Q: 1 A sender wants to compute the checksum for the ASCII text "RPSC". Which of the following is the correct 16-bit checksum (in hexadecimal) for the string "RPSC"? Given that each character's ASCII hexadecimal equivalent ('R' → 0x52, 'P' → 0x50, 'S' → 0x53, 'C' → 0x43).
5A6C
5B6D
A593
6A5C
[ Option A ]
A Checksum is a simple method used in data communication to detect errors in transmitted messages. The basic idea is to sum the numerical values of all data units using one’s complement arithmetic (end-around carry) , and then taking the one’s complement of the final sum.
End-around carry means add MSB carry-out back into LSB for one’s-complement addition.
Q: 2 Which of the following Multiple Access Protocols is not suitable for wired networks?
CSMA/CA
CSMA/CD
TGMA
TDMA
[ Option A ]
In networking, multiple access protocols are used to manage how devices share the same communication medium.
In wired networks (Ethernet), devices can easily detect collisions, so CSMA/CD is used. But in wireless networks, devices cannot detect collisions properly because they cannot listen while transmitting. Therefore, CSMA/CA is used in Wi-Fi, and it is not suitable for wired networks.
Q: 3 What network property is achieved through the use of the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) mechanism?
Reliability
Availability
Confidentiality
Scalability
[ Option A ]
Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) is a network protocol used to achieve Reliability in data transmission. Its primary function is to ensure that data packets sent from a sender are correctly received by the receiver. If an error is detected in a transmitted packet or if an acknowledgement is not received within a specified timeout period, ARQ triggers the retransmission of that packet until it is correctly received and acknowledged.
This mechanism helps to maintain data integrity and overcome issues such as lost or corrupted packets in unreliable communication channels.
Q: 4 For Stop-and-Wait ARQ, for 10 data packets sent, ________ acknowledgements are needed?
11
9
10
20
[ Option C ]
Stop-and-Wait ARQ is a protocol in which the sender transmits one data packet and waits for an acknowledgement before sending the next packet. Each data packet requires exactly one acknowledgement to confirm its successful receipt. Hence, if 10 data packets are sent, the receiver must send 10 acknowledgements.
Q: 5 Which of the following can work as error detecting and correcting code?
Cyclic Redundancy Checks
Hamming codes
Checksum
1D parity
[ Option B ]
In data communication, error detection and correction are essential for ensuring that transmitted data reaches the destination accurately. Most error control methods can only detect errors, while some can also correct them.
Hamming Code is a special type of code that can both detect and correct single-bit errors. It adds redundant bits called parity bits at specific positions in the data.
| CODE TYPE | PURPOSE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Parity Bit / 1D Parity | Error Detection. | Detects single-bit errors only. |
| Checksum | Error Detection. | Detects most errors in blocks of data. |
| Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) | Error Detection. | Detects burst errors effectively. |
| Hamming Code | Error Detection & Correction. | Detects and corrects single-bit errors. |
Q: 6 Checksum is used for—
Error Correction
Error Detection
Both (a) and (b)
None of these
[ Option B ]
A checksum is used in networking to verify data integrity. It works by adding binary values of data segments and sending the result with the packet. At the receiver’s end, the same calculation is done and compared. If they do not match, an error is detected. However, checksum only supports error detection, not correction.
| Checksum | CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) |
|---|---|
| Uses simple addition of data words. | Uses polynomial division (modulo-2 arithmetic). |
| Simple, fast, low overhead. | More complex, requires extra computation. |
| Detects single-bit errors and some small errors. | Detects burst errors, multiple bit errors, and more complex patterns. |
| Less reliable. | Highly reliable and accurate. |
| IP, TCP, UDP headers in networking. | Ethernet frames, storage devices, advanced communication protocols. |
Q: 7 The message 1001 is to be transmitted using the CRC polynomial x3+x+1 to protect it from errors. The message that should be transmitted is—
1001000
1001100
1001110
1001011
[ Option C ]
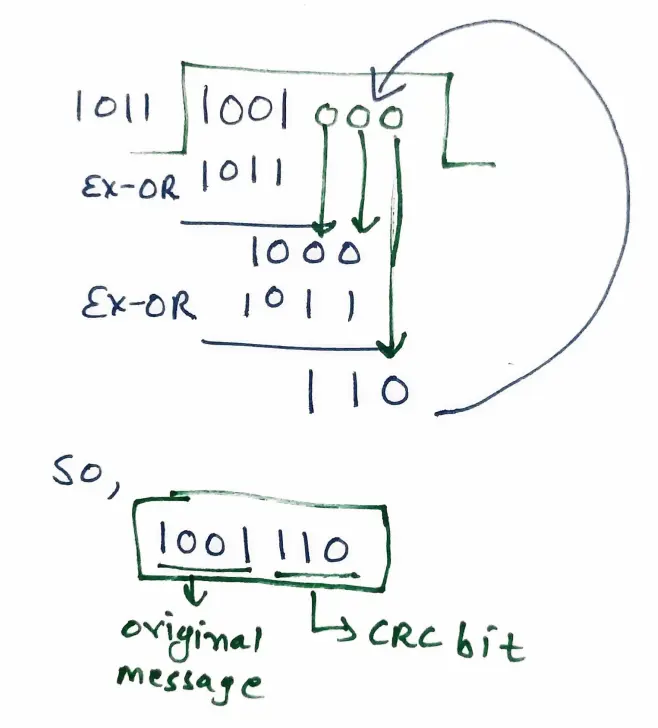
Given,
Message : 1001
CRC Polynomial (CRC Generator) : x3+x+1, binary 1011 (Degree 3)
Append 3 zero to the message because degree of polynomial is 3 or n-1 times (if n is CRC Generator).
Now perform Binary Division (Modulo 2):
Divide 1001000 by 1011 (Binary Division, XOR for Subtraction)
1001000 ÷ 1011, Remainder is 110.
This remainder is CRC bit.
Transmitted Message : Original Message + CRC Bits = 1001 + 110 = 1001110
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.