Q: 1 The cout in C++ stands for
class output
character output
common output
None of the above
[ Option B ]
The cout is a predefined object in C++ from the iostream library used for console output. Generally the name cout is breaks down as, "c" for character (handles character streams) and "out" for output. It works with the insertion or put to operator << to print data.
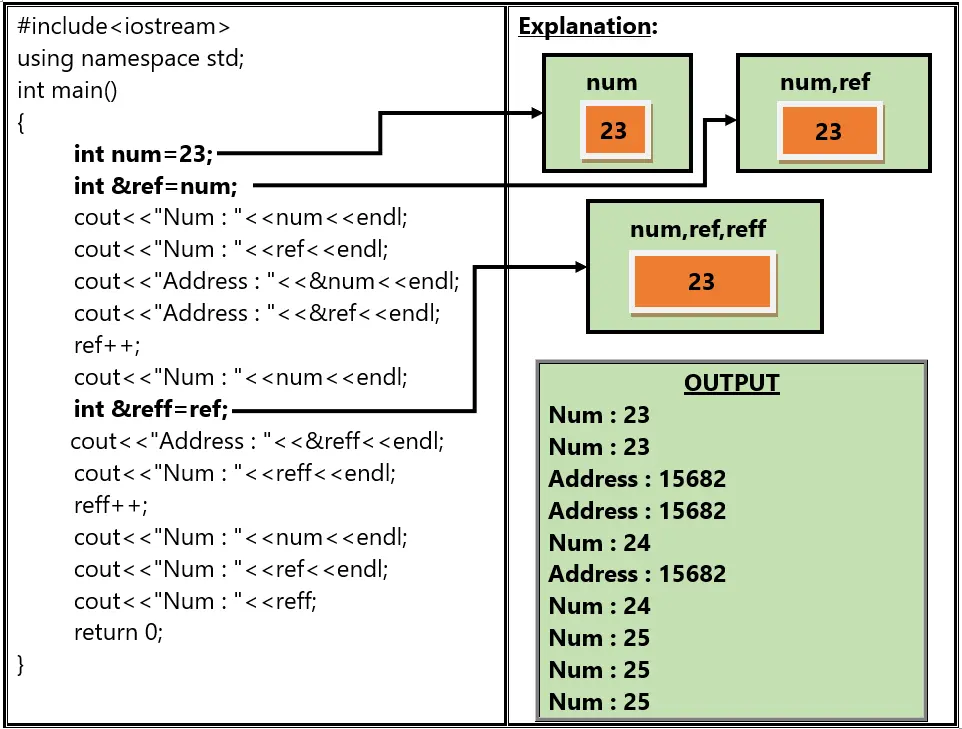
Q: 2 In C++, to create alias for previously defined variable, we use.
Pointer variable
Reference variable
Ordinary variable
None of these
[ Option B ]
In C++, an alias means another name for an already existing variable. This is done using a reference variable.
Syntax:
Data_type &Reference_Name= Referent;
Q: 3 If a semicolon is not used at the end of the statement, what message will be displayed by C++?
Semicolon Missing
Statement Missing
Error in Statements
None of the above
[ Option D ]
In C++, every statement must end with a semicolon. If a programmer forgets to write a semicolon, the compiler shows an error, but it does not display the messages given in the options.
Different C++ compilers show different error messages, such as “expected ‘;’ before …” or “missing ‘;’,” but none of these matches exactly with “Semicolon Missing,” “Statement Missing,” or “Error in Statements.”
Q: 4 Which of the following is user-defined header file extension used in C++?
hg
cpp
h
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, a header file contains declarations such as functions, classes, constants, and macros. These files are included in a program using the #include directive. There are two types of header files, predefine header files iostream.h, conio.h and user-defined header files created by the programmer.
User-defined header files in C++ typically use the extension “.h”. For example, #include "myheaderfile.h"
Q: 5 Which of the following is the original creator of the C++ language?
Dennis Ritchie/ Brain Kernighan
Ken Thompson
Bjarne Stroustrup
More than one of the above
[ Option C ]
C++ is an object-oriented programming language. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup at AT&T bell laboratories in the Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA in the year 1979. It is an extension to C with number of new features added.
The starting name of C++ was “C with Classes” and in 1983 the name is changed to C++.
The first use of class construct in a programming language occurred in 1962 in the language Simula67.
Q: 6 The preprocessor directive in C++ always starts with?
@
#
%
&
[ Option B ]
In C++, all preprocessor directives always start with the hash symbol (#). Preprocessor directives are processed before compilation. They are used for tasks like file inclusion, macro definition, and conditional compilation.
E.g.:
#include <iostream>
#define PI 3.14
Q: 7 Which shortcut key is used to compile and run the program in C++?
Alt+F9
Alt+F5
Ctrl+F9
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In the traditional Turbo C++ environment, two different shortcut keys are used:
Q: 8 Which of the following statements is true about the new and malloc?
I. The ‘new’ is a type of operator while ‘malloc’ is a kind of function.
II. The ‘new’ invokes a constructor, whereas ‘malloc’ does not invoke the constructor.
III. The ‘malloc’ returns void pointer and also needed to typecast whereas ‘new’ returns required pointer.
Only I
Only I and II
I, II and III
None of the above
[ Option C ]
In C++, new and malloc are both used for dynamic memory allocation, but they behave differently:
The new is an operator, while malloc is a function. This means new is handled by the compiler, whereas malloc is a library function from C. The statement (I) is true.
The new invokes the constructor for object initialization, while malloc only allocates raw memory and does not call any constructor. The statement (II) is true.
The malloc returns a void pointer, so it often needs typecasting in C++, whereas new automatically returns a pointer of the required type. The statement (III) is true.
| Feature | new | malloc() |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Operator. | Function. |
| Constructor | Called. | Not called. |
| Return Type | T* | void* |
Q: 9 The cin and cout is the?
Predefined function and defined in <iostream> header file.
Predefined object of class istream and ostream respectively.
Predefined function and used for implementing input/output functionality in C++.
None of the above.
[ Option B ]
In C++, cin and cout are not functions. They are objects created by the C++ standard library. The cin is a predefined object of the class istream (input stream) while the cout is a predefined object of the class ostream (output stream). Both are declared in the <iostream> header file and belong to the std namespace.
Q: 10 In C++, the operator << is known as ____________.
Insertion operator
Extraction operator
Double less than operator
Double greater than operator
[ Option A ]
In C++, the operator << is known as the insertion operator when used with output streams. It is used to insert data into an output stream, such as cout and sends (inserts) data from the program to the output device (screen).
Q: 11 Which of the following approaches is used by C++?
Left-right
Top-down
Bottom-up
None of the above
[ Option C ]
C++ uses the bottom-up approach, which is a core philosophy of object-oriented programming. In this approach, programs are built by first creating small, reusable components such as classes and objects, and then combining them to form larger and more complex systems.
| TOP-DOWN APPROACH | BOTTOM-UP APPROACH |
|---|---|
| Breaks the program into major modules first, then divides them into smaller parts. | Builds small components/modules first and combines them to form a complete system. |
| Used mostly in procedural programming. | Used mostly in object-oriented programming. |
| Focus on functions or procedures. | Focus on objects and classes. |
| The main function designed first. | Small reusable modules are designed first. |
| Lower reusability. | Higher reusability. |
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my Computer Science MCQs section carefully. Your support and interest mean a lot, and I truly appreciate you being part of this journey. Stay connected for more insights and updates! If you'd like to explore more tutorials and insights, check out my YouTube channel.
Don’t forget to subscribe and stay connected for future updates.