Q: 1 Which of the following is not range of frequency band operate in Industrial Scientific and Medical (ISM)?
902 – 928 MHz
2.4 – 4.835 GHz
5.725 – 5.850 GHz
1.5 – 1.6 GHz
[ Option D ]
Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) bands are portions of the radio spectrum reserved internationally for non-commercial purposes like industrial heating, medical equipment, and scientific experimentation. Over time, they have also been widely used for unlicensed wireless communication, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
Q: 2 The primary use of scramblers in Line Coding Schemes is to—
Make the data look random
Compress transmission data
Decrease signal bandwidth
Increase signal bandwidth
[ Option A ]
A scrambler is used in line coding schemes to modify the original data before transmission.
Q: 3 In digital modulation schemes using two carriers, a constellation diagram is particularly useful because it helps to
Measure only the frequency variations in the signal.
Visualize the amplitude and phase of each signal element.
Encode binary data directly without modulation.
Eliminate noise from the transmitted signal.
[ Option B ]
In digital communication, Modulation is the process of varying a carrier signal (sine wave) to transmit data. Digital modulation schemes often use two or more carriers, which can vary in amplitude, phase, or frequency to represent binary information.
A Constellation Diagram is a graphical representation of these modulated signals on a 2D plane, where the x-axis represents the in-phase component (I) and the y-axis represents the quadrature component (Q). Each point in the diagram corresponds to a unique amplitude and phase combination, allowing engineers to visualize the transmitted symbols and detect errors.
| TOOL | PURPOSE | OBSERVED PARAMETERS |
|---|---|---|
| Constellation Diagram | Visualization of digital modulation. | Amplitude and Phase. |
| Eye Diagram | Time-domain signal analysis. | Signal timing, Jitter, ISI. |
| Spectrum Analyzer | Frequency analysis. | Frequency, bandwidth, harmonics. |
Q: 4 Identify the diagram and write the type of conversion the system is performing.
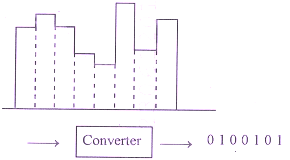
Digital to Analog
Digital to Digital
Analog to Digital
Analog to Analog
[ Option B ]
Q: 5 If the channel band is limited to 6 kHz and signal to noise ratio is 16, what would be the capacity of the channel?
15.15 kbps
24.74 kbps
30.12 kbps
52.18 kbps
[ Option B ]
Q: 6 Which type of channel does not represent any correlation between input and output symbols?
Noiseless channel
Lossless channel
Useless channel
Deterministic channel
[ Option C ]
A Useless Channel is a communication channel where there is no correlation between input and output symbols. This means the output is completely independent of the input, the received symbol gives no information about what was sent. In this, the channel capacity is zero because the output does not carry any meaningful information about the input.
A noiseless channel, output is exactly the same as input, so there is a perfect correlation between input and output.
A lossless channel, input can be uniquely determined from the output, so correlation still exists.
A deterministic channel, each input symbol corresponds to exactly one output symbol, hence strong correlation.
Q: 7 A receiver using Manchester decoding expects a transition in every bit period. If the line goes from high to high during one bit period, what does the receiver most likely interpret?
Bit 0
Bit 1
Bit error or synchronization loss
Bit 1 followed by Bit 0
[ Option C ]
In Manchester Encoding, each bit period must have a transition in the middle, Low to High for bit 1 and High to Low for bit 0. This transition helps maintain synchronization between sender and receiver. If the line stays high throughout a bit period (High to High), it means no transition occurred, violating the Manchester rule. Therefore, the receiver interprets it as a bit error or loss of synchronization.
Q: 8 We want to digitize a human voice signal. Assuming that each audio sample is represented using 8 bits and the human voice normally contains frequencies from 0 to 4000 Hz. What is the resulting bit rate of the digitized signal?
128 kbps
32 kbps
64 kbps
256 kbps
[ Option C ]
To digitize a human voice signal, the Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) method is used, which requires sampling the analog signal.
According to the Nyquist theorem, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the signal.
Since the human voice ranges up to 4000 Hz, the signal must be sampled at 8000 samples per second. If each sample is represented by 8 bits, the total bit rate becomes 8000 × 8 = 64,000 bits per second, or 64 kbps.
Q: 9 If a signal consists of V discrete levels and channel bandwidth is B, then according to Nyquist's theorem, the maximum data rate is:
4B log2V bits/sec
2V log2B bits/sec
2B log2V bits/sec
V log2B bits/sec
[ Option C ]
According to Nyquist’s theorem, the maximum data rate of a noiseless channel depends on its bandwidth (B) and the number of discrete signal levels (V) used in transmission.
Maximum Data Rate = 2B log2V bits per second
Q: 10 In the ________ encoding scheme, each 24 bits become four 6-bit chunks, and eventually are sent as 32 bits.
8 bits
Binary
Base 64
Quoted-Printable
[ Option C ]
In computer networks, binary data cannot always be transmitted directly over text-based protocols like email (SMTP) or web (HTTP). To solve this problem, Base64 encoding is used. Base64 takes every 24 bits of input data (3 bytes) and divides it into four groups of 6 bits each. Each 6-bit value is then mapped to a printable ASCII character.
Since each Base64 output is an ASCII character, it requires 8 bits of storage. Therefore, four characters × 8 bits = 32 bits of output are generated from the original 24 bits. This explains why Base64 increases the size of the encoded data by about 33%.
When encoding the string "SRK" into Base64, the process begins by converting each character into its ASCII binary form. The character S has an ASCII value of 83, which is 01010011 in binary. The character R has an ASCII value of 82, represented as 01010010. Finally, the character K has an ASCII value of 75, represented as 01001011. Together, the string "SRK" produces a 24-bit binary stream:
01010011 01010010 01001011
Next, these 24 bits are divided into groups of 6 bits each:
010100 110101 001001 001011
Each 6-bit group is then converted into its decimal equivalent:
Using the Base64 index table, these decimal values are mapped to their respective characters:
Thus, the final Base64 encoded output of the string "SRK" is: U1JL
Q: 11 For a noiseless channel, the ___________ formula defines the theoretical maximum bit rate.
Nyquist bit rate
Shannon bit rate
Ethernet bit rate
None bit rate
[ Option A ]
For a Noiseless communication channel, the theoretical maximum bit rate is determined by the Nyquist bit rate formula. The Nyquist formula calculates the highest possible data rate based on the channel bandwidth (B) and the number of discrete signal levels (M) used in transmission.
Maximum bit rate = 2 × B × log2(M)
In contrast, the Shannon bit rate formula considers noisy channels and accounts for signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), making it applicable when noise is present.
Q: 12 While transmission of data from a sender to receiver using Modem on Internet, the data is first converted to ________ from ________.
Analog, Analog
Analog, Digital
Digital, Analog
Digital, Digital
[ Option B ]
A Modem (Modulator-Demodulator) is a device that allows computers to communicate over telephone lines or other analog transmission media.
This process is called Modulation (Digital to Analog) and Demodulation (Analog to Digital), which is why the device is called a MODEM (Modulator-Demodulator).
Q: 13 Quantizing noise occurs in–
PCM
TDM
FDM
PPM
[ Option A ]
Quantizing noise occurs during the quantization process in Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). PCM converts an analog signal into a digital signal by sampling the amplitude of the analog signal at regular intervals and then quantizing these samples to the nearest value among a finite set of levels. The difference between the actual analog value and the quantized digital value is called quantization error or quantizing noise.
Q: 14 What is the maximum binary signal transmission rate of a noiseless 3-kHz channel?
12000 bps
6000 bps
3000 bps
1500 bps
[ Option B ]
The maximum data rate of a noiseless channel is determined by the Nyquist Theorem. It defines the theoretical upper limit for data transmission rate in an noiseless channel.
Maximum bit rate = 2×B×log2(M)
Where:
B = Bandwidth of the channel.
M = Number of discrete signal levels (symbols) used.
Given Values:
B=3000 Hz, M=2 (says binary signal and binary means two levels, 0 and 1)
Maximum bit rate = 2 × 3000 × log2(2) and log2(2)=1
So, Maximum bit rate = 2 × 3000 × 1 = 6000 bps.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.