Q: 1 What is a data structure?
A collection of algorithms.
A programming language
A type of computer hardware.
A way to store and organize data.
[ Option D ]
A data structure is particular way of storing and organizing data in computer system. So that it can be used efficiently.
Q: 2 Which of the following is a linear data structure?
Array
Graph
Tree
All of the above
[ Option A ]
Q: 3 Which of the following is NOT a basic operation performed on a data structure?
Encryption
Deletion
Insertion
More than one of the above
[ Option A ]
Data structure is way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. For example, dictionary is good example of organized data in which the words are arranged in a particular order.
| OPERATION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Insertion | Adding a new element to the data structure. |
| Deletion | Removing an existing element from the data structure. |
| Traversal | Accessing or visiting each element of the data structure. |
| Searching | Finding whether a particular element exists or not. |
| Sorting | Arranging elements in a particular order either in ascending or descending. |
| Update | Changing the value of an existing element. |
Q: 4 Which data structure is mainly used for implementing the recursive algorithm?
Queue
Stack
Binary tree
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Recursion is a technique where a function calls itself to solve smaller versions of the same problem until reaching a simple base case that stops the calls.
When a function calls itself, the computer must remember the current state of the function before jumping to the next call. To manage these multiple pending function calls, the system uses a stack.
Each time a function is called, a stack frame is pushed onto the stack, and when the function returns, the stack frame is popped.
Q: 5 Which of the following statements is true about Big-O notation?
It represents the lower bound of an algorithm’s runtime.
It represents the upper bound of an algorithm’s runtime.
It represents the average runtime of an algorithm.
More than one of the above
[ Option B ]
Big-O notation is used to describe how fast an algorithm grows in terms of its input size (n). It helps us understand the worst-case (upper bound) performance of an algorithm.
Q: 6 Which of the following data structures stores elements in a non-linear relationship?
Stack
Queue
Array
None of the above
[ Option D ]
A Data Structure is a way of storing and organizing data in computer system so that it can be used efficiently. Different data structures are used depending on what operations we need. Choosing the right data structure makes programs faster and easier to manage.
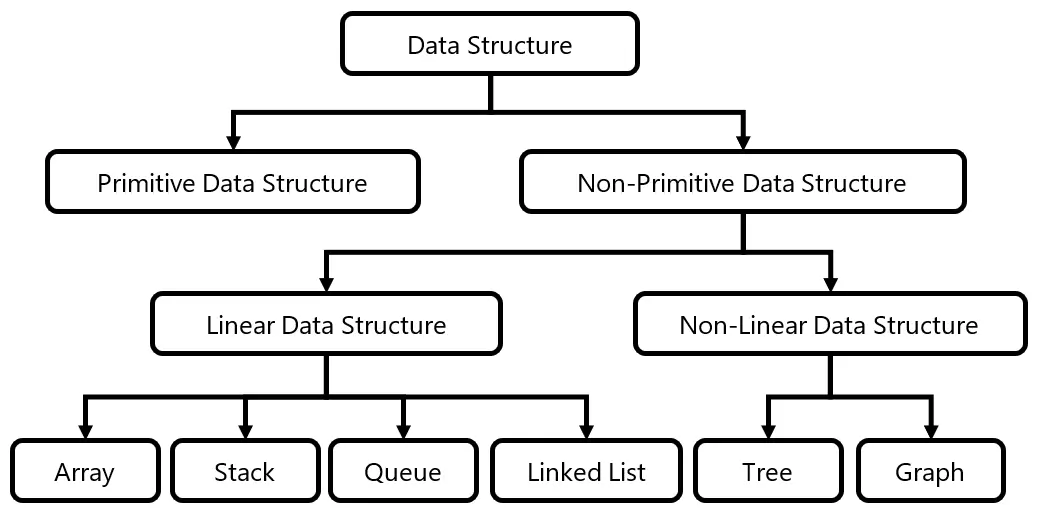
In a Linear data structure, elements are arranged one after another in a sequence. Each element has a unique predecessor and unique successor, except the first and last elements. Array, Stack, Queue, Linked List are example of linear data structure.
In a Non-Linear data structure, elements are not arranged sequentially. An element can connect to multiple elements, forming structures like hierarchical or networks. Tree and Graph are example of non-linear data structure.
Q: 7 An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is?
Same as an abstract class.
A data type that cannot be instantiated.
A data type for which only the operations defined on it can be used, but none else.
All of the above.
[ Option C ]
An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a data type that is defined by the set of operations that can be performed on it, not by how it is implemented.
Users of an ADT can only use the operations specified in its definition, while the internal representation and implementation details are hidden.
Q: 8 What type of data structure is used to store a group of elements in a non-linear manner?
Queue
Tree
Array
Stack
[ Option B ]
In computer science, data structures are classified into Linear and Non-Linear. Linear data structures arrange elements sequentially, where each element has a unique predecessor and successor (except the first and last) such as arrays, stacks, queues, and linked lists.
Non-Linear data structures do not follow this sequential order and allow for hierarchical or networked connections. In this one element can connect to multiple elements. Examples of non-linear data structure are Tree (hierarchical structure, parent-child relationships) and Graph (elements connected arbitrarily).
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.