directly taken from input A. Therefore, the minimum number of NAND gates required is zero.
Q: 9 The logical XOR operation of (4AC0)16 and (B53F)16 results?
(AACB)16
(0000)16
(FFFF)16
(ABCD)16
[ Option C ]
The XOR (Exclusive OR) is a logical operation in which the output is 1 when the inputs are different, and the output is 0 when the inputs are the same.
In other words, the output of an XOR gate is 1 when the number of 1’s at the input is odd, otherwise, the output is 0.
XOR operation between (4AC0)16 and (B53F)16:
| Hex Digit (1) | Hex Digit (2) | Binary (1) | Binary (2) | XOR Result | Hex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | B | 0100 | 1011 | 1111 | F |
| A | 5 | 1010 | 0101 | 1111 | F |
| C | 3 | 1100 | 0011 | 1111 | F |
| 0 | F | 0000 | 1111 | 1111 | F |
So, (4AC0)16 XOR (B53F)16 = (FFFF)16
Q: 10 Digital circuit can be made by the repeated use of the _________.
NAND gate
NOR gate
AND gate
More than one of the above
[ Option D ]
In digital electronics, a Universal Gate is a gate that can be used to build any digital circuit. Both NAND and NOR gates are considered universal gates. This means that by repeatedly using only NAND gates, we can construct AND, OR, NOT, XOR, XNOR and any other logic circuit. Similarly, by repeatedly using only NOR gates, we can implement all other logic functions as well.
Q: 11 Which of the following logic gates is called universal gate?
AND
OR
NAND
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
The gate through this we can design or construct any type of digital circuit without using any other gate is called universal gate. Basically, these are of two types:
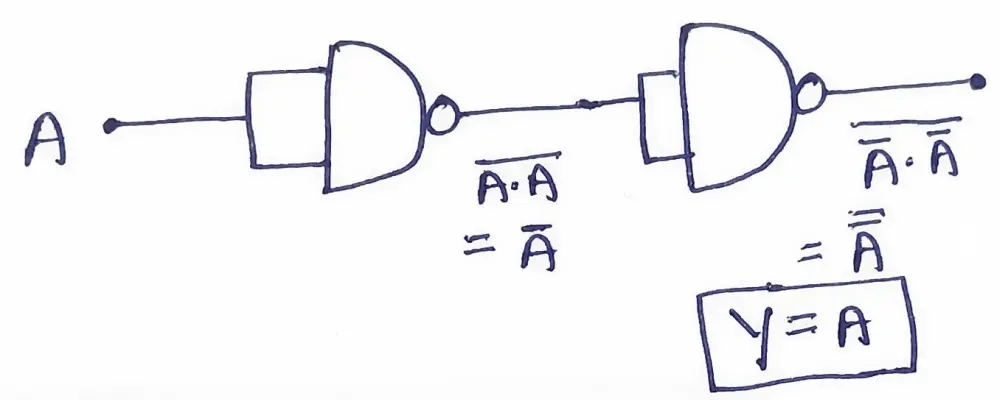
Q: 12 How many minimum numbers of two input NAND gates are required to design NOR gate?
6
4
5
3
[ Option B ]
A NOR gate performs the operation : (A+B)′
To design a NOR gate using only two-input NAND gates, a total of four NAND gates are required. Consider the below given circuit diagram.
Q: 13 The dual of the Boolean expression is obtained by
Interchanging all 0s and 1s
Interchanging all 0s and 1s, all + and ‘.’ Signs
Interchanging all 0s and 1s, all + and ‘.’ Signs and complementing all the variables
None of the above
[ Option B ]
Principle of Duality says, every algebraic expression remains valid if you interchange:
In simple words, for every Boolean law or expression, there exists a dual expression that is also valid. E.g.:
Q: 14 Which of the following is a functionally complete set of gates.
I. NAND
II. NOT
I but not II
II but not I
Neither I nor II
Both I and II
[ Option A ]
A functionally complete set of gates is a set using which any Boolean function can be implemented.
In digital circuit, the Universal Gates are functionally complete set of gates because a universal gate is a logic gate using which any Boolean function can be implemented without using any other type of gate.
The NAND and NOR gates are called universal gates because each of them alone is sufficient to construct all basic logic gates such as AND, OR and NOT.
Q: 15 Which of the following is correct for digital circuits?
They use analog signals for communication
They process information using continuous voltage levels
They are not suitable for high speed operations
None of the above
[ Option D ]
Digital circuits work with discrete (binary) voltage levels, usually represented as 0 (Low) and 1 (High). They do not use analog or continuous signals for processing, instead, they rely on step-like voltage changes.
The digital circuits are actually highly suitable for high-speed operations, that’s is why they are used in modern computers, microprocessors, and communication systems.
Q: 16 If signal passing through a gate is inhibited by sending a low into one of the inputs and the output is high, the gate is?
NOR
NAND
AND
OR
[ Option B ]
An inhibit gate is a logic gate in which the output of the circuit is controlled by a specific input called the inhibit (or control) input. When this inhibit input is applied with a particular logic level, it prevents or blocks the signal applied at the other input from affecting the output.
For a NAND gate, if any input is 0, the output becomes 1, regardless of the other input. Thus, when a low (0) is applied to one input, it inhibits the effect of the other input and forces the output to be high (1).
NAND ACTS AS AN INHIBIT GATE:
| CONTROL (INHIBIT) INPUT | SIGNAL INPUT | OUTPUT |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 or 1 | 1 (Blocked) |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
When the control input is 0, the output is forced to 1, so the signal input has no effect on the output.
Q: 17 An OR gate has 4 inputs. The number of words in truth table will be ________.
4
8
16
None of the above
[ Option C ]
A truth table shows all possible input combinations for a logic gate. If a gate has n inputs, the number of possible combinations is given by the formula 2ⁿ. For an OR gate with 4 inputs, the number of rows in the truth table will be 24=16. This means there are 16 different input combinations, each producing an output.
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | Y=A+B+C+D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q: 18 If there are 3 inputs of a logic gate, A, B, C with the output (A'+B'+C') then the logic gate is:
NOR
Ex-OR
OR
NAND
[ Option D ]
The given output expression is Y=A′+B′+C′. By applying De Morgan’s law, this can be rewritten as Y=(A⋅B⋅C)′. This form directly represents the operation of a NAND gate, since a NAND gate produces the complement of the AND operation.
Q: 19 A bulb in the staircase has two switches, one switch is at the ground floor and the other one is at the first floor. The bulb can be turned ON and also can be turned OFF by any of the switches irrespective of the state of the other switch. The logic of the switching of the bulb resembles.
XOR Gate
AND Gate
OR Gate
XNOR Gate
[ Option A ]
In a staircase wiring system, toggling either switch changes the state of the bulb. If the bulb is ON, it turns OFF and if it is OFF, it turns ON, regardless of the position of the other switch. This behavior matches the XOR (Exclusive OR) gate, where the output is 1 when the inputs are different and 0 when the inputs are the same.
Q: 20 What is the result of the operation 1010 AND 1100 in binary?
1000
1110
100
None of the above
[ Option A ]
The AND operation compares each corresponding bit of two binary numbers. The output is 1 only when both bits are 1, otherwise it is 0. 1010 AND 1100 = 1000
Q: 21 (FE35)16 XOR (CB15)16 is equal to
(FF35)16
(FF50)16
(3520)16
(3320)16
[ Option C ]
To perform XOR between two hexadecimal numbers, each hex digit is first converted into its 4-bit binary equivalent. For (FE35)₁₆ and (CB15)₁₆, the binary forms are 1111111000110101 and 1100101100010101, respectively. Performing bitwise XOR gives 0011 0101 0010 0000, which in hexadecimal is (3520)₁₆.
(FE35)16 ⊕ (CB15)16
First of all, write both numbers in binary form, so,
| Hexadecimal | Binary (4 bits) |
|---|---|
| F | 1111 |
| E | 1110 |
| 3 | 0011 |
| 5 | 0101 |
| C | 1100 |
| B | 1011 |
| 1 | 0001 |
| 5 | 0101 |
So,
FE35 = 1111 1110 0011 0101
CB15 = 1100 1011 0001 0101
Perform bitwise XOR:
| Pair | XOR result | Hexadecimal |
|---|---|---|
| F (1111) ⊕ C (1100) | 0011 | 3 |
| E (1110) ⊕ B (1011) | 0101 | 5 |
| 3 (0011) ⊕ 1 (0001) | 0010 | 2 |
| 5 (0101) ⊕ 5 (0101) | 0000 | 0 |
Finally, (FE35)16⊕(CB15)16 = (3520)16.
Q: 22 Let ⊕ and ⊙ denote the Exclusive-OR and Exclusive-NOR operation respectively. Which one of the following is not correct?
P’⊕Q’ = P⊙Q
P’⊕Q =P⊙Q
P’⊕Q’ = P⊕Q
(P⊕P’)⊕Q = (P⊙P’)⊙Q
[ Option A ]
As we know, XOR gives output 1 when inputs are different, while XNOR gives output 1 when inputs are the same.
Suppose A and B are two boolean variable then:
A XOR B = A⊕B = A’B+AB’
A XNOR B = A⊙B = A’B’+AB
Option (A):
P’⊕Q’ = P⊙Q
P’⊕Q’ = P’’Q’+P’Q’’
P’⊕Q’ = PQ’+P’Q
Therefore, P’⊕Q’ = P⊕Q not P⊙Q
Option (B):
P’⊕Q =P⊙Q
P’⊕Q = P’’Q+P’Q’
P’⊕Q = PQ+P’Q’
Therefore, P’⊕Q = P⊙Q
Option (C):
P’⊕Q’ = P⊕Q
As we already discussed in Option (A) P’⊕Q’ = P⊕Q
Option (D):
(P⊕P’)⊕Q = (P⊙P’)⊙Q
| LHS | RHS |
|---|---|
| (P⊕P’)⊕Q (P’P’+PP’’)⊕Q (P’+P) ⊕Q 1⊕Q 1’Q+1Q’ 0.Q+Q’ 0+Q’ Q’ | (P⊙P’)⊙Q (P’P’’+PP’)⊙Q (0+0)⊙Q 0⊙Q 0’.Q’+0.Q 1.Q’+0 Q’+0 Q’ |
Q: 23 To change upper to the lower case letter in ASCII, correct mask and operation should be?
0100000 and NOR
0100000 and NAND
1000000 and OR
0100000 and OR
[ Option D ]
In the ASCII coding system, uppercase and lowercase letters are represented by different binary patterns. The important point is that the difference between an uppercase letter and its corresponding lowercase letter is only one bit. This bit is known as the case bit and has a decimal value of 32, which in binary is 0100000. For example, the ASCII code of uppercase A is 1000001, while lowercase a is 1100001. The difference between them is the bit 0100000.
To change an uppercase letter into a lowercase letter, this case bit must be set to 1. In digital logic, the OR operation is used when we want to force a particular bit to become 1.
Therefore, performing an OR operation between the ASCII code of an uppercase letter and the mask 0100000 will convert it into the corresponding lowercase letter.
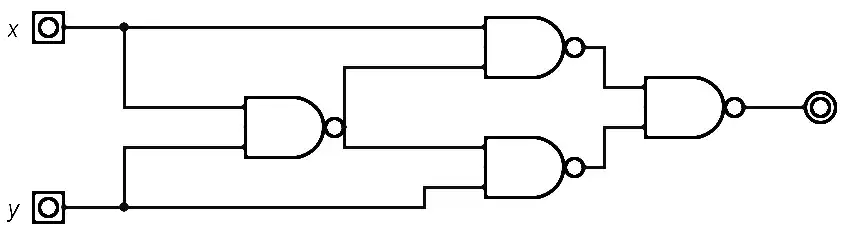
Q: 24 The minimum number of NAND gates required to implement Boolean function f=x’y+xy’ is
3
4
6
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The given Boolean function f=x’y+xy’ represents the XOR (Exclusive-OR) operation between variables x and y. It is well known that an XOR function can be implemented using 4 two-input NAND gates.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.